Abstract
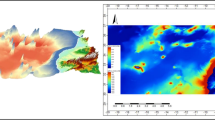
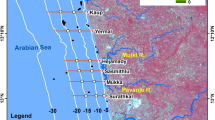
This article reports a preliminary work in which two site specific seasonal algorithms have been proposed for estimating the suspended sediments concentration (SSC) from the digital numbers recorded on Indian Remote sensing Satellite, IRS-P4 Ocean Colour Monitor (OCM) sensor. For estimation of SSC, the proposed algorithms utilize dark pixel deduction atmospheric correction technique. The computations are performed with respect to north east monsoon phase situations of Palk Strait coastal stretch. The algorithms performance was satisfactory during the north east monsoon period. Although the results obtained cannot be generalized, we suggest that the authority of proposed algorithms can be extended to other seasons with the addition of more temporal experimental validation data sets and with numeric constants adjusted to present existing conditions. (As this area was severely affected by Tsunami, it may have dissimilar conditions at present).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker ET and Lavelle JW (1984) The effect of particle size on the light attenuation coefficient of natural suspensions. J Geophys Res 89: 8197–8203
Clark JR (1995) Coastal zone management handbook. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, USA
Gordon HR, Clark DK, Brown JW, Brown OB, Evans RH and Broenkow WW (1983) Phyto-plankton pigment concentrations in the Middle Atlantic bight: Comparison of ship determinations and coastal zone color scanner measurements. Appl Opt 22: 20–36
Jensen JR (2000) Remote sensing of the environment: An earth resource perspective (Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall)
Kirk JTO (1994) Light and photosynthesis in aquatic ecosystems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Pak H, Beardsley GF, Heath GR and Curl H (1970) Light-scattering vectors of some marine particles. J Limnol Oceanogr 15:683–687
Raaj R (2003) Estimation of suspended sediments using OCM imagery. Project Phase I Report. Institute of Remote Sensing, Anna University, Chennai, India. (Unpubl.)
Ritchie JC, Schiebe FR and McHenry JR (1976) Remote sensing of suspended sediment in surface water. PE & RS 42:1539–1545
Strickland JDH and Parsons TR (1972) A practical handbook of sea-water analysis. Fisheries Research Board of Canada. 310p
Stumpf RP and Pennock JR (1989) Calibration of a general optical equation for remote sensing of suspended sediments in a moderately turbid estuary. J Geophys Res 94:14363–14371
Sydor M and Arnone RA (1997) Effect of suspended particulate and dissolved organic matter on remote sensing of coastal and riverine waters. Appl Opt 36:6905–6912
Tissot C (1987) Recent evolution of mangrove vegetation in the Cauvery delta: A palynological study. Ind J Mar Biol 29:16–22
UN ESCO (1994) Protocols for Joint Global Ocean Carbon Flux Study (JGOFS) Core Measurements, Manuals and Guides 29:170
Warrick JA, Mertes LAK, Siegel DA and Mackenzie C (2004) Estimating suspended sediment concentrations in turbid coastal waters of the Santa Barbara Channel with SeaWiFS. Int J Remote Sens 25(10):1995–2002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Raaj, R., Ramalingam, M., Ghosh, S.K. et al. Mapping of suspended sediments using site specific seasonal algorithms. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 36, 61–68 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-008-0006-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-008-0006-2