Abstract
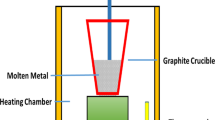
The present study considers friction and wear of aluminium matrix composites reinforced with TiB2 micro particles processed through the stir casting method rather than in-situ techniques adopted by earlier studies. Different weight percentages of TiB2 powders having average sizes of 5 - 40 micron were incorporated into molten LM4 aluminium matrix by stir casting method. The friction and wear behavior were studied for Al-TiB2 composites prepared according to specific dimensions by using a block-on-roller type multi-tribotester at room temperature. Normal loads of 25 - 75 N and rotational speed of 400 – 600 rpm were used for determination of friction and wear behavior. It is found that friction and wear decrease with increase in percentage of TiB2 reinforcement in the composite, while friction and wear increase with applied load and speed. Scanning electron microscopy studies the reveal presence of both abrasive and adhesive wear mechanisms with abrasive wear being predominant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suresh S, Mortensen A (1993) Fundamentals of Metal Matrix Composites. Butterworth-Heinemann
Chawla N, Chawla KK (2006) Metal Matrix Composites. Springer, New York
Kumar N, Gautam G, Gautam RK, Mohan A, Mohan S (2015) Synthesis and characterization of TiB2 reinforced aluminium matrix composites: A review. Journal of the Institute of Engineering India Series D, in press
Rohatgi PK (1993) Metal matrix composites. Def Sci J 43(4):323–349
Rittner M (2000) Metal matrix composites in the 21st century: markets and opportunities BCC Inc. BCC Inc., Norwalk, CT.
Kumar S, Subramanya Sarma V, Murty BS (2008) A statistical analysis on erosion wear behaviour of A356 alloy reinforced with in situ formed TiB2 particles. Mater Sci Eng A 476:333–340
Nami H, Adgi H, Sharifitabar M, Shamabadi H (2011) Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded Al/Mg2Si metal matrix cast composite. Mater Des 32:976
Sharifitabar M, Sarani A, Khorshahian S, Sharfiee Afarani M (2011) Fabrication of 5052Al/Al2O3 nanoceramic particle reinforced composite via friction stir processing route. Mater Des 32:4164–4172
Alidokht SA, Abdollah-Zadeh A, Soleymani S, Assadi H (2011) Microstructure and tribological performance of an aluminium alloy based hybrid composite produced by friction stir processing. Mater Des 32:2727
Miracle DB (2005) Metal matrix composites – from science to technological significance. Compos Sci Technol 65:2526–2540
Ghosh S, Sahoo P, Sutradhar G (2012) Wear behaviour of AL-SICp metal matrix composites and optimization using taguchi method and grey relational analysis. J Miner Mater Charact Eng 11:1085–1094
Rao RN, Das S (2011) Effect of applied pressure on the tribological behaviour of SiCp reinforced AA2024 alloy. Tribol Int 44:454–462
Sahin Y (2003) Preparation and some properties of SiC particle reinforced aluminium alloy composites. Mater Des 24:671–679
Ghosh S, Sahoo P, Sutradhar G (2013) Tribological performance optimization of Al-7.5%SiCp composites using taguchi method and grey relation analysis. Journal Composites 2013(Article ID 274527):1–9
Mandal D, Viswanathan S (2013) Effect of re-melting on particle distribution and interface formation in SiC reinforced 2124Al matrix composite. Mater Charact 86:21–27
Shorowordi KM, Laoui T, Haseeb ASMA, Celis JP, Froyen L (2003) Microstructure and interface characteristics of B4C, SiC and Al2O3 reinforced Al matrix composites: a comparative study. J Mater Process Technol 142:738–743
Mindivan H (2010) Reciprocal sliding wear behaviour of B4C particulate reinforced aluminum alloy composites. Mater Lett 64:405–407
Wang H, Li G, Zhao Y, Chen G (2010) In situ fabrication and microstructure of Al2O3 particles reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Mater Sci Eng A 527:2881–2885
Naveen kumar G, Narayanasamy R, Natarajan S, Kumaresh Babu SP, Sivaprasad K, Sivasankaran S (2010) Dry sliding wear behaviour of AA 6351-ZrB2 in situ composite at room temperature. Mater Des 31:1526–1532
Nukami T, Flemings MC (1995) In situ synthesis of TiC particulate-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Metall and Mater Trans A 26(7):1877–1884
Lakshmi S, Lu L, Gupta M (1998) In situ preparation of TiB2 reinforced Al based composites. J Mater Process Technol 73:160–166
Suresh S, Moorthi NSV, Vettivel SC, Selvakumar N (2014) Mechanical behavior and wear prediction of stir cast Al–TiB2 composites using response surface methodology. Mater Des 59:383–396
Tee KL, Lu L, Lai MO (2000) Wear performance of in-situ Al–TiB2 composite. Wear 240:59–64
