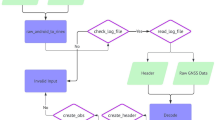
Abstract
Over the last 2 years, the Geomatics Research Group at the Politecnico di Torino has developed a low cost mobile mapping system, in which only low cost sensors are involved. The system is equipped with webcams, up to three MEMS IMU and up to four GNSS receivers. During this development, several (non negligible) problems have been solved in order to obtain good quality after the data processing. One of the main problems of the low cost systems concerns the occurrence of GNSS outages. In this case, the IMU can only estimate the trajectory and the attitude of the vehicle for short periods. For this reason, considering the high number of frames available (about 5–10 frames per second, fps), a vision-based navigation (VBN) approach, called GIMPHI (GNSS IMU and PHotogrammetry Integration), has been realized and tested. Using a novel auto-adaptive scale-invariant feature transform (A²SIFT) algorithm, tie points are extracted from sequences of images acquired according to unconventional geometric configuration (large affine transformation and rotations) andzz with large bad-textured areas. The GNSS/IMU navigation solutions have been refined by means of integration with a photogrammetric approach (bundle block adjustment) and a rigorous weight matrix has been adopted in order to consider the different accuracies of the various sensor observations (GNSS, IMU and images). A detailed description of this integrated approach is presented in this paper. The first tests and the achieved results are then shown in order to evaluate the reliability of the proposed approach.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battiato S, Gallo G, Puglisi G, Scellato S (2009) Improved feature-points tracking for video stabilization. Proceedings of SPIE Electronic Imaging. System Analysis for Digital Photography, San Jose, CA, January 2009
Brown RG, Hwang P (1997) Introduction to random signals and applied Kalman filtering, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
De Agostino M (2009) Performance of different low-cost GNSS/IMU Land Systems, ION GNSS 2009 Proceedings, Savannah, GA, September 2009
De Agostino M, Porporato C (2008) Development of an Italian low cost GNSS/INS system universally suitable for mobile mapping. IEEE Aerosp Electron Syst Mag 23(11):25–32
El-Sheimy N (1996) The development of VISAT: a mobile survey system for GIS applications. PhD Thesis, Department Of Geomatics Engineering, Univ. of Calgary, Calgary, AL
George M, Sukkarieh S (2005) Tightly coupled INS/GPS with bias estimation for UAV applications. In: Proceedings of Australasian Conference on Robotics and Automation 2005, Sidney, Australia
Groves P (2008) Principles of GNSS, inertial and multisensor integrated navigation system. Artech House, London
Lingua A, Rinaudo F (2000) Aerial triangulation data acquisition using a low cost digital photogrammetric system. In: International Archives of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, vol XXXIII/B2; pp 449–454
Lingua A, Marenchino D, Nex F (2009) Performance analysis of the SIFT operator for automatic feature extraction and matching in photogrammetric applications. Sensors 9(5):3745–3766. doi:10.3390/s90503745
Lowe D (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 60(2):91–110
Lu G (1995) Development of a GPS multi-antenna system for attitude determination. PhD Thesis, Department Of Geomatics Engineering, Univ. of Calgary, Calgary, AL
Piras M, Cina, A, Lingua A (2008) Low cost mobile mapping system: an Italian experience. In: PLANS 2008 proceedings, Monterey, CA, May 2008
Rousseeuw PJ, Leroy AM (1987) Robust regression and outlier detection. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ
Škaloud J (1999) Optimizing georeferencing of airborne survey systems by INS/DGPS. PhD Thesis, Department Of Geomatics Engineering, Univ. of Calgary, Calgary, AL, pp 90–108
Titterton D, Weston J (2004) Strapdown inertial navigation technology, 2nd edn. The American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Reston, VA
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank professors Horea Bendea and Ambrogio M. Manzino for their guidance and valuable advice about this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Agostino, M., Lingua, A., Marenchino, D. et al. GIMPHI: a new integration approach for early impact assessment. Appl Geomat 3, 241–249 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-011-0069-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-011-0069-6