Abstract
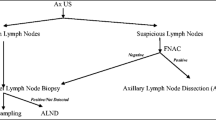
In breast cancer, axillary lymph node involvement directly impacts the patient survival and prognosis. Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) is a procedure of choice for axillary staging in early breast cancer. Currently, management options for axilla management are axillary lymph node dissection and sentinel node biopsy in node positive and in node negative respectively. Accuracy of current clinical methods for evaluating axilla is low. Hence, to select patients for appropriate procedure, ultrasound (USG) combined with fine-needle aspiration cytology (USG-FNAC) using vascular pedicle–based nodal mapping method is emerging as a good tool to address above issues. We evaluated the feasibility of ultrasound and needle aspiration cytology in a tertiary care center. All early breast cancer patients with clinically node-negative axilla and having palpable nodes with less than or equal to 5 cm tumor size in breast were screened by ultrasound of axilla to categorize the nodes as suspicious or non-suspicious based on radiological features and vascular pedicle–based nodal mapping method of axilla. Patients having suspicious nodes underwent ultrasound of axilla and needle aspiration; if found positive, patient underwent axillary node dissection. Sentinel node biopsy (SLNB) performed in all patients found negative on needle aspiration and in all patients having non-suspicious nodes on ultrasound axilla. Final histopathology was taken as gold standard. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value were calculated for ultrasound (USG) and ultrasound-guided needle aspiration (USG-FNAC). A total of 100 patients were included in which 58 had non-suspicious and 42 had suspicious nodes on ultrasound of axilla. Among suspicious group, 24 were positive on ultrasound-guided needle aspiration cytology and 18 were negative. In non-suspicious nodes, sentinel node biopsy was performed. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value for ultrasound were 61.5%, 75.6%, 69.5%, and 68.5% respectively. For ultrasound-guided needle aspiration (USG-FNAC), sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive value are 83%, 100%, 100%, and 72.6% respectively. The accuracy of ultrasound (USG) and ultrasound-guided needle aspiration (USG-FNAC) was 69% and 88.1%. The result of our study indicates the feasibility of USG and USG-FNAC in a high-volume center with good accuracy of around 70–80%. Approximately one-fourth (24%) of the total patients were taken up for axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) without performing SLNB.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee M, George J, Song EY, Roy A, Hryniuk W (2004) Tree-based model for breast cancer prognostication. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 22(13):2567–2575
Cianfrocca M (2004) Prognostic and predictive factors in early-stage breast cancer. Oncologist 9(6):606–616
Krag D, Weaver D, Ashikaga T, Moffat F, Klimberg VS, Shriver C, Feldman S, Kusminsky R, Gadd M, Kuhn J, Harlow S, Beitsch P, Whitworth P Jr, Foster R Jr, Dowlatshahi K (1998) The sentinel node in breast cancer — a multicenter validation study. N Engl J Med 339(14):941–946
Alkuwari E, Auger M (2008) Accuracy of fine-needle aspiration cytology of axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients: a study of 115 cases with cytologic-histologic correlation. Cancer. 114(2):89–93
Reynolds C, Mick R, Donohue JH, Grant CS, Farley DR, Callans LS, Orel SG, Keeney GL, Lawton TJ, Czerniecki BJ (1999) Sentinel lymph node biopsy with metastasis: can axillary dissection be avoided in some patients with breast cancer? J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 17(6):1720–1726
Lovrics PJ, Chen V, Coates G, Cornacchi SD, Goldsmith CH, Law C, Levine MN, Sanders K, Tandan VR (2004) A prospective evaluation of positron emission tomography scanning, sentinel lymph node biopsy, and standard axillary dissection for axillary staging in patients with early stage breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 11(9):846–853
Somasundar P, Gass J, Steinhoff M, Koeliker S, Dizon D, Cady B, Taneja C (2006) Role of ultrasound-guided axillary fine-needle aspiration in the management of invasive breast cancer. Am J Surg 192(4):458–461
Swenson KK, Nissen MJ, Ceronsky C, Swenson L, Lee MW, Tuttle TM (2002) Comparison of side effects between sentinel lymph node and axillary lymph node dissection for breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 9(8):745–753
Mincey BA, Bammer T, Atkinson EJ, Perez EA (2001) Role of axillary node dissection in patients with T1a and T1b breast cancer: Mayo Clinic experience. Arch Surg Chic Ill 1960 136(7):779–782
Bruneton JN, Caramella E, Héry M, Aubanel D, Manzino JJ, Picard JL (1986) Axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer: preoperative detection with US. Radiology. 158(2):325–326
Feng Y, Huang R, He Y, Lu A, Fan Z, Fan T, Qi M, Wang X, Cao W, Wang X, Xie Y, Wang T, Li J, Ouyang T (2015) Efficacy of physical examination, ultrasound, and ultrasound combined with fine-needle aspiration for axilla staging of primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 149(3):761–765
Jain A, Haisfield-Wolfe ME, Lange J, Ahuja N, Khouri N, Tsangaris T, Zhang Z, Balch C, Jacobs LK (2008) The role of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of axillary nodes in the staging of breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 15(2):462–471
