Abstract
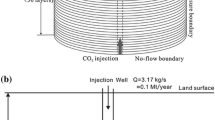
Carbon dioxide injection into deep saline aquifers results in a variety of strongly coupled physical and chemical processes. In this study, reactive transport simulations using a 2-D radial model were performed to investigate the fate of the injected CO2, the effect of CO2-water-rock interactions on mineral alteration, and the long-term CO2 sequestration mechanisms of the Liujiagou Formation sandstone at the Shenhua CCS (carbon capture and storage) pilot site of China. Carbon dioxide was injected at a constant rate of 0.1 Mt/year for 30 years, and the fluid flow and geochemical transport simulation was run for a period of 10 000 years by the TOUGHREACT code according to the underground conditions of the Liujiagou Formation. The results show that different trapping phases of CO2 vary with time. Sensitivity analyses indicate that plagioclase composition and chlorite presence are the most significant determinants of stable carbonate minerals and CO2 mineral trapping capacity. For arkosic arenite in the Liujiagou Formation, CO2 can be immobilized by precipitation of ankerite, magnesite, siderite, dawsonite, and calcite for different mineral compositions, with Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe2+ and Na+ provided by dissolution of calcite, albite (or oligoclase) and chlorite. This study can provide useful insights into the geochemistry of CO2 storage in other arkosic arenite (feldspar rich sandstone) formations at other pilots or target sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin, S. M., Weiss, D. J., Blunt, M. J., 2014. Reactive Transport Modelling of Geologic CO2 Sequestration in Saline Aquifers: The Influence of Pure CO2 and of Mixtures of CO2 with CH4 on the Sealing Capacity of Cap Rock at 37 °C and 100 bar. Chemical Geology, 367: 39–50. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.01.002
André, L., Audigane, P., Azaroual, M., et al., 2007. Numerical Modeling of Fluid-Rock Chemical Interactions at the Supercritical CO2-Liquid Interface during CO2 Injection into a Carbonate Reservoir, the Dogger Aquifer (Paris Basin, France). Energy Conversion and Management, 48(6): 1782–1797. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2007.01.006
Assayag, N., Matter, J., Ader, M., et al., 2009. Water-Rock Interactions during a CO2 Injection Field-Test: Implications on Host Rock Dissolution and Alteration Effects. Chemical Geology, 265(1–2): 227–235. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.02.007
Bacci, G., Korre, A., Durucan, S., 2011. An Experimental and Numerical Investigation into the Impact of Dissolution/Precipitation Mechanisms on CO2 Injectivity in the Wellbore and Far Field Regions. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 5(3): 579–588. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2010.05.007
Bachu, S., 2000. Sequestration of CO2 in Geological Media: Criteria and Approach for Site Selection in Response to Climate Change. Energy Conversion and Management, 41(9): 953–970. doi:10.1016/s0196-8904(99)00149-1
Balashov, V. N., Guthrie, G. D., Hakala, J. A., et al., 2013. Predictive Modeling of CO2 Sequestration in Deep Saline Sandstone Reservoirs: Impacts of Geochemical Kinetics. Applied Geochemistry, 30(2): 41–56. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.08.016
Bertier, P., Swennen, R., Laenen, B., et al., 2006. Experimental Identification of CO2-Water-Rock Interactions Caused by Sequestration of CO2 in Westphalian and Buntsandstein Sandstones of the Campine Basin (NE-Belgium). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 89(1–3): 10–14. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2005.11.005
British Petroleum (BP), 2010. BP Statistical Review of World Energy 2010. BP Plc, British China Shenhua Coal to Liquid Chemical Engineering Company, 2014. The Operation Report of the Shenhua 0.1 Mt CCS Demonstration Project, Ordos (in Chinese)
