Abstract
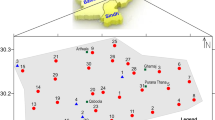
Teknaf Peninsula, located in a complex tectonic setting, is nearly unsuitable for inhabitants in terms of drinking water availability. Last couple of years, millions of Rohingya refugees migrated from Myanmar to Bangladesh and residing mostly in Hilly regions. Lada refugee camp is such a camp where thousands of people are living. Insufficient drinking water supply is posing a great threat on their health and lives. This camp is built in a hillock valley which is filled with Holocene sediments. Therefore, considering the miserable condition of about 20,000 refugees residing in this camp, groundwater resources are explored for this region deploying the electrical resistivity soundings (ES) survey. Using Schlumberger configuration, this survey is conducted at sixteen locations with different spreading (AB/2 = 100 m to 250 m). The result shows that the subsurface sequence of the area is broadly divided into two units, alluvium and sedimentary bedrock, respectively. Maximum thickness of alluvium is found about 81 m at center of the area. Alluvium is composed of mostly clay and silt. Few sandy lenses with variable thickness (2–41 m) are found at southwestern and eastern corners. Thickest lens of sand (41 m) is found at 21 m depth which might be the target for big diameter dug well, while the upper thick clayey layer would prevent vertical contamination. The compacted bedrock might have fractures but not identified. This study thus not found any potential groundwater resources at Lada camp and recommends detail study using electrical resistivity tomography at hilly region in Bangladesh.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed KM (2005) Management of groundwater arsenic disaster in Bangladesh. In: Bhattacharya P, Chandrasekharam D (eds) Natural arsenic in groundwater: occurrences, remediation and management- Bundschuh J. Taylor & Francis Group, London, pp 283–296. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203970829.sec5
Alam M, Alam MM, Curray JR, Rahman MLC, Gani MR (2003) An overview of the sedimentary geology of the Bengal Basin in relation to the regional tectonic framework and basin-fill history. Sediment Geol 155:179–208
Bugg SF, Lloyd JW (1976) A study of fresh water lens configuration in the Cayman Island using resistivity method. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 9(4):291–302
Curray JR (1991) Geological history of the Bengal geosyncline. J Assoc Explor Geophys XII:209–219
Emenike EA (2001) Geophysical exploration for groundwater in the sedimentary environment: a case study. Global J Pure Appl Sci 7(1):97–102
Kumar D (2012) Efficacy of electrical resistivity tomography technique in mapping shallow subsurface anomaly. J Geol Soc India 80:304–307
Kumar D, Ahmed S, Krishnamurthy SN, Dewandel B (2007) Reducing ambiguities in vertical electrical sounding interpretations: a geostatistical application. J Appl Geophys 62:16–32
Rahman MM, Woobaidullah ASM, Ahmed KM, Hasan MA, Hossain M, Bhattacharya P, von Bromssen M, Jacks G (2013) Evaluation of hydrogeological conditions through vertical electrical soundings survey in regions with high arsenic groundwater at Matlab, southeastern Bangladesh. J Earth Environ Sci Dhaka Univ 2(2):1–8
Serres YF (1969) Resistivity prospecting in a united nation groundwater project of Western Argentina. Geophys Prospect 17(4):449–467
Sultana S, Ahmed KM, Woobaidullah ASM, Rahman M, Alam MJ, Hasan M, Afroz T (2012) Identification of potable water sources in a complex geological terrain- a case study of Teknaf peninsula. Bangladesh J Geol 26:58–69
Umitsu M (1993) Late quaternary sedimentary environments and landforms in the Ganges Delta. Sediment Geol 83:177–186
UNDP (1982) Groundwater survey, the hydrogeological condition of Bangladesh. UNDP- United Nations Development Programme
Urish DW, Frohlich RK (1990) Surface electrical resistivity in coastal groundwater exploration. Geoexploration 26(4):267–289
Woobaidullah ASM, Hasan MA, Reza H, Noor A (1994) An analysis of resistivity sounding data for groundwater exploration in Dumdumia-Nayapara. Teknaf Dhaka Univ J Sci 42(2):229–234
Woobaidullah ASM, Ahmed KM, Hasan MA, Hasan MK (1998) Saline ground water management in Manda Upazila of Naogaon District, NW Bangladesh. J Geol Soc India 51:49–56
Woobaidullah ASM, Rahman MM, Uddin MZ (2014) Evaluation of hydrogeological condition through vertical electrical soundings survey at Manikganj Pourashava, Manikganj, central part of Bangldesh. Bangladesh J Sci Res 27(2):109–120
Funding
This research is financially supported by the NGO Forum for Public Health, Bangladesh to M.M Rahman and A.S.M Woobaidullah. We thank to Mohammed Hossain for his invaluable supports in arranging this grant to carry out the research work. We used the survey instruments from the Geology Department, University of Dhaka, Bangladesh. We are grateful to the Chairman of PME Department, Jessore University of Science and Technology, Bangladesh, for allowing us to carry out this research. We thank to S K Gosh and Rajib, Dhaka University for their valuable supports during survey. We are grateful to all local stakeholders for providing us supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Helder I. Chaminé
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, M.M., Woobaidullah, A.S.M. Groundwater resources exploration in a Hillock Valley at Lada refugee camp, Teknaf using electrical resistivity soundings. Arab J Geosci 13, 90 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5056-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5056-y