Abstract
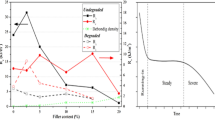
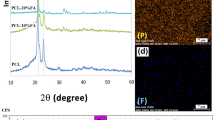
Composite polycaprolactone fibers at different mass fraction (0.025, 0.05, and 0.075) of incorporated calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and hydroxyapatite (HA) microparticles were produced by electrospinning. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the fiber sheets revealed that the average diameter of the as-spun fibers increases with increasing of filler content assuming into account defects connected with embedding microparticles. At highest content of inorganic fraction (0.075) of HA and CaCO3, a considerable amount of defects, notches, and beads in the fibers were observed. The Young’s modulus (E) and the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of the composites increased with addition of mass fraction of HA and CaCO3 microparticles. Regression analysis of mechanical properties of binary composites (polymer matrix/filler) was done, and as a result, the approximate equation for mechanical parameter prediction of nonwoven materials was obtained.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shao, Y., Qiao, F., Bernd, L., & Yiu, W. (2008). Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate—polymer composites. Composites: Part B, 39, 933–961.
Bostman, O., & Pihljamaki, H. (2000). Clinical biocompatibility of biodegradable orthopaedic implants for internal fixation. A Review Biomaterials, 21, 2615–2621.
Ondarcuhu, T., & Joachim, C. (1998). Drawing a single nanofibre over hundreds of microns. Europhysics Letters, 42(2), 215–220.
Feng, L., Li, S., et al. (2002). Super-hydrophobic surface of aligned polyacrylonitrile nanofibers. Angewandte Chemie(International ed. In English) 4171221–3.3.
Martin, C. R. (1996). Membrane-based synthesis of nanomaterials. Chemistry of Materials, 8(8), 1739–1746.
Ma, P. X., & Zhang, R. (1999). Synthetic nano-scale fibrous extracellular matrix. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 46(1), 60–72.
Liu, G., Ding, J., Qiao, L., Guo, A., Dymov, B. P., Gleeson, J. T., Hashimoto, T., & Saijo, K. (1999). Polystyrene-block-poly (2-cinnamoylethyl methacrylate) nanofibers—preparation, characterization, and liquid crystalline properties. Journal of Chemistry-A European, 5(9), 2740–2749.
Whitesides, G. M., & Grzybowski, B. (2002). Self-assembly at all scales. Science, 295(5564), 2418–2421.
Subbiah, T., Bhat, G. S., Tock, R. W., Param, S., & Ramkumar, S. S. (2005). Electrospinning of nanofibers. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 96(2), 557–569.
Ellison, C. J., Phatak, A., Giles, D. W., Macosko, C. W., & Bates, F. S. (2007). Melt blown nanofibers: fiber diameter distributions and onset of fiber breakup. Polymer, 48(11), 3306–3316.
Wang, Y., Shi, X., Ren, L., Yao, Y., Zhang, F., & Wang, D. A. (2010). Poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/titania composite microsphere-sintered scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications. Journal of Biomedicine Materials and Research B: Applied Biomaterials, 93, 84–92.
La Gatta, A., De Rosa, A., Laurienzo, P., Malinconico, M., De Rosa, M., & Schiraldi, C. A. (2005). Novel injectable poly (caprolactone)/calcium sulfate system for bone regeneration: synthesis and characterization. Macromolecular Bioscience, 5, 1108–1117.
Frieb, W., Warner, J., Schuth, F., Sing, K. S. W., & Weitkamp, J. (2002). Handbook of porous solids (pp. 29–23). Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
Hench, L. (1998). A forecast for the future. Biomaterials, 19, 1419–1423.
Seema, A. S., Wendorff, J. H., & Greiner, A. (2008). Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer, 49, 5603–5621.
Gorna, K., Hund, M., Vucak, M., & Gröhn, F. (2008). Amorphous calcium carbonate in form of spherical nanosized particles and its application as fillers for polymers. Materials Science and Engineering A, 477, 217–225.
Liang, J. (2007). Melt viscoelastic behavior in capillary extrusion of polypropylene/EPDM/glass bead ternary composites. Reinforced Plastic Composites: Part A, 38, 1502–1506.
Xie, X. L., Liu, Q. X., Li, R. K., Zhou, X. P., Zhang, Q. X., Yu, Z. Z., & Mai, Y. W. (2004). Rheological and mechanical properties of PVC/CaCO3 nanocomposites prepared by in situ polymerization. Polymer, 45, 6665–6673.
Di Lorenzo, M. L., Errico, M. E., & Avella, M. (2002). Thermal and morphological characterization of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/calcium carbonate nanocomposites. Materials Science, 37, 2351–2358.
Bartczak, Z., Argon, A. S., Cohen, R. E., & Weinberg, M. (1999). Toughness mechanism in semi-crystalline polymer blends: II. High-density polyethylene toughened with calcium carbonate filler particles. Polymer, 40, 2347–2365.
Zuiderduin, W. C., Westzaan, C., Huétink, J., & Gaymans, R. J. (2003). Toughening of polypropylene with calcium carbonate particles. Polymer, 44, 261–275.
Jiang, L., Zhang, J., & Wolcott, M. P. (2007). Comparison of polylactide/nano-sized calcium carbonate and polylactide/montmorillonite composites: reinforcing effects and toughening mechanisms. Polymer, 48, 7632–7644.