Corey, A. T., 1954. The Interrelation between Gas and Oil Relative Permeabilities. Producers Monthly, 19(1): 38–41
Credoz, A., Bildstein, O., Jullien, M., et al., 2009. Experimental and Modeling Study of Geochemical Reactivity between Clayey Caprocks and CO2 in Geological Storage Conditions. Energy Procedia, 1(1): 3445–3452. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2009.02.135
Eiken, O., Ringrose, P., Hermanrud, C., et al., 2011. Lessons Learned from 14 Years of CCS Operations: Sleipner, in Salah and Snøhvit. Energy Procedia, 4: 5541–5548. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2011.02.541
Gaus, I., Audigane, P., André, L., et al., 2008. Geochemical and Solute Transport Modelling for CO2 Storage, What to Expect from It?. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2(4): 605–625. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2008.02.011
Gaus, I., Azaroual, M., Czernichowski-Lauriol, I., 2005. Reactive Transport Modelling of the Impact of CO2 Injection on the Clayey Cap Rock at Sleipner (North Sea). Chemical Geology, 217(3–4): 319–337. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.12.016
Goddéris, Y., Williams, J. Z., Schott, J., et al., 2010. Time Evolution of the Mineralogical Composition of Mississippi Valley Loess over the Last 10 kyr: Climate and Geochemical Modeling. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(22): 6357–6374. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2010.08.023
Goodarzi, S., Settari, A., Keith, D., 2012. Geomechanical Modeling for CO2 Storage in Nisku Aquifer in Wabamun Lake Area in Canada. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 10(10): 113–122. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2012.05.020
Hellevang, H., Aagaard, P., Oelkers, E. H., et al., 2005. Can Dawsonite Permanently Trap CO2?. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(21): 8281–8287. doi:10.1021/es0504791
Hermanrud, C., Andresen, T., Eiken, O., et al., 2009. Storage of CO2 in Saline Aquifers-Lessons Learned from 10 Years of Injection into the Utsira Formation in the Sleipner Area. Energy Procedia, 1(1): 1997–2004. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2009.01.260
Hou, G. C., Zhang, M. S., Liu, F., 2008. The Ordos Basin Groundwater Investigation Research. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
IEA, 2008. CO2 Capture and Storage: A Key Carbon Abatement Option. OECD Publishing, Paris. doi:10.1787/9789264041417-en
IPCC, 2005. IPCC Special Report on Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage. Prepared by Working Group III of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In: Metz, B., Davidson, O., de Coninck, H. C., et al., eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 442
Izgec, O., Demiral, B., Bertin, H., et al., 2008. CO2 Injection into Saline Carbonate Aquifer Formations II: Comparison of Numerical Simulations to Experiments. Transport in Porous Media, 73(1): 57–74. doi:10.1007/s11242-007-9160-1
Kampman, N., Bickle, M., Wigley, M., et al., 2014. Fluid Flow and CO2-Fluid-Mineral Interactions during CO2-Storage in Sedimentary Basins. Chemical Geology, 369(14): 22–50. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.11.012
Kharaka, Y. K., Cole, D. R., Hovorka, S. D., et al., 2006. Gas-Water-Rock Interactions in Frio Formation Following CO2 Injection: Implications for the Storage of Greenhouse Gases in Sedimentary Basins. Geology, 34(7): 577–580. doi:10.1130/g22357a.1
Kharaka, Y. K., Thordsen, J. J., Hovorka, S. D., et al., 2009. Potential Environmental Issues of CO2 Storage in Deep Saline Aquifers: Geochemical Results from the Frio-I Brine Pilot Test, Texas, USA. Applied Geochemistry, 24(6): 1106–1112. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.02.010
