Abstract
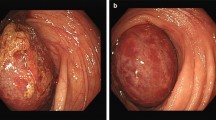
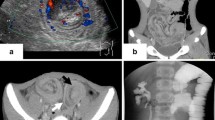
Intussusception is one of the most common paediatric emergencies, with a greater incidence during the first two years of life. Most cases are characterized as idiopathic. After this age, the incidence of intussusception steadily declines while, on the other hand, the possibility of an underlying causative disease, such as intestinal lymphoma, becomes increasingly stronger. We present the case of a 7-year-old Caucasian male that presented with non-reducible ileocolic intussusception due to a lead point, which proved to be a stage II Burkitt’s lymphoma. Resection, accompanied by chemotherapy, was successful, without complications, and with good response. Intestinal lymphomas may present with a varying clinical picture, from vague systematic symptoms to real surgical emergencies. General surgeons should be aware of that rare occasion where intussusception may be the result of an intestinal lymphoma, especially in children over the age of three, after which age an underlying lead point is more likely to exist.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waseem M, Rosenberg HK. Intussusception. Pediatr Emerg Care 2008; 24:793–800
Navarro OM, Daneman A, Chae A. Intussusception: the use of delayed, repeated reduction attempts and the management of intussusceptions due to pathologic lead points in pediatric patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2004; 182:1169–1176
González-Spínola J, Del Pozo G, Tejedor D, Blanco A. Intussusception: the accuracy of ultrasound-guided saline enema and the usefulness of a delayed attempt at reduction. J Pediatr Surg 1999; 34:1016–1020
Puri PHM. (ed.) Pediatric Surgery. Springer Surgery Atlas Series (ed.). SJR Lumley JSP. Springer. 2006; pp. 313–320
Delarue A, Bergeron C, Mechinaud-Lacroix F, Coze C, Raphael M, Patte C. [Pediatric non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: primary surgical management of patients presenting with abdominal symptoms. Recommendations of the Lymphoma Committee of the French Society to Combat Pediatric Cancers (SFCE)]. J Chir (Paris), 2008; 145:454–458
Fleming ID, Turk PS, Murphy SB, et al. Surgical implications of primary gastrointestinal lymphoma of childhood. Arch Surg 1990; 125:252–256
Gupta H, Davidoff AM, Pui CH. Clinical implications and surgical management of intussusception in pediatric patients with Burkitt lymphoma. J Pediatr Surg 2007; 42:998–1001; discussion 1001.
LaQuaglia MP, Stolar MK, Exelby P, et al. The role of surgery in abdominal non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: experience from the Childrens Cancer Study Group. J Pediatr Surg 1992; 27:230–235
Puri P, Guiney EJ. Small bowel tumours causing intussusception in childhood. Br J Surg 1985; 72:493–494
Munden MM, Bruzzi JF, Coley BD, Munden RF. Sonography of pediatric small-bowel intussusception: differentiating surgical from nonsurgical cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007; 188:275–279
Abbasoglu L, Gun F, Salman FT, Celik A,. Unuvar A, Gorgun O. The role of surgery in intraabdominal Burkitt’s lymphoma in children. Eur J Pediatr Surg 2003; 13:236–239
Dunning K, Mattei P. Burkitt lymphoma presenting as colonic ischemia and overwhelming sepsis. J Pediatr Surg 2007; 42:E15–E17
Link MP. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in children. Pediatr Clin North Am, 1985; 32:699–720
Murphy SB, Fairclough DL, Hutchinson RE, et al. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas of childhood: an analysis of the histology, staging, and response to treatment of 338 cases at a single institution. J Clin Oncol 1989; 7:186–193
Couanet D, Caillaud JM, Geoffray A, Montagne JP, Aubier F. Percutaneous thin needle biopsy of pediatric tumors. Ann Radiol (Paris) 1986; 29:293–300
Miron I, Frappaz D, Brunat-Mentigny M, et al. Initial management of advanced Burkitt lymphoma in children: is there still a place for surgery? Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1997; 14:555–561
Patte C, Auperin A, Michon J, Behrendt H, Leverger G, et al. The Societe Francaise d’Oncologie Pediatrique LMB89 protocol: highly effective multiagent chemotherapy tailored to the tumor burden and initial response in 561 unselected children with B-cell lymphomas and L3 leukemia. Blood, 2001; 97:3370–3379
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cyrochristos, D., Rapti, M. & Georgiou, G.K. Ileocaecal intussusception in a 7-year-old patient due to Burkitt’s lymphoma. Hellenic J Surg 86, 169–173 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13126-014-0121-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13126-014-0121-1