Jiang, L., Lam, Y. C., Tam, K. C., Chua, T. H., Sim, G. W., & Ang, L. S. (2005). Strengthening acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) with nano-sized and micron-sized calcium carbonate. Polymer, 46(243), 252.
Khatiwala, V. K., Shekhar, N., Aggarwal, S., & Mandal, U. K. (2008). Biodegradation of poly(caprolactone) (PCL) film by alcaligenes faecalis. Polymers and the Environment, 16, 61–67.
Lei, Y., Rai, B., Ho, K. H., & Teoh, S. H. (2007). In vitro degradation of novel bioactive polycaprolactone–20 % tricalcium phosphate composite scaffolds for bone engineering. Materials Science and Engineering, 27, 293–298.
Rai, B., Teoh, S. H., & Ho, K. H. (2005). An in vitro evaluation of PCL-TCP composites as delivery systems for platelet rich plasma. Journal of Controlled Release, 107, 330–342.
Wang, D. A., Feng, L. X., Ji, J., Sun, Y. H., Zheng, X. X., & Elisseeff, J. H. (2003). Novel human endothelial cell-engineering polyurethane biomaterials for cardiovascular biomedical applications. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. Part A, 65, 498–510.
Shi, X., Wang, Y., Ren, L., Gong, Y., & Wang, D. A. (2009). Enhancing alendronate release from a novel PLGA/hydroxyapatite microspheric system for bone repairing applications. Pharmaceutical Research, 26, 442–430.
Huang, Y., Liu, H., He, P., Yuan, L., Xiong, H., Xu, Y. M., & Yu, Y. (2010). Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of modified bamboo fiber/PCL composites. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 116, 2119–2125.
Patcharaporn, W., Prasit, P., & Pitt, S. (2007). Osteoblastic phenotype expression of MC3T3-E1 cultured on electrospun polycaprolactone fiber mats filled with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules, 8, 2602–2610.
Sanaz, A., Samira, S., & Asma, F. (2012). Enhancement of mechanical and thermal properties of polycaprolactone/chitosan blend by calcium carbonate nanoparticles. Journal of Molecular Science, 13, 4508–4522.
Gomes, M. E., & Reis, R. L. (2004). Biodegradable polymers and composites in biomedical application: from catgut to tissue engineering. International Materials Reviears, 48, 263.
Zargarian, S. S., & Vahid, H. (2010). A nanofibrous composite scaffold of PCL/hydroxyapatite-chitosan/PVA prepared by electrospinning. Journal of Iranian Polymer, 19(6), 457–468.
Patcharaporn, W., Neeracha, S., Prasit, P., & Pitt, S. (2006). Preparation and characterization of novel bone scaffolds based on electrospun polycaprolactone fibers filled with nanoparticles. Macromolecular Bioscience, 6, 70–77.
Wolberg, J. (2005). Data analysis using the method of least squares: extracting the most information from experiments, Springer.
Piggott, M. (2002). Load bearing fibre composites. Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Madsen, B., Joffe, R., Peltola, H., & Nattinen, K. (2011). Short cellulosic fiber/starch acetate composites: micromechanical modeling of Young’s modulus. Journal of Composite Materials, 45, 2119–2131.
Sun, J. J., Bae, C. J., Koh, Y. H., Kim, H. E., & Kim, H. W. (2007). Fabrication of hydroxyapatite-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) scaffolds by a combination of the extrusion and bi-axial lamination processes. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Medicine, 18(6), 1017–1023.
Thomason, J. L. (2009). The influence of fiber length, diameter and concentration on the strength and strain to failure of glass fiber-reinforced polyamide 6, 6. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 40, 114–124.
Jeong, J. S., Moon, J. S., Jeon, S. Y., Park, J. H., Alegaonkar, P. S., & Yoo, J. B. (2007). Mechanical properties of electrospun PVA/MWNTs composite nanofibers. Thin Solid Films, 515, 5136–5141.
Zhou, J., Tang, J., Meng, H., & Yu, J. (2008). Study on PP/calcium sulfate whisker composite. Engineering Plastics Application, 36, 19–22.
Kamal, K. G., Akshay, K., Pradeep, K. M., Pradeep, S., Sujata, M., Narendra, K. S., Abhinay, M., & Pralay, M. (2012). Polycaprolactone composites with TiO2 for potential nanobiomaterials: tunable properties using different phases. Journal of Physics and Chemistry Chemistry and Physics, 14, 12844–12853.
Wang, J., & Cheung, M. K. (2002). Miscibility and morphology in crystalline/amorphous blends by DSC, FTIR and C solid state NMR. Polymer, 43, 1357–1364.
Parakhonskiy, B. V., Yashchenok, A. M., Svenskaya, Y. U., Fattah, H. A., Inozemtseva, O. A., Tessarolo, F., Antolini, R., & Gorin, D. A. (2014). Size controlled hydroxyapatite and calcium carbonate particles: synthesis and their application as templates for SERS platform. Journal of Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 118, 243–248.
Acknowledgments
The reported study was partially supported by RFBR, research project No. 12-03-33088 mol_a_ved, Government of the Russian Federation (grant №14.Z50.31.0004 to support scientific research projects implemented under the supervision of leading scientists at Russian institutions and Russian institutions of higher education).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Metwally, H.A., Ardazishvili, R.V., Severyukhina, A.N. et al. The Influence of Hydroxyapatite and Calcium Carbonate Microparticles on the Mechanical Properties of Nonwoven Composite Materials Based on Polycaprolactone. BioNanoSci. 5, 22–30 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-014-0158-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-014-0158-1