Abstract
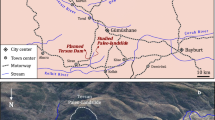
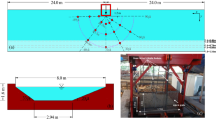
The impulsive wave is considered as one of the most notably secondary hazards induced by landslides in reservoir areas. The impulsive wave with considerable wave amplitude is able to cause serious damage to the dam body, shoreline properties and lives. To investigate and predict the wave characteristics, many experimental studies employed the generalized channels rather than the realistic topography. Deviation from the idealized geometries may result in non-negligible effects due to the wave refraction or reflection with complex topography. To consider the topography effect, a prototype scaled experiment was conducted. A series of tests with different collocation of parameters were performed. The experimental results were then summarized to propose empirical equations to predict the maximum wave amplitude, and wave decay in channel direction. The generalized empirical equations can obtain better results for wave features prediction by compared with those derived from the idealized models. Furthermore, a 3D numerical modeling corresponding to the physical experiment was conducted based on the SPH method. The wave characteristics in the sliding and channel directions were investigated in detail including the maximum wave amplitude, wave run-up, wave arrival time and wave crest amplitude decay. The comparison between the simulation and experiment indicates the promising accuracy of the SPH simulation in determining the general features even with complex river topography. Finally, the limitation and applicability of both the experimental and numerical methods in analyzing the practical engineering problems were discussed. Combination of the both methods can benefit the hazard prevention and reduction for landslide generated impulsive waves in reservoir area.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aida I (1975) Numerical experiments of the tsunami associated with the collapse of Mt. Mayuyama in 1792. J Seismol Soc Jpn 28:449–460
Ataie-Ashtiani B, Nik-Khah A (2008) Impulsive waves caused by subaerial landslides. Environ Fluid Mech 8:263–280. doi:10.1007/s10652-008-9074-7
Ataie-Ashtiani B, Shobeyri G (2008) Numerical simulation of landslide impulsive waves by incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 56:209–232
Ataie-Ashtiani B, Yavari-Ramshe S (2011) Numerical simulation of wave generated by landslide incidents in dam reservoirs. Landslides 8:417–432. doi:10.1007/s10346-011-0258-8
Bosa S, Petti M (2011) Shallow water numerical model of the wave generated by the Vajont landslide. Environ Model Softw 26:406–418. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2010.10.001
Camfield FE (1980) Tsunami Engineering. Special report No.6. US Army Corps of Engineers, Costal Engineering Research Center. Fort Belvoir, Va
Crespo A, Gómez-Gesteira M, Dalrymple RA (2007) Boundary conditions generated by dynamic particles in SPH methods, 5th edn. CMC-TECH Science Press, Norcross, p 173
Crespo AC, Dominguez JM, Barreiro A et al (2011) GPUs, a new tool of acceleration in CFD: efficiency and reliability on smoothed particle hydrodynamics methods. PLoS One 6:e20685. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020685
Crespo A, Domínguez J, Gesteira M et al (2012) User guide for DualSPHysics code. SPHysics project, v2.0 edition. http://dual.sphysics.org/files/3313/8753/4540/DualSPHysics_v3.0_GUIDE.pdf. Accessed Dec 2013
Dai F, Deng J, Tham L et al (2004) A large landslide in Zigui County, Three Gorges area. Can Geotech J 41:1233–1240. doi:10.1139/T04-049
Das K, Janetzke R, Basu D et al (2009) Numerical simulations of tsunami wave generation by submarine and aerial landslides using RANS and SPH models. In: ASME 2009 28th international conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering, 2009. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, pp 581–594
de Carvalho RF, do Carmo JSA (2007) Landslides into reservoirs and their impacts on banks. Environ Fluid Mech 7:481–493
Fine I, Rabinovich A, Bornhold B et al (2005) The Grand Banks landslide-generated tsunami of November 18, 1929: preliminary analysis and numerical modeling. Mar Geol 215:45–57. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2004.11.007
Fritz HM (2001) Lituya Bay case rockslide impact and wave run-up. Sci Tsunami Hazards 19:3–22
Fritz H, Hager W, Minor H-E (2003) Landslide generated impulse waves. 2. Hydrodynamic impact craters. Exp Fluids 35:520–532. doi:10.1007/s00348-003-0660-7
Fritz H, Hager W, Minor H-E (2004) Near field characteristics of landslide generated impulse waves. J Waterw Port Coast Ocean Eng 130:287–302
Geist EL, Lynett PJ, Chaytor JD (2009) Hydrodynamic modeling of tsunamis from the Currituck landslide. Mar Geol 264:41–52. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2008.09.005
Gomez-Gesteira M, Crespo AJ, Rogers BD et al (2012) SPHysics–development of a free-surface fluid solver–Part 2: efficiency and test cases. Comput Geosci 48:300–307. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2012.02.028
Heinrich P, Mangeney A, Guibourg S et al (1998) Simulation of water waves generated by a potential debris avalanche in Montserrat, Lesser Antilles. Geophys Res Lett 25:3697–3700. doi:10.1029/98gl01407
Heinrich P, Guibourg S, Mangeney A et al (1999) Numerical modeling of a landslide-generated tsunami following a potential explosion of the Montserrat volcano. Phys Chem Earth Part A 24:163–168. doi:10.1016/S1464-1895(99)00013-7
Heller V (2007) Landslide generated impuls waves. Diss., Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule ETH Zürich, Nr. 17531, 2007, Place
