Abstract
Introduction
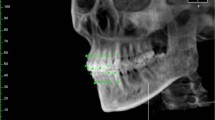
The position and inclination of the long axis of teeth in the human dentition can be described by a set of rules. The purpose of this study was to analyze the architecture of the mandibular dentition of adult Caucasians using virtual three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of skulls and mandibles.
Method
In this study 40 skulls from the Weissbach collection at the Vienna Natural History Museum were scanned using cone beam computed tomography. Several angular and linear measurements obtained from the reconstructed images were analyzed.
Results
The inclination of second premolars and first molars was nearest to vertical and mesial inclination became progressively greater for molars. The angular relationship between the tooth long axis and the closing axis of lower incisors ranged from 95 to 98°, while the tooth axis of buccal teeth with the contralateral condyle sequentially increased from canines to third molars. The architecture of occlusion showed that the Bonwill triangle was equilateral with a length of approximately 100 mm (about 4 inches) on one side, the Balkwill angle was approximately 25° and there was a distance of approximately 38 mm between the condyle and occlusal plane (DPO). The angle of the condylar axis inclined to correlate to the 3D structure of the mandible.
Conclusions
This study defines the 3D architecture of occlusion including tooth axis, condyle and shape of the mandible. The results make it possible to consider new aspects of the biomechanics of 3D reconstruction of occlusion.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews LF. The six keys to normal occlusion. Am J Orthod. 1972;62:296–309.
Basili C, Costa HN, Sasaguri K, Akimoto S, Slavicek R, Sato S. Comparison of the position of the mandibular fossa using 3D CBCT in different skeletal frames in human caucasic skulls. Int J Stomatol Occl Med. 2009;4:179–90.
Basili C, Otsuka T, Kubota M, Slavicek R, Sato S. Three-dimensional CT analysis of vomer bone in the architecture of craniofacial structures in caucasic human skulls. Int J Stomatol Occl Med. 2009;4:191–204.
Basili C, Slavicek R, Tajima K, Sato S. A three-dimensional computerized tomography study of the relationship between cranial base angle and maxillofacial architecture in caucasic human skull. Int J Stomatol Occl Med. 2009;4:205–15.
Bauer R, Gutowski A. Gnathology, introduction to theory and practice. Berlin: Quintessenz; 1976.
Björk A, Skieller V. Facial development and tooth eruption. An implant study at the age of puberty. Am J Orthodont. 1972;62:339–83.
Dawson PE. Evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of occlusal problems. 2nd ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 1989. pp. 85–91, 365–81.
Dos Santos J, De Rijk WG. Occlusal contacts: vectorial analysis of forces transmitted to TMJ and teeth. J Craniomand Pract. 1993;2:18–25.
Ferrario VF, Sforza C, Colombo A, Ciusa V, Serrao G. Three-dimensional inclination of the dental axes in healthy permanent dentitions—A cross-sectional study in a normal population. Angle Orthod. 2001;71:257–64.
Ferrario VF, Sforza CH, Miani JR. Statistical evaluation of Monson’s sphere in healthy permanent dentition in man. Arch Oral Biol. 1997;42:365–9.
Kim K-M, Sasaguri K, Akimoto S, Sato S. Mandibular rotation and occlusal development during facial growth. Int J Stomatol Occl Med. 2009;2:122–30.
Krarup S, Darvann T, Marsh L, Kreiborg S. Three-dimensional analysis of mandibular growth and tooth eruption. J Anat. 2005;207:669–82.
Orthlieb JD. The curve of Spee: understanding the sagittal organization of mandibular teeth. J Craniomand Pract. 1997;15:333–40.
Osborn JW. Orientation of the masseter muscle and the curve of Spee in relation to crushing forces on the molar teeth of primates. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1993;92:99–106.
Osborn JW. Relationship between the mandibular condyle and the occlusal plane during hominid evolution: some of its effects on jaw mechanics. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1987;73:193–207.
Page H. The occlusal curve. Dental Digest. 1952;19–21.
Pameijer JHN. Periodontal and occlusal factors in crown and bridge procedures. Amsterdam: Dental Center for Postgraduate Courses; 1985.
Prichard JF. The diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease in general dental practice. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1979. pp. 463–503.
Smukler H. Equilibration in the natural and restored dentition. Chicago: Quintessence; 1991. pp. 51–65.
Spee FG. Die Verschiebungsbahn des Unterkiefers am Schädel. Arch Anat Physiol. 1890;16:285–94.
Tylman SD. Theory and practice of crown and bridge prosthodontics. 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 1970.
Wiskott A, Belser U. A rationale for a simplified occlusal design in restorative dentistry: historical review and clinical guidelines. J Prosthetic Dent. 1995;73:169–83.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukoe, H., Basili, C., Slavicek, R. et al. Three-dimensional analyses of the mandible and the occlusal architecture of mandibular dentition. J. Stomat. Occ. Med. 5, 119–129 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12548-012-0053-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12548-012-0053-8