Ahn HS, Kim SM, Jang M, La Yun B, Kim S-W, Kang E et al (2013) Comparison of sonography with sonographically guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy and core-needle biopsy for initial axillary staging of breast cancer. J Ultrasound Med 32(12):2177–2184
Choy N, Lipson J, Porter C, Ozawa M, Kieryn A, Pal S, Kao J, Trinh L,Wheeler A, Ikeda D, Jensen K, Allison K,Wapnir I (2015) Initial results with preoperative tattooing of biopsied axillary lymph nodes and correlation to sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer pa- tients. Ann Surg Oncol 22(2):377–382
Gipponi M, Fregatti P, Garlaschi A, Murelli F, Margarino C, Depaoli F, Baccini P, Gallo M, Friedman D (2016) Axillary ultra- sound and fine-needle aspiration cytology in the preoperative stag- ing of axillary node metastasis in breast cancer patients. Breast 30: 146–150
Mainiero MB, Cinelli CM, Koelliker SL, Graves TA, Chung MA (2010) Axillary ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration in the preoperative evaluation of the breast cancer patient: an algorithm based on tumor size and lymph node appearance. Am J Roentgenol 195(5):1261–1267
Bedi DG, Krishnamurthy R, Krishnamurthy S, Edeiken BS, Le-Petross H, Fornage BD et al (2008) Cortical morphologic features of axillary lymph nodes as a predictor of metastasis in breast cancer: in vitro sonographic study. Am J Roentgenol 191(3):646–652
Cools-Lartigue J, Sinclair A, Trabulsi N, Meguerditchian A, Mesurolle B, Fuhrer R, Meterissian S (2013) Preoperative axillary ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the diagnosis of axillary metastases in patients with breast cancer: predictors of accuracy and future implications. Ann Surg Oncol 20(3):819–827
Holwitt DM, Swatske ME, Gillanders WE, Monsees BS, Gao F, Aft RL, Eberlein TJ, Margenthaler JA (2008) Scientific presentation award: the combination of axillary ultrasound and ultrasound-guided biopsy is an accurate predictor of axillary stage in clinically node-negative breast cancer patients. Am J Surg 196(4):477–482
Kim WH, Kim HJ, Jung JH, Park HY, Lee J, Kim WW, Park JY, Cheon H, Lee SM, Cho SH, Shin KM, Kim GC (2017) Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of non-palpable and suspicious axillary lymph nodes with subsequent removal after tattooing: false-negative results and concordance with sentinel lymph nodes. Ultrasound Med Biol 43(11):2576–2581
Houssami N, Ciatto S, Turner RM, Cody HS, Macaskill P (2011) Preoperative ultrasound-guided needle biopsy of axillary nodes in invasive breast cancer: meta-analysis of its accuracy and utility in staging the axilla. Ann Surg 254(2):243–251
Zhang F, Zhang J, Meng Q, Zhang X (2018) Ultrasound combined with fine needle aspiration cytology for the assessment of axillary lymph nodes in patients with early stage breast cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). [cited 2018 Dec 11];97(7). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5839868/
Kuenen-Boumeester V, Menke-Pluymers M, de Kanter AY, Obdeijn I-MA, Urich D, Van Der Kwast TH (2003) Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology of axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients. A preoperative staging procedure. Eur J Cancer 39(2):170–174
Hu X, Zhou X, Yang H, Wei W, Jiang Y, Liu J (2018 Jun) Axillary ultrasound and fine needle aspiration biopsy in the preoperative diagnosis of axillary metastases in early-stage breast cancer. Oncol Lett 15(6):8477–8483
Park S, Koo JS, Kim GM, Sohn J, Kim SI, Cho YU et al (2018) Feasibility of charcoal tattooing of cytology-proven metastatic axillary lymph node at diagnosis and sentinel lymph node biopsy after Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Cancer Res Treat Off J Korean Cancer Assoc 50(3):801–812
Liu Q, Xing P, Dong H, Zhao T, Jin F (2018) Preoperative assessment of axillary lymph node status in breast cancer patients by ultrasonography combined with mammography: a STROBE compliant article. Medicine (Baltimore) 97(30):e11441
Verbanck J, Vandewiele I, De Winter H, Tytgat J, Van Aelst F, Tanghe W (1997) Value of axillary ultrasonography and sonographically guided puncture of axillary nodes: a prospective study in 144 consecutive patients. J Clin Ultrasound 25(2):53–56
Park SH, Kim MJ, Park B-W, Moon HJ, Kwak JY, Kim E-K (2011) Impact of preoperative ultrasonography and fine-needle aspiration of axillary lymph nodes on surgical management of primary breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 18(3):738–744
Agha RA, Borrelli MR, Vella-Baldacchino M, Thavayogan R, Orgill DP, for the STROCSS Group (2017) The STROCSS statement: strengthening the reporting of cohort studies in surgery. Int J Surg 46:198–202
Shrivastava V, Singh S, Singh S, Maurya AK, Maurya AK, Singh M, Singh M, Sam S, Sam S, Gupta SK, Gupta SK (2016) The accuracy of USG and USG guided FNAC axilla in predicting nodal metastasis in a clinically lymph node negative cancer breast patient. Int J Res Med Sci 5(1):196–200
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
IECPG-292/07.09.2017, RT 2/16.10.2017
Consent to Participate
Taken.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R., Deo, S.V.S., Dhamija, E. et al. To Evaluate the Accuracy of Axillary Staging Using Ultrasound and Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology (USG-FNAC) in Early Breast Cancer Patients—a Prospective Study. Indian J Surg Oncol 11, 726–734 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-020-01222-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-020-01222-3