Abstract
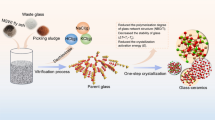
Municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash is a by-product from municipal waste incineration. According to incomplete statistics, each year more than one million tons MSWI fly ash was produced in China. Owing to high heavy elements content, widely used disposal methods of landfill are not suitable for MSWI fly ash treatment. In this study, by using MSWI fly ash as raw materials, glass–ceramics was synthesized for the solidification of heavy metals and waste recycle. Process parameters, including composition, heat treatment temperature and time, were studied and optimized. Under optimizing conditions, the product has good properties of density of 3.42 g·cm−3 and Vickers hardness of 6.91 GPa. Moreover, the leaching concentration of heavy metal elements meets allowable values of toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP). This study offers an alternative for MSWI fly ash recycle.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei D, Jianguo J, Ye X. Characterization and composition of municipal solid waste in cities in southeast China. Waste Manag. 2014;34(11):5.
Barbara K, Graedel RTE. Challenges in metal recycling. Science. 2012;337(6095):700.
Zhou JZ, Wu SM, Pan Y, Zhang L, Cao ZB, Zhang XQ. Enrichment of heavy metals in fine particles of municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) fly ash and associated health risk. Waste Manag. 2015;43:239. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2015.06.026.
Lin KL, Chen BY. Understanding biotoxicity for reusability of municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) ash. J Hazard Mater. 2006;138(1):9.
Ferreira C, Ribeiro A, Ottosen L. Possible applications for municipal solid waste fly ash. J Hazard Mater. 2003;96(2):201.
Ferreira M, Salvo M, Smeacetto F, Augier L, Barbieri L, Corradi A, Lancellotti I. Glass matrix composites from solid materials. J Hazard Mater. 2001;21(4):453.
Shi HS, Kan LL. Leaching behavior of heavy metals from municipal solid wastes incineration (MSWI) fly ash used in concrete. J Hazard Mater. 2009;164(2–3):750.
Zacco A, Borgese L, Gianoncelli A, Struis RPWJ, Depero LE, Bontemp E. Review of fly ash inertisation treatments and recycling. Environ Chem Lett. 2014;12(1):153.
Zhang ZK, Zhang L, Li AM. Development of a sintering process for recycling oil shale fly ash and municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash into glass ceramic composite. Waste Manag. 2015;2015(38):185.
Zhao YC, Song LJ, Li GJ. Chemical stabilization of MSW incinerator fly ashes. J Hazard Mater. 2002;95(1–2):47.
Ning ZQ, Zhai YC, Xie HW, Song QS, Yu K. Recovery of silica from sodium silicate solution of calcined boron mud. Rare Met. 2016;35(2):204.
Nie ZR, Ma LW, Xi XL. “Complexation-precipitation” metal separation method system and its application in secondary resources. Rare Met. 2014;33(4):369.
Mymrin V, Ribeiro RAC, Alekseev K, Zelinskaya E, Tolmacheva N, Catai R. Environment friendly ceramics from hazardous industrial wastes. Ceram Int. 2014;40(7):9427.
Mymrin V, Alekseev KP, Zelinskaya EV, Tolmacheva NA, Catai RE. Industrial sewage slurry utilization for red ceramics production. Constr Build Mater. 2014;66:168. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.05.036.
Yang J, Zhang SG, Pan DA, Liu B, Wu CL, Volinsky AA. Treatment method of hazardous pickling sludge by reusing as glass-ceramics nucleation agent. Rare Met. 2016;35(3):269.
Yang JK, Xiao B, Boccaccini AR. Preparation of low melting temperature glass–ceramics from municipal waste incineration fly ash. Fuel. 2009;88(7):1275.
Erol M, Küçükbayrak S, Ersoy-Meriçboyu A. Production of glass-ceramics obtained from industrial wastes by means of controlled nucleation and crystallization. Chem Eng J. 2007;132(1):335.
Erol M, Küçükbayrak S, Ersoy-Meriçboyu A. Comparison of the properties of glass, glass-ceramic and ceramic materials produced from coal fly ash. J Hazard Mater. 2008;153(1–2):418.
Ljatifia E, Kamushevaa A, Grozdanova A, Paunovića P, Karamanovb A. Optimal thermal cycle for production of glass–ceramic based on wastes from ferronickel manufacture. Ceram Int. 2015;41(9):11379.
Li M, Zhang Y, Wang XH, Yang JG, Qiao S, Zheng SL, Zhang Y. Extraction of copper, zinc and cadmium from copper–cadmium-bearing slag by oxidative acid leaching process. Rare Met. 2016;. doi:10.1007/s12598-016-0759-7.
Luo XF, Ren LC, Xie WT, Qian L, Wang YZ. Microstructure, sintering and properties of CaO–Al2O3–B2O3–SiO2 glass/Al2O3 composites with different CaO contents. J Mater Sci Mater El. 2016;27(5):5446.
Kavouras P, Komninou PH, Chrissafis K, Kaimakamis G, Kokkou S, Paraskevopoulos K, Karakostas TH. Microstructural changes of processed vitrified solid waste products. J Eur Ceram Soc Ceram Int. 2003;23(8):1305.
Qu G, Hu X, Cui L, Lu A. Synthesis, crystallization behavior and microstructure of oxynitride glass-ceramics with different modifier elements. Ceram Int. 2014;40(3):4213.
Russel C. Nanocrystallization of CaF2 from Na2O/K2O/CaO/CaF2/Al2O3/SiO2 glasses. Chem Mater. 2006;17(23):5843.
Yang J, Liu B, Zhang SG, Volinsky AA. Glass-ceramics one-step crystallization accomplished by building Ca2+ and Mg2+ fast diffusion layer around diopside crystal. J Alloy Compd. 2016;688:709.
Yang ZH, Wang B, Cormack AN. The local structure of Fe in Li(Al, Fe)Si2O6 glasses from molecular dynamics simulations. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2016;444:16.
Rezvani M, Eftekhari-Yekta B, Solati-Hashjin M, Marghussian VK. Effect of Cr2O3, Fe2O3 and TiO2 nucleants on the crystallization behaviour of SiO2–Al2O3–CaO–MgO(R2O) glass-ceramics. Ceram Int. 2005;31(1):75.
Kim JM, Kim HS. Processing and properties of a glass-ceramic from coal fly ash from a thermal power plant through an economic process. J Eur Ceram Soc Ceram Int. 2004;24(9):2825.
Mukherjee DP, Molla AR, Das SK. The influence of MgF2 content on the characteristic improvement of machinable glass ceramics. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2016;433:51. doi:10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2015.11.031.
Sheng JW, Huang BX, Zhang J, Zhang H, Sheng JY, Yu S, Zhang MJ. Production of glass from coal fly ash. Fuel. 2003;82(2):181.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. U1360202, 51472030, 51672024 and 51502014), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. FRF-TP-16-027A3) and the Innovation Project of Yunnan Province New Material Preparation and Processing Key Laboratory (No. 2016cx05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, WD., Liu, B., Luo, X. et al. Production of glass–ceramics using Municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Rare Met. 38, 245–251 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0976-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0976-8