Abstract
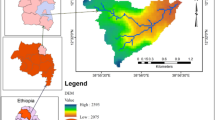
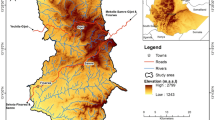
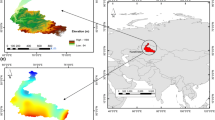
The present comparative study is multi-temporal in nature. The Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE), remote sensing, and GIS were used to model the soil loss estimation for soil conservation and vegetation rehabilitation in Nun Nadi watershed for the years 2000 and 2009. The estimated mean soil loss for the year 2000 and 2009 is 3,283.11 and 1,419.39 Mg ha−1 year−1, respectively. The study finds that about 80 % area has low or least risk of erosion and about 7 % is exposed to high or very high risk which indicates the improvement in terms of soil loss if we compare the data of both the time periods. The findings show that the rainfall, LULC change, and elevation are the main responsible factors for the soil loss in Nun Nadi watershed. Conservation measures have been adopted; however, the problem still remains serious and demands urgent attention.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angima SD, Stott DE, O’Neill MK, Ong CK, Weesies GA (2003) Soil erosion prediction using RUSLE for central Kenyan highland conditions. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 97:295–308
Dabral PP, Baithuri N, Pandey A (2008) Soil erosion assessment in a hilly catchment of north eastern India using USLE, GIS and Remote Sensing. Water Resource Management 22:1783–1798
Edmund M, Twumasi Y (2007) The application of GIS and remote sensing in the conservation of watershed: the case study of Pearl River watershed in Mississippi. USDA-CRESS water conference, Savannah, GA
Erenstein OCA (1999) The economics of soil conservation in developing countries: the case of crop residue mulching. Wageningen University, Wageningen
Garbrecht J, Martz LW (1997) The assignment of drainage direction over flat surfaces in raster digital elevation models. Journal of Hydrology 193:204–213
Grønsten HA, Lundekvam H (2006) Prediction of surface runoff and soil loss in southeastern Norway using the WEPP Hillslope model. Soil and Tillage Research 85(1–2):186–199
Hauck FW (1985) Soil erosion and its control in developing countries. Soil erosion and conservation. Soil Conservation Society of American. Ankeny, Iowa, pp 718–728
Kumar S, Sharma S (2005) Soil erosion risk assessment based on model using remote sensing and GIS. Hydrology Journal 28(1&2):47–58
Ma JW, Xue Y, Ma CF, Wang ZG (2003) A data fusion approach for soil erosion monitoring in the Upper Yangtze River Basin of China based on the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) model. International Journal of Remote Sensing 24(23):4777–4789
Mcroberts RE, Nelson MD, Wendt DG (2002) Stratified estimation of forest area using satellite imagery, inventory data, and the k-Nearest Neighbors technique. Remote Sensing of Environment 82:457–468
Millward AA, Mersey JE (1999) Adapting the RUSLE to model soil erosion potential in a mountainous tropical watershed. Catena 38:109–129
Moore ID, Burch G (1986) Physical basis of the length–slope factor in the universal soil loss equation. Soil Science Society of America Journal 50:1294–1298
Narayana D, Ram B (1983) Estimation of soil erosion from India. Irrigation Drainage Division ASCE 109(4):419–434
Pandey A, Chowdary VM, Mal BC (2007) Identification of critical erosion prone areas in the small agricultural watershed using USLE. GIS and remote sensing, Water Resource Management 21:729–746
Renard KG, Freidmund JR (1994) Using monthly precipitation data to estimate the R-factor in the RUSLE. Journal of Hydrology 157:287–306
Renard KG, Foster GR, Weesies GA, Mccool DK, Yoder DC (1997) Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). U.S. Dept. Of Agriculture, Agric. Handbook No. 703, 404 p
Renata C, Borivoj S (2002) Soil erosion by water: contemporary research methods and their use. Acta Univ Palacki Olomuc Fac Rer Nat Geographica 37:23–30
Renschler C, Diekkruger B, Mannaerts C (1997) Regionalization in surface runoff and soil erosion risk evaluation, in regionalization of hydrology. IAHS-AISH 254:233–241
Silleos GN (1990) Mapping and Evaluation of Agricultural Lands (Giahoudi-Giapouli Thessaloniki)
Singh G, Babu R, Narain P, Bhushan LS, Abrol IP (1992) Soil erosion rates in India. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 47(1):97–99
Tarboton DG (1997) A new method for the determination of flow directions and contributing areas in grid digital elevation models. Water Resources Research 33(2):309–319
United States Department of Agriculture, USDA, 1981. Handbook no. 282.
Valor E, Caselles V (1996) Mapping land surface emissivity from NDVI: application to European. African and South American areas, Remote Sensing Environment 57:167–184
Vimal K (2000) Problems and prospects of watershed development in India, Occasional Paper-12, NABARD.
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses—a guide to conservation planning. U.S. Dept. Of Agriculture, Agric. Handbook No. 537, 58 p
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Wen A, Feng M (2003) Assessment of soil losses on cultivated land by using the 137Cs technique in the Upper Yangtze River Basin of China. Soil and Tillage Research 69(1–2):99–106
Acknowledgment
We are thankful to Dr. Suresh Kumar of IIRS Dehradun for his consistent support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naqvi, H.R., Mallick, J., Devi, L.M. et al. Multi-temporal annual soil loss risk mapping employing Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model in Nun Nadi Watershed, Uttrakhand (India). Arab J Geosci 6, 4045–4056 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0661-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0661-z