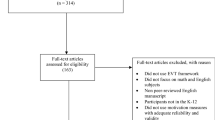
Abstract
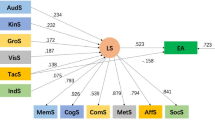
This current study sought to examine the role of creativity, metacognition and VAK learning style in foreign language achievement. To collect the data, a sample of 122 Iranian English as Foreign Language learners participated in this research. Participants completed Creativity Instrument by Abedi (Creat Res J 14(2):267–276, 2002), Metacognitive Awareness Inventory by Schraw and Dennison (Contemp Educ Psychol 19:460–475, 1994), and visual, aural, and kinesthetic (VAK) learning style initially designed by Chislett and Chapman (VAK Learning Styles Self-Assessment Questionnaire, 2005. http://www.businessballs.com) and modified and validated by the present study researchers using confirmatory factor analysis. Learners’ scores at the end of the term were aggregated as the measure of foreign language achievement. Its reliability was also checked and approved applying Cronbach’s α. According to the findings, all three independent variables positively and significantly predict students’ language achievement, creativity (14.63%); metacognition (29.78%); and VAK learning style (7.20%). Although each of them had a unique impact on foreign language achievement, metacognition outweighs creativity and VAK learning style as the predictor of foreign language achievement. Furthermore, there is a significant difference between genders on all the variables.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedi, J. (2002). A latent-variable modeling approach to assessing reliability and validity of a creativity instrument. Creativity Research Journal, 14, 267–276.
Ai, X. (1999). Creativity and academic achievement: An investigation of gender differences. Creativity Research Journal, 12, 329–337.
Atkinson, S. (2004). A comparison of the relationship between creativity, learning style preference and achievement at GCSE and degree level in the context of design and technology project work. Paper presented at the DATA International Research Conference on Creativity and Innovation, Sunderland University, England.
Bratko, D., Chamorro-Premuzic, T., & Saks, Z. (2006). Personality and school performance: Incremental validity of self- and peer-ratings over intelligence. Personality and Individual Differences, 41, 131–142.
Busato, V. V., Prins, F. J., Elshout, J. J., & Hamaker, C. (2000). Intellectual ability, learning style, achievement motivation and academic success of psychology students in higher education. Personality and Individual Differences, 29, 1057–1068.
Chamorro-Premuzik, T., & Furnham, A. (2003). Personality traits and academic examination performance. European Journal of Personality, 17, 237–250.
Chamot, A. U., & O’Malley, J. M. (1994). The CALLA handbook: Implementing the cognitive academic language learning approach. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
Chislett, V., & Chapman, A. (2005). VAK learning styles self-assessment questionnaire. Retrieved from http://www.businessballs.com.
Coutinho, S. A. (2007). The relationship between goals, metacognition, and academic success. Educate, 7, 39–47.
Craft, A. (2001). Little c creativity. In A. Craft, B. Jeffrey, & M. Liebling (Eds.), Creativity in education (pp. 45–61). London: Continuum.
Dita, S. (2009). The metalinguistic awareness of Filipino bilingual children. Philippine ESL Journal, 3, 6–37.
Dornyei, Z. (2005). The psychology of language learner: Individual differences in second language acquisition. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Dunning, D., Johnson, K., Ehrlinger, J., & Kruger, J. (2003) Why people fail to recognize their own incompetence. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 12, 83–87.
Ekstrand, L. H. (1977). Social and individual frame factors in second language learning. In T. Skutnabb-Kangas (Ed.), Papers from the first Nordic conference on bilingualism (pp. 40–61). Helsinki: University of Helsinki.
Everson, H. T., & Tobias, S. (1998). The ability to estimate knowledge and performance in college: A metacognitive analysis. Instructional Science, 26, 65–79.
Fisher, R. (2005). Teaching children to think (2nd ed.). Cheltenham: Nelson Thornes.
Flavell, J. H. (1976). Metacognitive aspects of problem solving. In L. B. Resnick (Ed.), The nature of intelligence (pp. 231–236). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Flavell, J. H. (1979). Metacognition and cognitive monitoring: A new area of psychological inquiry. American Psychologist, 34, 906–911.
Fortner, V. (1986). Generalization of creative productive-thinking training to LD students’ written expression. Learning Disability Quarterly, 9, 274–284.
Genesee, F. (1976). The role of intelligence in second language learning. Language Learning, 26, 267–280.
