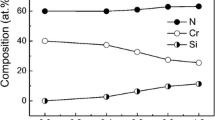
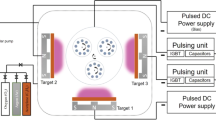
Abstract
For high-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HIPIMS), the peak power applied to the target is of great importance for regulating the ionization degree of the metal target and ion/atom flux ratio. In this work, chromium (Cr) films were deposited on 316-L stainless steel substrates and silicon (100) wafers with different peak powers by HIPIMS. The relationship between peak target power and properties of Cr films was explored in detail. The resulting structure and mechanical properties of deposited Cr films were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), indentation hardness and scratch tester. The results indicate that the ionization degree of metal target and ion/atom flux ratio increase with the increase in peak power but without the loss of deposition rate at the same time. At low ionization degree, the deposited Cr film has low compressive residual stress and low hardness but good adhesion strength. When the ionization degree of target metal increases with increasing peak power, Cr film exhibits finer size and smoother surface with improved hardness but decreased adhesion strength.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seok JW, Jadeed NM, Lin RY. Sputter-deposited nanocrystalline Cr and CrN coatings on steels. Surf Coat Technol. 2001;138(1):14.
Walter KC, Scheuer JT, McIntyre PC, Kodali P, Yu N, Nastasi M. Increased wear resistance of electrodeposited chromium through applications of plasma source ion implantation techniques. Surf Coat Technol. 1996;85(1–2):1.
Mazille HMJ. Chemical vapour deposition of chromium onto nickel. Thin Solid Films. 1980;65(1):67.
Pérez FJ, Pedraza F, Hierro MP, Carpintero MC, Gómez C. Chromising of stainless steels by the use of the CVD-FBR technology. Surf Coat Technol. 2004;184(1):47.
Bolelli G, Cannillo V, Lusvarghi L, Riccò S. Mechanical and tribological properties of electrolytic hard chrome and HVOF-sprayed coatings. Surf Coat Technol. 2006;200(9):2995.
Vetushka A, Ehiasarian AP. Plasma dynamic in chromium and titanium HIPIMS discharges. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2008;41(1):015.
Theiß S, Bibinov N, Bagcivan N, Ewering M, Awakowicz P, Bobzin K. Time resolved optical emission spectroscopy of an HPPMS coating process. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2010;43(7):075.
Macák K, Kouznetsov V, Schneider J, Helmersson U, Petrov I. Ionized sputter deposition using an extremely high plasma density pulsed magnetron discharge. J Vac Sci Technol A: Vac Surf Films. 2000;18(4):1533.
Hecimovic A, Burcalova KM, Ehiasarian AP. Origins of ion energy distribution function (IEDF) in high power impulse magnetron sputtering (HIPIMS) plasma discharge. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2008;41(9):095.
Vlček J, Kudláček P, Burcalová K, Musil J. Ion flux characteristics in high-power pulsed magnetron sputtering discharges. Europhys Lett (EPL). 2007;77(4):45002.
Lattemann M, Ehiasarian AP, Bohlmark J, Persson PÅO, Helmersson U. Investigation of high power impulse magnetron sputtering pretreated interfaces for adhesion enhancement of hard coatings on steel. Surf Coat Technol. 2006;200(22–23):6495.
Sarakinos K, Alami J, Konstantinidis S. High power pulsed magnetron sputtering: a review on scientific and engineering state of the art. Surf Coat Technol. 2010;204(11):1661.
Olaya JJ, Rodil SE, Muhl S, Sánchez E. Comparative study of chromium nitride coatings deposited by unbalanced and balanced magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films. 2005;474(1–2):119.
Olaya JJ, Wei G, Rodil SE, Muhl S, Bhushan B. Influence of the ion–atom flux ratio on the mechanical properties of chromium nitride thin films. Vacuum. 2007;81(5):610.
Kim K, Park M, Lee W, Kim HW, Lee JG, Lee C. Effects of sputtering power on mechanical properties of Cr films deposited by magnetron sputtering. Mater Sci Technol. 2008;24(7):838.
Ehiasariana AP, Newa R, Munz WD, Hultmanb L, Helmerssonb U, Kouznetsov V. Influence of high power densities on the composition of pulsed magnetron plasmas. Vacuum. 2002;65(2):147.
