Abstract
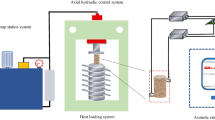
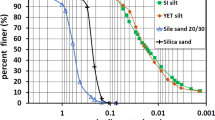
The hydraulic conductivity is highly influenced by the state of confinement and effective pressure applied. Hydraulic conductivity evaluated using indirect (i.e., oedometer tests) or direct techniques such as constant or falling head methods induces lateral confinement. The most reliable direct measurement tests are those considering triaxial or flexible wall setup such that field conditions are simulated. The ASTM D5084 and BS1337-6: 1990 are appropriate approaches to give reliable hydraulic conductivity values. Both tests require considerable time due to various stages of saturation, consolidation, and permeation. This study provides a comparison between indirect hydraulic conductivity tests and standard flexible wall tests in order to cut down the time needed to perform the test for different sand-Alqatif clay mixtures. Sand-clay mixtures used as liners for waste containment or water barriers are very sensitive to the hydraulic conductivity and need to be designed for different values of effective pressures. This research presents prediction equations derived from a series of direct and indirect tests carried out for sand-Alqatif clay mixtures. The results indicated that oedometer tests underestimated the hydraulic conductivity by 2 to 3 orders of magnitude at different effective pressures. The hydraulic conductivity was found to vary with effective pressures indicating that near surface material yields higher hydraulic conductivity than deeply seated similar soils.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeele WV (1986) The influence of Bentonite on the permeability of sandy silts. Nucl Chem Waste Manag 6:81–88
Akgun H (2010) Geotechnical characterization and performance assessment of bentonite/sand mixtures for underground waste repository sealing. Appl Clay Sci 49:394–399
Al-Rawas AA, Yahiae AM, Abdulaziz SA, Salem A (2006) Sand–attapulgite clay mixtures as a landfill liner. Geotech Geol Eng 24:1365–1383
Ameta NK, Abhay SW (2008) "Effect of bentonite on permeability of dune sand." EJGE.Vol13 , Bund. A
ASTM D698 - 02 “Standard Test Methods for Laboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil Using Standard Effort (12 400 ftlbf/ft3 (600 kN m/m3) , Vol. 15.09, Annual book of ASTM Standards, West Conshohocken, PA
ASTM D5084-03.“Standard Test Methods for Measurement ofHydraulicConductivity of Saturated Porous Materials Using a Flexible Wall Permeameter.”American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshocken, PA
Anderson C, Sivakumar V (2008) "Permeability of natural clay liners: Effect of accelerated permeability testing on soil structure".The 12th International Conference on Computer Methods and Advances in Geomechanics (IACMAG), Goa, India.p 1443–1450
Azam S (2003) Influence of mineralogy on swelling and consolidation of soils in eastern Saudi Arabia. Can Geotech J 40(5):964–975
BS1377-6 (1990) Soils for civil engineering purposes. Consolidation and permeability tests in hydraulic cells and with pore pressure measurement (AMD 8261), British Standards Institution
Chalermyanont T, Arrykul S (2005) "Compacted sand-bentonite mixtures for hydraulic containment liners."Songklanakarin J Sci Technol;Vol.27 No.2
Chapuis RR (1990) Sand-bentonite liners; Predicting permeability from laboratory tests. Can Geotech J 27:47–57
Cui YJ, Tang AM, Loiseau C, Delage P (2008) Determining the unsaturated hydraulic conductivity of a compacted sand-bentonite mixture under constant-volume and free-swell conditions. Phys Chem Earth A/B/C 33(Supplement 1):462–S471
Gibson AM (1985) "Permeability testing on clayey soil and silty sand- bentonite mixture using acid liquor". Hydraulic Barriers in Soil and Rock, ASTM, S7P874, 140–154
Gleason MH, Daniel DE, Eykholt GR (1997) Calcuim and Sodium Bentonite for Hydraulic Containment Applications. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 123(5):438–445
Gueddouda MK, Lamara M, Abou-bekr N, Taibi S (2010) Hydraulic behaviour of dune sand bentonite mixtures under confining stress. Global J Res Eng 10(Issue 1):31, Ver 1.0
Kaoser S, Barrington S, Elektorowicz M, Ayadat T (2006) The influence of hydraulic gradient and rate of erosion on hydraulic conductivity of sand-bentonitemixtures. Soil Sediment Contam 15(5):481–496
Kenney TC, van Veen WA, Swallow MA, Sungaila MA (1992) Hydraulic conductivity of compacted bentonite-sand mixture. Can Geotech J 29:364–374
Komine H (2004) Simplified evaluation on hydraulic conductivities of sand–bentonite mixture backfill. Appl Clay Sci 26:13–19
Langdon M, Al Hussaini J, Walden PJ, Sangha CM (1996) An assessment of permeability of clay liners: two case histories. Geol Soc Lond Eng Geol Spec Publ 11:291–297
Lundgren TA (1981) "Some Bentonite Sealants in Soil Mixed Blankets."In Proceedings of the 10thInternational Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Stockholm, 2, 349–354
Mollins LH, Stewaet DI, Cousens TW (1996) Predicting the properties of Bentonite –Sand Mixtures. Clay Miner 31:243–252
Mohamedzein YE, Al-Rawas AA, Al-Aghbari MY, Qatan A, Al-Rawas. Abdul-Hamid (2005) "Assessment of crushed shales for use as compacted landfill liners", J Eng Geol, 271 – 281
Murray EJ (2003) "Procedure for the determination of the permeability of clayey soils in a triaxial cell using the accelerated permeability test", R &D Technical Report, P1-398/TR/1, Environment Agency, Bristol, BS32 4UD, England, 194p
Obrike E, C. C. Osadebe, S. S. Omoniyi (2009) "Geotechnical analysis of two Nigerian soils for use as clay liners". Bull Eng Geol Environ, p 417–419
Shackelford CD (1994) “Waste-soil interactions that alter hydraulic conductivity.”Hydraulic conductivity and waste contaminant transport in soil, ASTM STP 1142, D. E. Daniel and S. J. Trautwein, eds., ASTM, West Conshohoken, Pa., 111–168
Sallfors G, Peirce J, Petersson E (1986) Clay Liners Construction and Quality Control. ASCE J Environ Eng 112(2):13–24
Tavakoli HR, Shafiee A, Jafari MK (2010) ”Hydraulic conductivity of compacted composite clays.”Int J Civ Struct Eng, Volume 1, No 3
Tavenas F, Leblond P, Jean P, Leroueil S (1983) Permeability of natural soft clays. Part I: Methods of laboratory measurement. Can Geotech J 20:629–644
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST) for providing research grant for this work through National Plan for Science, Technology and Innovation (MAARIFAH) Project No. ENV-1183-02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dafalla, M., Shaker, A.A., Elkady, T. et al. Effects of confining pressure and effective stress on hydraulic conductivity of sand-clay mixtures. Arab J Geosci 8, 9993–10001 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1925-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1925-1