Karbalaei Akbari M, Baharvandi HR, Shirvanimoghaddam K (2015) Tensile and fracture behavior of nano/micro TiB2 particle reinforced casting A356 aluminum alloy composites. Mater Des 66:150–161
Sivaprasada K, Kumaresh Babu SP, Natarajana S, Narayanasamy R, Anil kumar B, Dinesh G (2008) Study on abrasive and erosive wear behaviour of Al 6063/TiB2 in situ composites. Mater Sc Eng A 498:495–500
Tian SF, Jiang LT, Guo Q, Wu GH (2014) Effect of surface roughness on tribological properties of TiB2/Al composites. Mater Des 53:129–136
Lu L, Lai MO, Chen FL (1997) Al–4 wt % Cu composite reinforced with in situ TiB2 particles Acta. Materilia 45:4297–4309
Kennedy AR, Karantzalis AE, Wyatt SM (1999) The microstructure and mechanical properties of TiC and TiB2-reinforced cast metal matrix composites. J Mater Sci 34:933–940
Mandal A, Murty BS, Chakraborty M (2009) Sliding wear behaviour of T6 treated A356-TiB2 in-situ composites. Wear 266:865–872
Niranjan K, Lakshminarayanan PR (2013) Dry sliding wear behavior of in-situ Al-TiB2 composites. Mater Des 47:167– 173
Tjong SC, Tam KF (2006) Mechanical and thermal expansion behavior of hipped aluminum–TiB2 composites. Mater Chem Phys 97:91–97
Xue J, Wang J, Han Y, Li P, Sun B (2011) Effects of CeO2 additive on the microstructure and mechanical properties of in situ TiB2/Al composite. J Alloys Compd 509:1573–1578
Rosso M (2006) Ceramic and metal matrix composites: Routes and properties. J Mater Process Technol 175:364–375
Tee KL, Lu L, Lai MO (1999) Synthesis of in situ Al-TiB2 composites using stir cast route. Compos Struct 47:589–593
Chan F, Mao F, Chen Z, Han J, Yan G, Wang T (2015) Application of synchrotron radiation X-ray computed tomography to investigate the agglomerating behavior of TiB2 particles in aluminum. J Alloys Compd 622:831–836
ünlü BS (2008) Investigation of tribological and mechanical properties Al2O3–SiC reinforced Al composites manufactured by casting or P/M method. Mater Des 29:2002–2008
Y. Yang X (2007) Ultrasonic cavitation based nonmanufacturing of bulk aluminum matrix nanocomposites. J Manuf Sci Eng 129:497–501
Suresh S, Moorthi NS, Vettivel SC, Selvakumar N (2014) Effect of graphaite addition on mechanical behavior of Al6061/TiB2 hybrid composite using acoustic emission. Mater Sci Eng A 612:16–27
Hashim J, Looney L, Hasmi MSJ (2001) The wettability of SiC particles by molten aluminum alloy. J Mater Process Technol 119:324–328
Hashmi J (2001) The production of cast metal matrix composite by a modified stir casting method. J Teknol 35(A):9–20
Ray S (1993) Synthesis of cast metal matrix particulate composites. J Mater Sci 28(20):5397–5413
Anand Partheeban CM, Rajendran M, Vettivel SC, Suresh S, Moorthi NSV (2015) Mechanical behavior and failure analysis using online acoustic emission on nano-graphite reinforced Al6061–10TiB2 hybrid composite using powder metallurgy. Mater Sci Eng A 632:1–13
Vijay SJ, Murugan N (2010) Influence of tool pin profile on the metallurgical and mechanical properties of friction stir welded Al–10 wt. % TiB2 metal matrix composite. Mater Des 31:3585–3589
Michael Rajan HB, Ramabalan S, Dinaharan I, Vijay SJ (2014) Effect of TiB2 content and temperature on sliding wear behavior of AA7075/TiB2 in situ aluminium cast composites. Arch civil Mech Eng 14:72–79
Natarajan S, Narayansamy R, Kumaresh Babu SP, Dinesh G, Anil Kumar B, Sivaprasad K (2009) Sliding wear behavior of Al 6063/TiB2 in situ composites at elevated temperatures. Mater Des 30:2521–2531
Baradeswaran A, Elaya Perumal A, Davim JP (2013) Effect of B4C on mechanical properties and tribological behaviour of AA6061-b4c composites. J Balkan Tribol Assoc 19(2):239–248
Basavarajappa S, Chandramohan G, Davim JP (2007) Application of Taguchi techniques to study dry sliding wear behaviour of metal matrix composites. Mater Des 28(4):1393–1398
Bezzazi M, Khamlichi A, Jabbouri A, Reis P, Davim JP (2007) Experimental characterization of frictional behavior of clutch facings using pin-on-disk machine. Mater Des 28(7):2148–2153
Davim JP (ed) (2010) Tribology of composite materials. NOVA Publishers, New York. ISBN: 978-1-61668-319-1
Davim JP (ed) (2013) Tribology of nanocomposites. Springer, Heidelberg. ISBN: 978-3-642-33881-6
Davim JP (ed) (2012) wear of advanced materials. ISTE-Wiley, London. ISBN: 978-1-84821-352-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poria, S., Sahoo, P. & Sutradhar, G. Tribological Characterization of Stir-cast Aluminium-TiB2 Metal Matrix Composites. Silicon 8, 591–599 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9437-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9437-5