Abstract
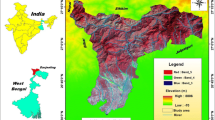
This paper mainly deals with the integrated approach of remote sensing and Geographical Information System (GIS) to delineate groundwater prospective zones in Narava basin, Visakhapatnam region. The various thematic maps generated for delineating groundwater potential zones are geomorphology, geology, lineament density, drainage density, slope and land use/land cover (LULC). Weighted index overlay (WIO) technique is used to investigate a number of choice possibilities and evaluate suitability according to the associated weight of each unit. The integrated map of the area shows different zones of groundwater prospects, viz. very good (18.9% of the area), good (26.4% of the area), moderate (17.1% of the area) and poor (37.6% of the area). The categorization of groundwater potential was in good agreement with the available water column in the basin area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apdham, M.I., Jpahan, C.S., Mpazumder, Q.H., Hpossain, M.M.A. and Hpaque, A.M. (2010) Study on groundwater recharge potentiality of Barind tract, Rajshahi district, Bangladesh using GIS and remote sensing technique. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.75, pp.432–438.
Apvtar, R., Spingh, C.K., Sphashtri, S., Spingh, A. and Mpukherjee, S. (2010) Identification and analysis of groundwater potential zones in Ken-Betwa river linking area using remote sensing and geographic information system. Geocarto Int., v.25, pp.379–396.
CGWB. (2007) Manual on artificial recharge of groundwater. Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water Resources, Govt. of India, New Delhi.
Cphandra, S., Rpao, V.A., Kprishnamurthy, N.S., Dputta, S. and Aphmed, S. (2006) Integrated studies for characterization of lineaments used to locate groundwater potential zones in a hard rock region of Karnataka, India. Hydrogeol. Jour., v.14, pp.1042–1051.
Cphowdhury, A., Jpha, M.K. and Cphowdary, V.M. (2010) Delineation of groundwater recharge zones and identification of artificial recharge sites in West Medinipur district, West Bengal, using RS, GIS and MCDM techniques. Env. Earth Sci., v.59, pp.1209–1222.
Cphowdhury, A., Jpha, M.K., Cphowdary, V.M. and Mpal, B.C. (2009) Integrated remote sensing and GIS-based approach for assessing groundwater potential in West Medinipur district, West Bengal, India. Int. Jour. Remote Sensing, v.30, pp.231–250.
Dpinesh Kpumar, P.K., Gpopinath, G. and Speralathan, P. (2007) Application of remote sensing and GIS for the demarcation of groundwater potential zones of a river basin in Kerala, southwest coast of India. Int. Jour. Remote Sensing, v.28, pp.5583–5601.
Epdward, A.S. (1974) Aquifer tests in large diameter wells in India. Groundwater, v.12, pp.265–272.
Gpupta, M. and Sprivastava, P.K. (2010) Integrating GIS and remote sensing for identification of groundwater potential zones in the hilly terrain of Pavagarh, Gujarat, India. Water Int., v.35, pp.233–245.
GWD (2006) Ground Water Resource 2004-05, Andhra Pradesh. Ground Water Department, Govt. of Andhra
Pradesh, Hyderabad. IMSD. (1995) Integrated mission for sustainable development technical guidelines. National Remote Sensing Agency, Department of Space, Govt. of India.
Jpaiswal, R.K., Mpukherjee, S., Kprishnamurthy, J. and Spaxena, R. (2003) Role of remote sensing and GIS techniques for generation of groundwater prospect zones towards rural development-an approach. Int. Jour. Remote Sensing, v.24, pp.993–1008.
Jpaved, A. and Wpani, M.H. (2009) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Kakund watershed, Eastern Rajasthan, using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.73, pp.229–236.
Jpha, M.K., Cphowdary, V.M. and Cphowdhury, A. (2010) Groundwater assessment in Salboni Block, West Bengal (India) using remote sensing, geographical information system and multicriteria decision analysis techniques. Hydrogeol. Jour., v.18, pp.1713–1728.
Kprishnamurthy, J., Mpani, A.N., Jpayaram, V. and Mpanivel, M. (2000) Groundwater resources development in hard rock terrain: an approach using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Int. Jour. Appld Earth Obser. Geoinformatics, v.2, pp.204–215.