Jing FJ, Yin TL, Yukimura K, Sun H, Leng YX, Huang N. Titanium film deposition by high-power impulse magnetron sputtering: influence of pulse duration. Vacuum. 2012;86(12):2114.
Yukimura K, Mieda R, Tamagaki H, Okimoto T. Electrical characteristics of arc-free high-power pulsed sputtering glow plasma. Surf Coat Technol. 2008;202(22–23):5246.
Horwat D, Anders A. Spatial distribution of average charge state and deposition rate in high power impulse magnetron sputtering of copper. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2008;41(13):135.
Shefford PB, William DN. Mechanical properties of compositionally modulated Au-Ni thin films: nanoindentation and microcantilever deflection experiments. Mater Res Soc. 1994;9(12):3131.
Sibillano T, Ancona A, Rizzi D, Rodil SS, Nieto JR, Konuk AR, Aarts R, Huis AJ. Study on the correlation between plasma electron temperature and penetration depth in laser welding processes. Phys Procedia. 2010;5(Part B):429.
Christou C, Barber ZH. Ionization of sputtered material in a planar magnetron discharge. J Vac Sci Technol A: Vac Surf Films. 2000;18(6):2897.
Christie DJ. Target material pathways model for high power pulsed magnetron sputtering. J Vac Sci Technol A: Vac Surf Films. 2005;23(2):330.
Christie DJ. Fundamentals of high power pulsed magnetron sputtering: visualization of mechanisms for rate reduction and increased ion fraction. Czech J Phys. 2006;56(2):B93.
Alami J, Gudmundsson JT, Bohlmark J, Birch J, Helmersson U. Plasma dynamics in a highly ionized pulsed magnetron discharge. Plasma Sources Sci Technol. 2005;14(3):525.
Wu BH, Wang Y, Yu Y, Jiang F, Sun H, Jing FJ, Zhu SF, Wu YP, Leng YX, Huang N. Modulate the deposition rate through changing the combination of frequency and pulse width at constant duty cycle. Surf Coat Technol. 2015;281(3):27.
Pauleau Y. Generation and evolution of residual stresses in physical vapour-deposited thin films. Vacuum. 2001;61(2):175.
Windischmann H. Intrinsic stress in sputter-deposited thin films. Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci. 1992;17(6):547.
Feng YC, Laughlin DE, Lambeth DN. Formation of crystallographic texture in rf sputter-deposited Cr thin films. J Appl Phys. 1994;76(11):7311.
Ferrec A, Keraudy J, Jacq S, Schuster F, Jouan PY, Djouadi MA. Correlation between mass-spectrometer measurements and thin film characteristics using dcMS and HiPIMS discharges. Surf Coat Technol. 2014;250(18):52.
Chiang KTK, Wei RH. Growth morphology and corrosion resistance of magnetron sputtered Cr films. Surf Coat Technol. 2011;206(7):1660.
Lee JW, Tien SK, Kuo YC, Chen CM. The mechanical properties evaluation of the CrN coatings deposited by the pulsed DC reactive magnetron sputtering. Surf Coat Technol. 2006;200(10):3330.
LaFontaine WR, Yost B, Li CY. Effect of residual stress and adhesion on the hardness of copper films deposited on silicon. Mat Res Soc. 1990;5(4):776.
Sellers J. Asymmetric bipolar pulsed DC: the enabling technology for reactive PVD. Surf Coat Technol. 1998;98(1):1245.
Lin JL, Moore JJ, Sproul WD, Mishra B, Wu ZL. Modulated pulse power sputtered chromium coatings. Thin Solid Films. 2009;518(5):1566.
Janssen GCAM. Stress and strain in polycrystalline thin films. Thin Solid Films. 2007;515(17):6654.
Moona MW, Jensen HM, Hutchinson JW, Oh KH, Evans AG. The characterization of telephone cord buckling of compressed thin films on substrates. J Mech Phys Solids. 2002;50(11):2355.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Joint Fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China and China Academy of Engineering Physics (No. U1330113), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31300787) and the Overseas Famous Teacher Program of Chinese Education Ministry (No. MS2010XNJT070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wu, BH., Jiang, F. et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Cr films deposited with different peak powers by high-power impulse magnetron sputtering. Rare Met. 42, 327–335 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0897-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0897-6