Kihm, J. H., Kim, J. M., Wang, S., et al., 2012. Hydrogeochemical Numerical Simulation of Impacts of Mineralogical Compositions and Convective Fluid Flow on Trapping Mechanisms and Efficiency of Carbon Dioxide Injected into Deep Saline Sandstone Aquifers. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 117(B6): 6204. doi:10.1029/2011jb008906
Li, D. S., 2004. Return to Petroleum Geology of Ordos Basin. Petroleum Exploration & Development, 31(6): 1–7 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, Q., Liu, G. Z., Liu, X. H., et al., 2013. Application of a Health, Safety, and Environmental Screening and Ranking Framework to the Shenhua CCS Project. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 17(5): 504–514. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.06.005
Li, X. Q., Hou, D. J., Hu, G. Y., 2005. Formation Fluid Characteristics and Gas Accumulation of the Central Gas Field of Ordos Basin. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Liu, H. J., Hou, Z. M., Were, P., et al., 2015. Modelling CO2-Brine-Rock Interactions in the Upper Paleozoic Formations of Ordos Basin Used for CO2 Sequestration. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(5): 2205–2222. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3571-4
Liu, N. N., Liu, L., Ming, X. R., et al., 2014. Petrologic and Geochemical Characteristics and Carbon Sequestration Capability of the Permian Shiqianfeng Formation around Ejin Horo Banner of Ordos Basin. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 33(2): 255–262 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liu, N., Liu, L., Qu, X. Y., et al., 2011. Genesis of Authigene Carbonate Minerals in the Upper Cretaceous Reservoir, Honggang Anticline, Songliao Basin: A Natural Analog for Mineral Trapping of Natural CO2 Storage. Sedimentary Geology, 237(3/4): 166–178. doi:10.1016/j.sedgeo.2011.02.012
Lu, J. M., Kharaka, Y. K., Thordsen, J. J., et al., 2012. CO2-Rock-Brine Interactions in Lower Tuscaloosa Formation at Cranfield CO2 Sequestration Site, Mississippi, U.S.A.. Chemical Geology, 291(1): 269–277. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.10.020
Lu, J., Kordi, M., Hovorka, S. D., et al., 2013. Reservoir Characterization and Complications for Trapping Mechanisms at Cranfield CO2 Injection Site. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 18(7): 361–374. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2012.10.007
Lu, P., Fu, Q., Seyfried, W. E., et al., 2011. Navajo Sandstone-Brine-CO2 Interaction: Implications for Geological Carbon Sequestration. Environmental Earth Sciences, 62(1): 101–118. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0501-y
Luengen, H. B., Endemann, G., Schmö le, P., 2011. Measures to Reduce CO2 and Other Emissions in the Steel Industry in Germany and Europe. World Iron & Steel, 16(5): 42–50
Mitiku, A. B., Li, D., Bauer, S., et al., 2013. Geochemical Modelling of CO2-Water-Rock Interactions in a Potential Storage Formation of the North German Sedimentary Basin. Applied Geochemistry, 36(3): 168–186. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.06.008
Moore, J., Adams, M., Allis, R., et al., 2005. Mineralogical and Geochemical Consequences of the Long-Term Presence of CO2 in Natural Reservoirs: An Example from the Springerville-St. Johns Field, Arizona, and New Mexico, U.S.A.. Chemical Geology, 217(3/4): 365–385. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.12.019
Oelkers, E. H., Gislason, S. R., Matter, J., 2008. Mineral Carbonation of CO2. Elements, 4(5): 333–337. doi:10.2113/gselements.4.5.333
Okuyama, Y., Todaka, N., Sasaki, M., et al., 2013. Reactive Transport Simulation Study of Geochemical CO2 Trapping on the Tokyo Bay Model–With Focus on the Behavior of Dawsonite. Applied Geochemistry, 30(2): 57–66. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.07.009
