Abstract
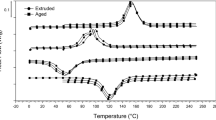
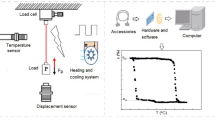
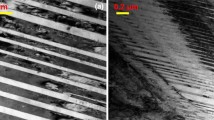
Smart actuators, using materials with a memory, are an attractive alternative to conventional actuators due to their unique properties, such as high energy density, low power-to-weight ratio, simplicity of design, and miniaturization of size. However, the continuous cyclic operation of such devices, within their transformation temperature range, leads to the degradation of their functional properties. In this paper, the degradation of functional properties, such as recovery strain, permanent strain, and critical transition temperatures, of an Ni45Ti50Cu5 (at.%) shape memory alloy, aged at four different temperatures, ranging from 450 to 600 °C, was experimentally investigated under constant stress. The results reveal that all alloys underwent a single-step transition from B2 → B19’ at all aging temperatures. The aging temperature has a significant impact on recovery strain and permanent strain. The permanent strain accumulation after every cycle is minimized as the temperature of aging is raised to 550 °C due to the strengthening of the matrix by precipitate particles. Above this temperature, it starts to increase due to the coarsening of the precipitate particles. Aging treatment also helps to achieve faster cyclic stability during thermomechanical cycling.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Humbeeck J, Adv. Eng. Mater3(11) (2001) 837.
Mohd Jani J, Leary M, Subic A, and Gibson M A, Mater. Des. 56 (2014) 1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.11.084.
Menna C, Auricchio F, and Asprone D, Applications of Shape Memory Alloys in Structural Engineering, Elsevier Ltd, New York (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-099920-3.00013-9.
Otsuka K, and Wayman C M, Shape Memory Materials, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1999).
Otsuka K, and Ren X, Prog. Mater. Sci. 50 (2005) 511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2004.10.001.
Lexcellent C, Shape-memory Alloys Handbook, Wiley, New York (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118577776.
Calhoun C, Wheeler R, Baxevanis T, and Lagoudas D C, Scr. Mater. 95 (2015) 58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.10.005.
Eggeler G, Hornbogen E, Yawny A, Heckmann A, and Wagner M, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 378 (2004) 24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.10.327.
Lagoudas D C, Miller D A, Rong L, and Kumar P K, Smart Mater. Struct. 18 (2009) 85021.
Morgan N B, and Friend C M, Le J. Phys. IV. 11 (2001) Pr8. https://doi.org/10.1051/jp4:2001855.
Zarnetta R, Takahashi R, Young M L, Savan A, Furuya Y, Thienhaus S, Maaß B, Rahim M, Frenzel J, Brunken H, others, Chu Y S, Srivastava V, James R D, Takeuchi I, Eggeler G, and Ludwig A, Adv. Funct. Mater. 20 (2010) 1917. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200902336.
Tong Y, Gu H, James H, Qi W, Shuitcev A V, and Li L, J. Alloys Compd. 782 (2019) 343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.219.
Cui J, Chu Y S, Famodu O, Furuya Y, Hattrick-Simpers J, James R D, Ludwig A, Thienhaus S, Wuttig M, Zhang Z, and Takeuchi I, Nat. Mater. 5 (2006) 286. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1593.
Gu H, Bumke L, Chluba C, Quandt E, and James R D, Mater. Today. 21 (2018) 265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2017.10.002.
Chen X, Srivastava V, Dabade V, and James R D, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 61 (2013) 2566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2013.08.004.
Jiang S, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Liu S, Li H U, and Zhao C, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25 (2015) 4063. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(15)64056-0.
Jiang S Y, Zhao Y N, Zhang Y Q, Hu L, and Liang Y L, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (English Ed.) 23 (2013) 3658. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62914-3.
Radi A, Khalil-Allafi J, Etminanfar M R, Pourbabak S, Schryvers D, and Amin-Ahmadi B, Mater. Des. 142 (2018) 93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2018.01.024.
Qin Q, Peng H, Fan Q, Zhang L, and Wen Y, J. Alloys Compd. 739 (2018) 873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.12.128.
Zheng Y, Jiang F, Li L, Yang H, and Liu Y, Acta Mater. 56 (2008) 736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2007.10.020.
Chang S H, Lin K H, and Wu S K, Materials (Basel). (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070704.
Huang W, Mater. Des. 23 (2002) 11.
Nam T H, Saburi T, Nakata Y, and Shimizu K, Mater. Trans. JIM. 31 (1990) 1050.
Bricknell R H, Melton K N, and Mercier O, Metall. Trans. A. 10 (1979) 693. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02658390.
Nam T H, Saburi T, and Shimizu K K K, Mater. Trans. JIM. 31 (1990) 959. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans1989.31.959.
Nespoli A, and Besseghini S, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 103 (2011) 821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-1042-z.
Van Humbeeck J, Le J. Phys. IV. 01 (1991) C4-189. https://doi.org/10.1051/jp4:1991429.
Padula S, Qiu S, Gaydosh D, Noebe R, Bigelow G, Garg A, and Vaidyanathan R, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 43 (2012) 4610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1267-5.
Saikrishna C N, Ramaiah K V, Prabhu S A, and Bhaumik S K, Bull. Mater. Sci. 32 (2009) 343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-009-0049-1.
Akin E, Effect of Aging Heat Treatments on Ni52Ti48 Shape Memory Alloy, Texas A & M University, College Station (2011).
Bhaumik S K, Saikrishna C N, Ramaiah K V, and Venkataswamy M A, in: Key Engineering Materials (2008), pp 301–316. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.378-379.301.
Omrani E, and Shokuhfar A, Int. J. Metall. Met. Phys. 4 (2019) 034.
Phillips F R, Wheeler R W, Geltmacher A B, and Lagoudas D C, Int. J. Fatigue 124 (2019) 315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2018.12.019.
Basavarajappa N S S, Arun K V, and Yadav S M, J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 09 (2010) 811. https://doi.org/10.4236/jmmce.2010.99058.
Soto-Parra D E, Flores-Zúñiga H, López Cuéllar E, Ochoa-Gamboa R A, and Ríos-Jara D, Mater. Res. 17 (2014) 1023. https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-1439.265814.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of the Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology, India, under the grant of CRG/2019/002267.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swaminathan, G., Sampath, V. & Adarsh, S.H. Influence of Aging Temperature on Functional Fatigue Behavior of a Ti50Ni45Cu5 Shape Memory Alloy. Trans Indian Inst Met 74, 2435–2446 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02209-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02209-6