Ghonsooly, B., & Shoqi, S. (2012). The effects of foreign language learning on creativity. English Language Teaching Journal, 5, 161–167.
Guilford, J. P. (1950). Creativity. American Psychologist, 5, 444–454.
Guilford, J. P. (1959). Three faces of intellect. American Psychologist, 14, 469–479.
Keefe, J. W. (1982). Assessing student learning styles. In J. W. Keefe (Ed.), Student learning styles and brain behaviour (pp. 1–18). Reston, VA: National Association of Secondary School Principals.
Kruger, J., & Dunning, D. (1999) Unskilled and unaware of it: How differences in recognizing one’s own incompetence lead to inflated self-assessments. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 77, 1121–1134.
Li, Y., Medwell, J., Wray, D., Wang, L., & Liu, X. (2016). Learning styles: A review of validity and usefulness. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 4, 90–94.
Lujan, H. L., & DiCarlo, S. E. (2005). First-year medical students prefer multiple learning styles. Advances in Physiology Education, 30, 13–16.
Meera, K. P., & Remya, P. (2010). Effect of extensive reading and creativity on achievement in English language. E-Journal of All India Association for Educational Research, 22, 16–22.
Naderi, H., Abdullah, R., Aizan, H. T., Sharir, J., & Kumar, V. (2009). Creativity, age and gender as predictors of academic achievement among undergraduate students. Journal of American Science, 5, 101–112.
Othman, N., & Amiruddin, M. H. (2010). Different perspectives of learning styles from VARK model. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 7, 652–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.10.088.
Ottó, I. (1998). The relationship between individual differences in learner creativity and language learning success. TESOL Quarterly, 32, 763–773.
Palaniappan, A. K. (2007). Academic achievement of groups formed based on creativity and intelligence. Paper presented at the 13th international conference on thinking, Norrköping.
Pishghadam, R., & Khajavy, G. H. H. (2013). Intelligence and metacognition as predictors of foreign language achievement: A structural equation modeling approach. Learning and Individual Differences, 24, 176–181.
Pishghadam, R., Khodadady, E., & Zabihi, R. (2011). Learner creativity in foreign language achievement. European Journal of Educational Studies, 3, 465–472.
Raoofi, S., Chan, S. H., Mukundan, J., & Rashid, S. M. (2014). Metacognition and second/foreign language learning. English Language Teaching, 7, 36–49.
Russo, C. (2004). A comparative study of creativity and cognitive problem-solving strategies of high-iq and average students. The Gifted Child Quarterly, 48, 179–190.
Schraw, G., & Dennison, R. S. (1994). Assessing metacognitive awareness. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 19, 460–475.
Schreiber, J. B., Nora, A., Stage, F. K., Barlow, E. A. & King, J. (2006). Reporting structural equation modeling and confirmatory factor analysis results: a review. The Journal of Educational Research, 99, 323–337.
Su, Y. H. (2009). Idea creation: The need to develop creativity in lifelong learning practices. International Journal of Lifelong Education, 28, 705–717.
Surjono, H. D. (2011). The design of adaptive E-learning system based on student’s learning styles. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies, 2, 2350–2353.
Sutrisno, S. (2007). Students’ creativity and its relation to English learning achievement. Unpublished Thesis. Semarang State University, Brebes.
Tunmer, W. E., & Cole, P. (1985). Learning to read: A metalinguistic act. In C. S. Simon (Ed.), Communication skills and classroom success: Therapy methodologies for language learning disabled children (pp. 179–198). London: Taylor and Francis.
Vaishnav, R. S., & Chirayu, K. C. (2013). Learning style and academic achievement of secondary school students. Voice of Research, 1, 1–4.
Veenman, M. V. J., & Van Hout-Wolters, B. H. A. M. (2001). The assessment of metacognitive skillfulness. In F. Oser, & U. Baets (Eds.), 9th European conference on learning and instruction, abstract volume (pp. 278). Mainz, Aachen.
Zafar, Sh, & Meenakshi, K. (2012). Individual learner differences and second language acquisition: A review. Journal of Language Teaching and Research, 3, 639–646.
Zapalska, A., & Brozik, D. (2006). Learning style and online education. Campus-Wide Information Systems, 23, 325–335.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khodabakhshzadeh, H., Hosseinnia, M. & Rahimian, S. Learning Style, Metacognition and Creativity as Predictors of the Foreign Language Achievement: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach. Psychol Stud 62, 377–385 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12646-017-0427-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12646-017-0427-5