Abstract
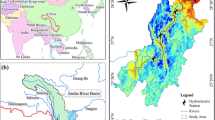
Based on the geographical information system (GIS) and revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE), the parameter factors are calculated by means of the observed rainfall, soil data, digital elevation model (DEM), and remote sensing (RS) image data to obtain the moduli of the soil erosion, discuss its spatial distribution characteristics, and propose the planning of soil and water conservation measures further according to the distribution of soil erosion intensity, the sandy soil and the thickness of soil layer distribution in the area along the Yangtze River in Jiangsu Province. The study results show that the total amount of soil loss in the area is 6.5 million (t a−1) approximately, the average soil erosion modulus is 3.839 (t ha−1a−1), and the total erosion area is 16,935.1km2, accounting for 33.2% of the total area along the Yangtze River in Jiangsu Province. The intensity of soil erosion is mainly micro or slight, which is distributed all over the area, with dispersed distribution on the most domain and concentrated distribution in specific part; however, severe or worse soil erosion seldom occurs, which is only scattered in the hilly and mountainous areas on the south bank of the Yangtze River and the surrounding area of the Taihu Lake if any. The soil erosion area of cultivated land is the largest, and the second one is the urban land, accounting for 49.1% and 27.4% of the total erosion area, respectively. 99.7% of the total soil erosion occurs in the areas with an elevation of less than 100 m, while 98.6% soil erosion occurs in the areas with a slope within 0–15 degree. The map of soil and water conservation measure planning is drawn, and the two most widespread measures for soil and water conservation in the study area are ecological restoration and soil conservation tillage, which are mostly concentrated in the plain area of the north of the Yangtze River with an underdeveloped economy in comparison with the south bank.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bathrellos GD, Gaki-Papanastassiou K, Skilodimou HD, Papanastassiou D, Chousianitis KG (2012) Potential suitability for urban planning and industry development using natural hazard maps and geological-geomorphological parameters. Environ Earth Sci 66:537–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1263-x
Bathrellos GD, Gaki-Papanastassiou K, Skilodimou HD, Skianis GA, Chousianitis KG (2013) Assessment of rural community and agricultural development using geomorphological-geological factors and GIS in the Trikala prefecture (Central Greece). Stoch Env Res Risk A 27:573–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-012-0602-0
Batista PVG, Silva MLN, Silva BPC, Curi N, Bueno IT, Acérbi Júnior FW, Davies J, Quinton J (2017) Modelling spatially distributed soil losses Grande River Basin. Brazil Catena 157:139–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.05.025
Beskow S, Mello CR, Norton LD, Curi N, Viola MR, Avanzi JC (2009) Soil erosion prediction in the Grande River Basin, Brazil using distributed modeling. Catena 79:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2009.05.010
Bhattarai R, Dutta D (2007) Estimation of soil erosion and sediment yield using GIS at catchment scale. Water Resour Manag 21:1635–1647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-006-9118-z
Cilek A, Berberoglu S, Kirkby M, Irvine B, Donmez C, Erdogan MA (2015) Erosion modelling in a Mediterranean subcatchment under climate change scenarios using pan-European soil erosion risk assessment (PESERA). In: Schreier G, Skrovseth PE, Staudenrausch H (eds) 36th international symposium on remote sensing of environment, vol 47. International Archives of the Photogrammetry Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, vol W3. pp 359–365. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprsarchives-XL-7-W3-359-2015
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations,FAO SOILS PORTAL, Harmonized World Soil Database v 1.2, (2017) http://www.fao.org/soils-portal/soil-survey/soil-maps-and-databases/harmonized-world-soil-database-v12/en/. Accessed 15 Feb 2018
Ganasri BP, Ramesh H (2016) Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS - a case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geosci Front 7:953–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2015.10.007
Gao J, Meng Y (2009) Quantitative Research on Soil Erosion along East Route of South to North Water Transfer Project in Jiangsu Province Based on GIS and RUSLE. Acta Agriculture Jiangxi 21:164–168
Geospatial Data Cloud (2017) http://www.gscloud.cn/. Accessed 30 Jan 2018
Jiangsu Statiscal Yearbook (2017) http://www.jssb.gov.cn/2017nj/indexc.htm. Accessed 25 May 2018
Kinnell PIA (2017) A comparison of the abilities of the USLE-M, RUSLE2 and WEPP to model event erosion from bare fallow areas. Sci Total Environ 596:32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.046
Kothyari UC, Jain SK (1997) Sediment yield estimation using GIS Hydrological Sciences Journal. J Des Sci Hydrol 42:833–843. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626669709492082
Li L (2011) Research on rainfall erosivity in Jiangsu Province Disssertation Nanjing Agricultural University
Mahala A (2018) Soil erosion estimation using RUSLE and GIS techniques-a study of a plateau fringe region of tropical environment. Arab J Geosci 11:335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3703-3
