Abstract
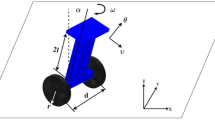
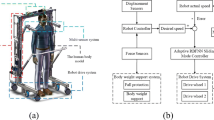
The robot is a very complex multi-input multi-output nonlinear system. Due to the inaccuracy of measurement and modeling, coupled with changes in load and the effects of external disturbances, it is virtually impossible to obtain a complete kinetic model. The strong robustness of sliding mode variable structure control makes it particularly suitable for solving the trajectory tracking problem of robots. In this paper, a better real-time adaptive control framework is designed to realize the robust target tracking of mobile robots. Based on the TSK neural network, an efficient control framework combining neural network controller and compensation controller is proposed. Based on the new framework research and improvement of neural network controller, considering the factors of emotional influence decision-making, the existing brain emotional learning neural network is improved and researched, and the brain-emotion learning neural network with radial basis function is proposed. The simulation results show that the trajectory tracking ability, anti-disturbance ability and robustness of the mobile robot are improved to some extent, which verifies the feasibility and efficiency of the proposed control method.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouteraa Y, Abdallah IB (2017) A gesture-based telemanipulation control for a robotic arm with biofeedback-based grasp. Ind Robot 44(5):575–587
Chen G, Song Y, Guan Y (2018) Terminal sliding mode-based consensus tracking control for networked uncertain mechanical systems on digraphs. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(3):749–756
Cui R, Chen L, Yang C et al (2017) Extended state observer-based integral sliding mode control for an underwater robot with unknown disturbances and uncertain nonlinearities. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 64(8):6785–6795
Delavari H (2017) A novel fractional adaptive active sliding mode controller for synchronization of non-identical chaotic systems with disturbance and uncertainty. Int J Dyn Control 5(1):102–114
Elgammal AAA, El-Naggar MF (2017) MOPSO-based optimal control of shunt active power filter using a variable structure fuzzy logic sliding mode controller for hybrid (FC-PV-Wind-Battery) energy utilisation scheme. IET Renew Power Gener 11(8):1148–1156
Guo X, Liang Z, Li C (2018) Finite time tracking control of mobile robot based on non-singular fast terminal sliding mode. Syst Sci Control Eng Open Access J 6(1):492–500
He W, Dong Y (2018) Adaptive fuzzy neural network control for a constrained robot using impedance learning. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(4):1174–1186
Jung S (2018) Improvement of tracking control of a sliding mode controller for robot manipulators by a neural network. Int J Control Autom Syst 16(2):937–943
Le AT, Joo YH, Le QT et al (2017) Adaptive neural network second-order sliding mode control of dual arm robots. Int J Control Autom Syst 15(5):1–9
Li P, Bao G, Fang X et al (2018) Adaptive robust sliding mode trajectory tracking control for 6 degree-of-freedom industrial assembly robot with disturbances. Assem Autom 38(3):259–267
Lin FJ, Chen SG, Sun IF (2017) Intelligent sliding-mode position control using recurrent wavelet fuzzy neural network for electrical power steering system. Int J Fuzzy Syst 19(1):1–18
Mukherjee J, Mukherjee S, Kar IN (2017) Sliding mode control of planar snake robot with uncertainty using virtual holonomic constraints. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 2(2):1077–1084
Nasir MT, El-Ferik S (2017) Adaptive sliding-mode cluster space control of a non-holonomic multi-robot system with applications. IET Control Theory Appl 11(8):1264–1273
Panwar V (2017) Wavelet neural network-based H∞ trajectory tracking for robot manipulators using fast terminal sliding mode control. Robotica. 35(7):1–16
Saafan MM, Abdelsalam MM, Elksas MS et al (2017) An adaptive neuro-fuzzy sliding mode controller for MIMO systems with disturbance. Chin J Chem Eng 25(04):87–100
Van M (2018) An enhanced robust fault tolerant control based on an adaptive fuzzy PID-nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control for uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 23(3):1362–1371
Wang H, Zheng TQ (2017) RBF network adaptive control based on SMC compensation for six-axis manipulator. J Northeast Univ 38(11):1601–1606
Wen S, Chen MZQ, Zeng Z et al (2017) Adaptive neural-fuzzy sliding-mode fault-tolerant control for uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 47(8):2268–2278
Xiu C, Hou J, Zang Y et al (2017) Synchronous control of hysteretic creep chaotic neural network. IEEE Access. 4:8617–8624
Yen VT, Nan WY, Cuong PV et al (2017) Robust adaptive sliding mode control for industrial robot manipulator using fuzzy wavelet neural networks. Int J Control Autom Syst 15(6):2930–2941
Zhao B, Yu H, Yu J et al (2018) Port-controlled hamiltonian and sliding mode control of gantry robot based on induction motor drives. IEEE Access 6:43840–43849
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, T., Luo, Z. & Wang, G. Adaptive sliding mode control of robot based on fuzzy neural network. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 11, 6235–6247 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-01809-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-01809-2