Olajire, A. A., 2013. A Review of Mineral Carbonation Technology in Sequestration of CO2. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 109: 364–392. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2013.03.013
Petroleum Geology Group of Oilfield, 1992. Petroleum Geology of China (Vol. 12) Changqing Oil Field. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing. 490 (in Chinese)
Rosenbauer, R. J., Koksalan, T., Palandri, J. L., 2005. Experimental Investigation of CO2-Brine-Rock Interactions at Elevated Temperature and Pressure: Implications for CO2 Sequestration in Deep-Saline Aquifers. Fuel Processing Technology, 86(14/15): 1581–1597. doi:10.1016/j.fuproc.2005.01.011
Tambach, T. J., Koenen, M., Wasch, L. J., et al., 2015. Geochemical Evaluation of CO2 Injection and Containment in a Depleted Gas Field. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 32: 61–80. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2014.10.005
Thomas, M. W., Stewart, M., Trotz, M., et al., 2012. Geochemical Modeling of CO2 Sequestration in Deep, Saline, Dolomitic-Limestone Aquifers: Critical Evaluation of Thermodynamic Sub-Models. Chemical Geology, 306/307: 29–39. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.02.019
Trémosa, J., Castillo, C., Vong, C. Q., et al., 2014. Long-Term Assessment of Geochemical Reactivity of CO2 Storage in Highly Saline Aquifers: Application to Ketzin, In Salah and Snøhvit Storage Sites. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 20: 2–26. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.10.022
van Genuchten, M. T. V., 1980. A Closed-Form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 44(5): 892–898. doi:10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x
Wang, H. Y., 2012. Study on the Interaction of CO2 Fluid with Sandstone in Shiqianfeng: [Dissertation]. Jilin University, Changchun (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, L., Shen, Z. L., Hu, L. S., et al., 2014. Modeling and Measurement of CO2 Solubility in Salty Aqueous Solutions and Application in the Erdos Basin. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 377: 45–55. doi:10.1016/j.fluid.2014.06.016
Wang, Y. S., 2014. The Research Report of the Shenhua 0.1 Mt CCS Demonstration Project. China Shenhua Coal Liquefaction Co., Ltd., Ordos. Unpulished Results (in Chinese)
Wang, Y., Crandall, D., Bruner, K., et al., 2013. Core and Pore Scale Characterization of Liujiagou Outcrop Sandstone, Ordos Basin, China for CO2 Aquifer Storage. Energy Procedia, 37: 5055–5062. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2013.06.419
Watson, M. N., Zwingmann, N., Lemon, N. M., 2004. The Ladbroke Grove-Katnook Carbon Dioxide Natural Laboratory: A Recent CO2 Accumulation in a Lithic Sandstone Reservoir. Energy, 29(9/10): 1457–1466. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2004.03.079
White, S. P., Allis, R. G., Moore, J., et al., 2005. Simulation of Reactive Transport of Injected CO2 on the Colorado Plateau, Utah, U.S.A.. Chemical Geology, 217(3/4): 387–405. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.12.020
Whittaker, S., Rostron, B., Hawkes, C., et al., 2011. A Decade of CO2 Injection into Depleting Oil Fields: Monitoring and Research Activities of the IEA GHG Weyburn-Midale CO2 Monitoring and Storage Project. Energy Procedia, 4: 6069–6076. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2011.02.612
Wigand, M., Carey, J. W., Schü tt, H., et al., 2008. Geochemical Effects of CO2 Sequestration in Sandstones under Simulated In-Situ Conditions of Deep Saline Aquifers. Applied Geochemistry, 23(9): 2735–2745. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.06.006
Wolery, T. J., 1992. Software Package for Geochemical Modeling of Aqueous System: Package Overview and Installation Guide (Version 8.0). Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Report UCRL-MA-110662 PT I, Livermore, California, U.S.A.