Mhangara P, Kakembo V, Lim KJ (2012) Soil erosion risk assessment of the Keiskamma catchment, South Africa using GIS and remote sensing. Environ Earth Sci 65:2087–2102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1190-x
Ministry of water resources of the People’s Republic of China (2008) The Standards for Classification and Gradation of Soil Erosion. http://www.std.gov.cn/hb/search/stdHBDetailed?id=5DDA8BA2DB3718DEE05397BE0A0A95A7. Accessed Oct 10 2017
Ministry of water resources of the People’s Republic of China (2008) Technical specification for comprehensive control of soil and water conservation -Technique for erosion control of slope land. http://www.std.gov.cn/gb/search/gbDetailed?id=71F772D7620AD3A7E05397BE0A0AB82A. Accessed Oct 25 2017
Mirzaee S, Ghorbani-Dashtaki S, Mohammadi J, Asadzadeh F, Kerry R (2017) Modeling WEPP erodibility parameters in calcareous soils in Northwest Iran. Ecol Indic 74:302–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.11.040
Naqvi HR, Mallick J, Devi LM, Siddiqui MA (2013) Multi-temporal annual soil loss risk mapping employing revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) model in Nun Nadi Watershed, Uttrakhand (India). Arab J Geosci 6:4045–4056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0661-z
National Meteorological Information Center (2017) http://data.cma.cn/. Accessed 10 Jan 2018
Olivares B, Verbist K, Lobo D, Vargas R, Silva O (2011) Evaluation of the USLE model to estimate water erosion in an Alfisol. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 11:71–84. https://doi.org/10.4067/s0718-95162011000200007
Pradeep GS, Krishnan MVN, Vijith H (2015) Identification of critical soil erosion prone areas and annual average soil loss in an upland agricultural watershed of Western Ghats, using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and RUSLE techniques. Arab J Geosci 8:3697–3711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1460-5
Prasannakumar V, Vijith H, Abinod S, Geetha N (2012) Estimation of soil erosion risk within a small mountainous sub-watershed in Kerala, India, using revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) and geo-information technology. Geosci Front 3:209–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2011.11.003
Rahman MR, Shi ZH, Chongfa C (2009) Soil erosion hazard evaluation-an integrated use of remote sensing, GIS and statistical approaches with biophysical parameters towards management strategies. Ecol Model 220:1724–1734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2009.04.004
Renard K, Foster GR, Weesies GA, McCool DK, Yoder DC (1997) Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the revised soil loss equation (RUSLE) US Dept of Agriculture. Agric Handbook 703:404
Rozos D, Skilodimou HD, Loupasakis C, Bathrellos GD (2013) Application of the revised universal soil loss equation model on landslide prevention. An example from N. Euboea (Evia) Island, Greece. Environ Earth Sci 70:3255–3266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2390-3
Sonnenborg TO, Christiansen JR, Pang B, Bruge A, Stisen S, Gundersen P (2017) Analyzing the hydrological impact of afforestation and tree species in two catchments with contrasting soil properties using the spatially distributed model MIKE SHE SWET. Agric For Meteorol 239:118–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.03.001
United States Department of Agriculture(1965), National Soil Erosion Research: West Lafayette, IN, RUSLE History. https://www.ars.usda.gov/midwest-area/west-lafayette-in/national-soil-erosion-research/docs/usle-database/usle-history/. Accessed 18 Dec 2017
Williams JR, Renard KG, Dyke PT (1983) EPIC, Method for Assessing Erosion's Effects on Soil Productivity J Soil Water Conserv 38:381–393
Williams J, Nearing M, Nicks A, Skidmore E, Valentin C, King K, Savabi R (1996) Using soil erosion models for global change studies. J Soil Water Conserv 51:381–385
Wischmemier W, Smith D (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses: a guide to conservation planning United States Department of Agriculture - handbook 537
Xia M (2013) Research on prediction model and application of soil erosion in the hilly area-a case study of Jiagu mountain, Ganyu county, Jiangsu Province Nanjing agricultural university dissertation
You S, Li W (1999) Estimation of soil erosion supported by GIS-A case study in Guanji Township, Taihe county, JiangXi province. J Nat Resour 14:63–69
Zhang Y, Yang H, Du MY, Tang XY, Zhang H, Peng BZ (2003a) Soil erosion study on hillside in southern Jiangsu Province using the cesium-137 tracer technique. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 49:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2003.10409983
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Peng BZ, Yang H (2003b) Soil erosion and its impacts on environment in Yixing tea plantation of Jiangsu province. Chin Geogr Sci 13:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-003-0008-5
Zhang Y, Peng BZ, Gao X, Yang H (2004) Degradation of soil properties due to erosion on sloping land in southern Jiangsu Province. China Pedosphere 14:17–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: O. Kisi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, G., Yuan, T., Zhang, Y. et al. Integrated study on soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS in Yangtze River Basin of Jiangsu Province (China). Arab J Geosci 12, 173 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4331-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4331-2