Heller, V, Hager WH, Minor HE (2009) Landslide generated impulse waves in reservoirs. VAW Publication, Zurich, pp 1–9
Heller V, Hager WH (2010) Impulse product parameter in landslide generated impulse waves. J Waterw Port Coast Ocean Eng 136:145–155. doi:10.1061/(Asce)Ww.1943-5460.0000037
Heller V, Hager W (2011) Wave types of landslide generated impulse waves. Ocean Eng 38:630–640. doi:10.1016/j.oceaneng.2010.12.010
Huang Z, Law KT, Liu H et al (2009) The chaotic characteristics of landslide evolution: a case study of Xintan landslide. Environ Geol 56:1585–1591. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1256-6
Huang B, Yin Y, Chen X et al (2014) Experimental modeling of tsunamis generated by subaerial landslides: two case studies of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ Earth Sci 71:3813–3825. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2765-5
Hughes SA (2005) Physical models and laboratory techniques in coastal engineering. World Scientific Publishing Co Pte Ltd, Singapore
Kamphuis, J, Bowering R (1970) Impulse waves generated by landslides. In: Proceedings of 12th Coastal Engineering Conference, Washington DC, vol 1. ASCE, New York, pp 575–588
Li D, Yin K, Leo C (2010) Analysis of Baishuihe landslide influenced by the effects of reservoir water and rainfall. Environ Earth Sci 60:677–687. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0206-2
Liu M, Liu G (2010) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH): an overview and recent developments. Arch Comput Methods Eng 17:25–76. doi:10.1007/s11831-010-9040-7
McMurtry G, Watts P, Fryer G et al (2004) Giant landslides, mega-tsunamis, and paleo-sea level in the Hawaiian Islands. Mar Geol 203:219–233. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00306-2
Mishiue M, Hinokidani O, Miyamoto K (1999) Study on the Mayuyama tsunami disaster in 1792. In: Proceedings of the 28th congress of IAHR, CD, 1999
Miyagi T, Kasai F, Yamashina S (2008) Huge landslide triggered by earthquake at the Aratozawa Dam area, Tohoku, Japan. In: Proceedings of the First World Landslide Forum. ICL, ISDR, Tokyo, Japan, 2008, pp 421–424
Miyagi T, Yamashina S, Esaka F et al (2011) Massive landslide triggered by 2008 Iwate–Miyagi inland earthquake in the Aratozawa Dam area, Tohoku, Japan. Landslides 8:99–108. doi:10.1007/s10346-010-0226-8
Monaghan JJ (1992) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Ann Rev Astron Astrophys 30:543–574. doi:10.1146/annurev.aa.30.090192.002551
Monaghan JJ (1994) Simulating free surface flows with SPH. J Comput Phys 110:399–406. doi:10.1006/jcph.1994.1034
Noda E (1970) Water waves generated by landslides. J Waterw Harb Coast Eng Div 96:835–855
Panizzo A, De Girolamo P, Di Risio M et al (2005) Great landslide events in Italian artificial reservoirs. Nat Hazard Earth Syst Sci 5:733–740
Pérez G, García-Navarro P, Vázquez-Cendón M (2006) One-dimensional model of shallow water surface waves generated by landslides. J Hydraul Eng 132:462–473
Petley D (2010) Landslide hazards. In: Alcantara-Ayala I, Goudie A (eds) Geomorphological hazards and disaster prevention. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 63–74
Qiu L-C (2008) Two-dimensional SPH simulations of landslide-generated water waves. J Hydraul Eng 134:668–671. doi:10.1061/(Asce)0733-9429(2008)134:5(668)
Quecedo M, Pastor M, Herreros M (2004) Numerical modelling of impulse wave generated by fast landslides. Int J Numer Meth Eng 59:1633–1656. doi:10.1002/nme.934
Risley JC, Walder JS, Denlinger RP (2006) Usoi Dam wave overtopping and flood routing in the Bartang and Panj Rivers, Tajikistan. Nat Hazards 38:375–390. doi:10.1007/s11069-005-1923-9
Semenza E, Ghirotti M (2000) History of the 1963 Vaiont slide: the importance of geological factors. Bull Eng Geol Environ 59:87–97
Vacondio R, Rogers B, Stansby P et al (2013) Variable resolution for SPH: a dynamic particle coalescing and splitting scheme. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 256:132–148. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2012.12.014
Viroulet S, Cébron D, Kimmoun O et al (2013) Shallow water waves generated by subaerial solid landslides. Geophys J Int 193:747–762. doi:10.1093/gji/ggs133
Walder JS, Watts P, Sorensen OE et al (2003) Tsunamis generated by subaerial mass flows. J Geophys Res: Solid Earth 1978–2012:108. doi:10.1029/2001jb000707
Watts P, Grilli S, Kirby J et al (2003) Landslide tsunami case studies using a Boussinesq model and a fully nonlinear tsunami generation model. Nat Hazard Earth Syst Sci 3(5):391–402
Wroniszewski PA, Verschaeve JC, Pedersen GK (2014) Benchmarking of Navier-Stokes codes for free surface simulations by means of a solitary wave. Coast Eng 91:1–17. doi:10.1016/j.coastaleng.2014.04.012
Zhao, L, Mao J, Bai X et al (2015) Finite element simulation of impulse wave generated by landslides using a three-phase model and the conservative level set method. Landslides 1–12. doi:10.1007/s10346-014-0552-3
Acknowledgements
This study has received support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41002103 and 41572292). Also, this work was supported by Kyushu University Interdisciplinary Programs in Education and Projects in Research Development. These supports are gratefully acknowledged. Finally, the authors greatly appreciate the careful review and thoughtful suggestions by the anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Chen, G., Yin, K. et al. Modeling of landslide generated impulsive waves considering complex topography in reservoir area. Environ Earth Sci 75, 372 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5252-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5252-y