Wu, X. Z., 2013. Carbon Dioxide Capture and Geological Storage: The First Massive Exploration in China. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Xie, H. P., Li, X. C., Fang, Z. M., et al., 2014. Carbon Geological Utilization and Storage in China: Current Status and Perspectives. Acta Geotechnica, 9(1): 7–27. doi:10.1007/s11440013-0277-9
Xu, T. F., Apps, J. A., Pruess, K., 2004. Numerical Simulation of CO2 Disposal by Mineral Trapping in Deep Aquifers. Applied Geochemistry, 19(6): 917–936. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.11.003
Xu, T. F., Kharaka, Y. K., Doughty, C., et al., 2010. Reactive Transport Modeling to Study Changes in Water Chemistry Induced by CO2 Injection at the Frio-I Brine Pilot. Chemical Geology, 271(3/4): 153–164. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.01.006
Xu, T. F., Apps, J. A., Pruess, K., 2005. Mineral Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide in a Sandstone-Shale System. Chemical Geology, 217(3/4): 295–318. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.12.015
Xu, T. F., Sonnenthal, E., Spycher, N., et al., 2006. TOUGHREACT—A Simulation Program for Non-Isothermal Multiphase Reactive Geochemical Transport in Variably Saturated Geologic Media: Applications to Geothermal Injectivity and CO2 Geological Sequestration. Computers & Geosciences, 32(2): 145–165. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2005.06.014
Xu, T. F., Spycher, N., Sonnenthal, E., et al., 2012. TOUGHREACT User’s Guide: A Simulation Program for Non-Isothermal Multiphase Reactive Transport in Variably Saturated Geologic Media, Version 2.0. Earth Sciences Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, CA94720
Yang, G. D., Li, Y. L., Cheng, P., et al., 2011. Assessment of CO2 Geological Storage Potential of Some Sedimentary Basins in China (Poster). 2011 GCEP Research Symposium: Addressing the Changing Energy Landscape. Stanford University, Stanford
Yang, G. D., Li, Y. L., Ma, X., et al., 2014. Effect of Chlorite on CO2-Water-Rock Interaction. Earth Science–Journal of China University of Geosciences, 39(4): 462–472. doi:10.3799/dqkx.2014.044 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, S., DePaolo, D. J., Xu, T. F., et al., 2013. Mineralization of Carbon Dioxide Sequestered in Volcanogenic Sandstone Reservoir Rocks. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 18: 315–328. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.08.001
Zhang, W., Li, Y. L., Xu, T. F., et al., 2009. Long-Term Variations of CO2 Trapped in Different Mechanisms in Deep Saline Formations: A Case Study of the Songliao Basin, China. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 3(2): 161–180. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2008.07.007
Zhao, R. R., Cheng, J. M., 2016. Using Hydraulic Barrier Control CO2 Plume Migration in Sloping Reservoir. Earth Science–Journal of China University of Geosciences, 41(4): 675–682 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhu, H. T., Liu, K. Y., Yang, X. H., et al., 2013. Sedimentary Controls on the Sequence Stratigraphic Architecture in Intra-Cratonic Basins: An Example from the Lower Permian Shanxi Formation, Ordos Basin, Northern China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 45: 42–54. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.04.0
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the Global Climate and Energy Project (No. 2384638-43106-A), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41072180), the Special Scientific Research Fund of Public Welfare Profession of the Ministry of Land and Resources of China (No. 201211063), and a bilateral project of China Australia Geological Storage of CO2 Project Phase 2 (CAGS2). We would like to thank Dr. Sizhen Peng, Jiutian Zhang (The Administrative Centre for China’s Agenda 21) and Maoshan Chen (The Shenhua Group Corporation Limited) for their insightful suggestions on the manuscript. Two anonymous reviewers are also gratefully acknowledged. The final publication is available at Springer via http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12583-016-0919-6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6857-1163
http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4192-5371
Yang, G. D., Li, Y. L., Atrens, A., et al., 2017. Reactive Transport Modeling of Long-Term CO2 Sequestration Mechanisms at the Shenhua CCS Demonstration Project, China. Journal of Earth Science, 28(3): 457-472. doi:10.1007/s12583-016-0919-6. http://en.earth-science.net
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, G., Li, Y., Atrens, A. et al. Reactive transport modeling of long-term CO2 sequestration mechanisms at the Shenhua CCS demonstration project, China. J. Earth Sci. 28, 457–472 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-016-0919-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-016-0919-6