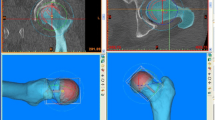
Abstract
This paper presents a light-weight software system that enables virtual three-dimensional (3D) surgical planning of hip replacement surgery for extracting 3D surgical parameters such as the position and the orientation of femoral resection plane, the interference-free trajectory of prosthesis implantation, and the final assembled position. According to the specification of an individual patient, the system allows the surgeon to design a hip prosthesis that most closely recovers the original function of the joint. Since it is based upon the 3D anatomy, the system overcomes a geometrical mismatch between prosthesis-bone interfaces which is the main limitation of 2D-based approach. The closely customized prosthesis-bone fit appears to increase the durability of hip prosthesis, and enhances the load distribution and the stability. Detailed steps of the system are described, and typical example is presented to validate the methodology. The result shows that the proposed pilot surgical planning system is applicable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jun, Y. and Choi, K., “Design of patient-specific hip implants based on the 3D geometry of the human femur,” Adv. Eng. Softw., Vol. 41, No. 4, pp. 537–547, 2010.
Park, W. M., Kim, Y. H., Kim, K. and Oh, T. Y., “Nondestructive Biomechanical Analysis to Evaluate Surgical Planning for Hip Joint Diseases,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 10, No. 3, pp. 127–131, 2009.
Montgomery, K., Stephanides, M. and Schendel, S., “Development and application of a virtual environment for reconstructive surgery,” Computer Aided Surgery, Vol. 5, No. 2, pp. 90–97, 2000.
Cimerman, M. and Kristan, A., “Preoperative planning in pelvic and acetabular surgery: The value of advanced computerized planning modules,” Injury, Vol. 38, No. 4, pp. 442–449, 2007.
Dick, C., Georgii, J., Burgkart, R. and Westermann, R., “A 3D Simulation System for Hip Joint Replacement Planning,” World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Vol. 25, No. 4, pp. 363–366, 2009.
Pawlikowski, M., Skalski, K. and Haraburda, M., “Process of hip joint prosthesis design including bone remodeling phenomenon,” Computers & Structures, Vol. 81, No. 8–11, pp. 887–893, 2003.
Wehmoller, M., Warnke, P. H., Zilian, C. and Eufinger, H., “Implant design and production-a new approach by selective laser melting,” International Congress Series, Vol. 1281, pp. 690–695, 2005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jun, Y., Park, S. Polygon-based 3D surgical planning system for hip operation. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 12, 157–160 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-011-0021-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-011-0021-z