Mpondal, S.MD., Ppandey, A.C. and Gparg, R.D. (2008) Groundwater prospects evaluation based on hydrogeomorphological mapping using high resolution satellite images: a case study in Uttarakhand. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sens., v.36, pp.69–76.
Mpurthy, K.S.R. and Mpamob, A.G. (2009) Multi-criteria decision evaluation in groundwater zones identification in Moyale-Teltele subbasin, South Ethiopia. Int. Jour. Remote Sensing, v.30, pp.2729–2740.
Npag, S.K. (2005) Application of lineament density and hydrogeomorphology to delineate groundwater potential zones of Baghmundi block in Prulia district, West Bengal. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.33, pp.521–529.
Npagarajan, M. and Spingh, S. (2009) Assessment of groundwater potential zones using GIS technique. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.37, pp.69–77.
Npageswara Rpao, K. and Nparendra, K. (2006) Mapping and evaluation of urban sprawling in the Mehadrigedda watershed in Visakhapatnam metropolitan region using remote sensing and GIS. Curr. Sci., v.91, pp.1552–1557.
NRSA (1999) National rural drinking water mission methodology manual for preparation of groundwater prospects maps. National Remote Sensing Agency, Govt. of India, Hyderabad.
Ppratap, K., Rpavindran, K.V. and Pprabakaran, B. (2000) Groundwater prospect zoning using remote sensing and geographical information system: a case study in Dala-Renukoot area, Sonbhadra district, Uttar Pradesh. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.28, pp.249–263.
Ppreeja, K.R., Jposeph, S., Tphomas, J. and Vpijith, H. (2011) Identification of groundwater potential zones of a tropical river basin (Kerala, India) using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.39, pp.83–94.
Spander, P. (2007) Lineaments in groundwater exploration: a review of applications and limitations. Hydrogeol. Jour., v.15, pp.71–74.
Sphahid, S., Npath, S.K. and Rpay, J. (2000) Groundwater potential modeling in softrock using a GIS. Int. Jour. Remote Sensing, v.21, pp.1919–1924.
Spilverman, B.W. (1986) Density estimation for statistics and data analysis. New York: Chapman and Hall.
Spreedevi, P.D., Spubrahmanyam, K. and Aphmed, S. (2005) Integrated approach for delineating potential zones to explore for groundwater in the Pageru River basin, Kuddapah District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Hydrogeol. Jour., v.13, pp.534–545.
Sptrahler, A.N. (1964) Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basins and channel networks In. Handbook of applied hydrology, Section 4-II. McGraw Hill Book Company, New York, pp.39–76.
Spubba Rpao, N. (2009) A numerical scheme for groundwater development in a watershed basin of basement terrain: a case study from India. Hydrogeol. Jour., v.17, pp.379–396.
Spuja Rpose, R.S. and Kprishnan, N. (2009) Spatial analysis of groundwater potential using remote sensing and GIS in the Kanyakumari and Nambiyar basins, India. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.37, pp.681–692.
Tphomas, B.C., Kpuriakose, S.L. and Jpaydev, S.K. (2009) A method for groundwater prospect zonation in data poor areas using remote sensing and GIS: a case study in Kalikavu Panchayath of Malappuram district, Kerala, India. Int. Jour. Digital Earth, v.2, pp.155–170.
Tpodd, D.K. and Mpays, L.W. (2005) Groundwater Hydrology. 3rd ed., Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.
Vpijith, H. (2007) Groundwater potential in the hard rock terrain of Western Ghats: a case study from Kottayam district, Kerala using Resourcesat (IRS-P6) data and GIS techniques. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.35, pp.163–171.
Wpisler, C.O. and Bprater, B.F. (1959) Hydrology. New York: Willey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narendra, K., Nageswara Rao, K. & Swarna Latha, P. Integrating remote sensing and GIS for identification of groundwater prospective zones in the Narava basin, Visakhapatnam region, Andhra Pradesh. J Geol Soc India 81, 248–260 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-013-0028-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-013-0028-4