Abstract
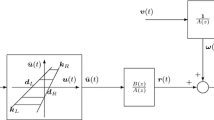
In this paper, an on-line algorithm for identification of sandwich systems with backlash is proposed. In this method, the sandwich systems with backlash can be transformed into a special model where all the model parameters are separated based on the so-called key term separation principle. In this case, a piecewise model with linear coefficients combining with nonlinear variables is obtained. Thus, an extended recursive identification algorithm is used to estimate the parameters of the proposed model. Finally, the modeling results on an X-Y positioning stage are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. K. Pearson, “Nonlinear input/output modeling,” J. Process Control, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 197–211, 1995.
G. Tao, X. Ma, and Y. Ling, “Optimal and nonlinear decoupling control of systems with sandwiched backlash,” Automatica, vol. 37, pp. 165–176, 2001.
J. Vörös, “Recursive identification of Hammerstein systems with discontinuous nonlinearities containing dead-zones,” IEEE Trans. on Automatic Control, vol. 48, no. 12, pp. 2203–2206, 2003.
J. Vörös, “Identification of nonlinear dynamic system using extended Hammerstein and Wiener models,” Control-Theory and Advanced Technology, vol. 10, pp. 1203–1212, 1995.
C. Z. Fang, System Identification, Qinghua University Press, Beijing, 2004.
L. Ljung, “Analysis of recursive stochastic algorithms,” IEEE Trans. on Automatic Control, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 271–287, 1977.
V. Cerone and D. Regruto, “Bounding the parameters of linear systems with input backlash,” Proc. of American Control Conference, pp. 4476–4481, 2005
M. Nordin and P. O. Gutman, “Controlling mechanical systems with backlash—a survey,” Automatica, vol. 38, pp. 1633–1649, 2002.
X. Hong, R. J. Mitchell, S. Chen, C. J. Harris, K. Li, and G. W. Irwin, “Model selection approaches for non-linear system identification: a review,” International Journal of Systems Science, vol. 39, no. 10, pp. 925–946, 2008.
M. Boutayeb and M. Darouach, “Recursive identification method for MISO Wiener-Hammerstein model,” IEEE Trans. on Automatic Control, vol. 40, no. 2, pp. 287–291, 1995.
A. H. Tan and K. Godfrey, “Identification of Wiener-Hammerstein models using linear interpolation in frequency domain,” IEEE Trans. on Instrumentation and Measurement, vol. 51, no. 3, pp. 509–521, 2002.
P. Crama and J. Schoukens, “Computing an initial estimate of a Wiener-Hammerstein system with a random phase multisine excitation,” IEEE Trans. on Instrumentation and Measurement, vol. 54, no. 1, pp. 117–122, 2005.
S. A. Billings and S. Y. Fakhouri, “Identification of a class of nonlinear systems using correlation analysis,” Proc. IEE. vol. 125, pp. 691–697, 1978.
A. Kibangou and G. Favier, “Wiener-Hammerstein systems modeling using diagonal Volterra kernels coefficients,” IEEE Signal Proc. Letters, vol. 13, no. 6, pp. 381–384, 2006.
S. Billings and S. Fakhouri, “Identification of systems containing linear dynamics and static nonlinear elements,” Automatica, vol. 18, pp. 15–26, 1982.
N. Bershad, P. Celka, and S. Mc Laughlin, “Analysis of stochastic gradient identification of Wiener-Hammerstein systems for nonlinearities with Hermite polynomial expansions,” IEEE Trans. Signal Proc., vol. 49, no. 5, pp. 1060–1072, 2001.
S. Billings and S. Fakhouri, “Identification of nonlinear systems using correlation analysis and pseudorandom inputs,” Int. J. Systems Science, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 261–279, 1980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Editorial Board member Won-Jong Kim under the direction of Editor Young Il lee. This work was supported by the projects of Shanghai Normal University (DZL811, DRL904 and DYL201005); the projects of Shanghai Education Commission (09ZZ141 and 11YZ92); the project of NSFC (Grant No. 60971004), and the projects of Science and Techn. Commission of Shanghai (09220503000, 10JC1412200 and 09ZR1423400).
Ruili Dong received her Ph.D. degree in Control Engineering from Shanghai Jiaotong University in 2009. Presently, she is a lecturer at the College of Mechanical and Electronic Engineering, Shanghai Normal University, China. Her research interests include identification of nonlinear systems, and mechatronics.
Yonghong Tan obtained his Ph.D. degree in Electrical Engineering from University of Ghent, Belgium in 1996. Now, he is a full professor at College of Mechanical and Electronic Engineering, Shanghai Normal University, China. His research interests include identification and control of nonlinear systems, mechatronics, and biomedical signal processing.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, R., Tan, Y. On-line identification algorithm and convergence analysis for sandwich systems with backlash. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 9, 588–594 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-011-0320-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-011-0320-2