Abstract
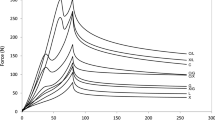
The effects of incorporating guar gum (GG) and gum arabic (GA) in cheese-making milk with various fat contents (0.4, 0.9, and 1.4 %) on chemical and rheological properties of Iranian white cheese were evaluated by response surface method (RSM). As GG concentration increased, dry matter content of cheese samples decreased due to the high water binding capacity of this gum. A similar trend was also observed for GA at concentrations less than 150 ppm. The higher the GG concentration, the higher was the free fatty acid content of cheese samples. GA at concentrations more than 150 ppm, increased the storage modulus (G′), causing an undesirable hard texture for the product. The G′ and stress at fracture (бf) of samples decreased by the increasing concentration of GG incorporated into the cheese-making milk. Response surface minimization of rheological indices for Iranian white cheese showed that combination of two hydrocolloids (GG in the concentration range 75–170 ppm and GA at concentrations <75 ppm) would provide the softest texture.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC, Association of Official Analytical Chemists (1997) Official Methods of Analytical, 16th edn., 3rd rev. Arlington, VA, USA
Azarnia S, Ehsani MR, Mirhadi SA (1997) Evaluation of the physico chemical characteristic of the curd during the ripening of Iranian Brine cheese. Int Dairy J 7:473–478
Drake MA, Swanson BG (1995) Reduced- and low-fat cheese thecnology: a review. Trend Food Sci Tech 6:366–369
Derringer G, Suich R (1980) Simultaneous optimization of several response variables. J Quality Tech 12(4):214–219
James CS (1995) Analytical chemistry of foods. Blackie Academic & Professional, Glasgow
Kahyaoglu T, Kaya S (2003) Effects of heat treatment and fat reduction on the rheological and functional properties of Gaziyantep cheese. Int Dairy J 13:867–875
Katsiari MC, Voutsinas LP, Kondyli E, Alichanidis E (2002) Flavour enhancement of low-fat Feta-type cheese using a commercial adjunct culture. Food Chem 79:193–198
Kavas G, Oysun G, Kinik O, Uysal H (2004) Effects of some fat replacers on chemical, physical and sensory attributes of low-fat white pickled cheese. Food Chem 88:381–388
Koca N, Metin M (2004) Textural, melting and sensory properties of low fat fresh Kashar cheeses produced by using fat replacer. Int Dairy J 14:365–373
Konuklar G, Inglett GE, Warner K, Carriere CJ (2004) Use of β-glucan hydrocolloidal suspension in the manufacture of low-fat Cheddar cheese: textural properties by instrumental methods and sensory panels. Food Hydrocolloid 18:535–545
Kumar SS, Balasubramanian S, Biswas AK, Chatli MK, Devatkal SK, Sahoo J (2011) Efficacy of soy protein isolate as a fat replacer on physico-chemical and sensory characteristics of low-fat paneer. J Food Sci Technol 48(4):498–501
Madadlou A, Emam-Djomeh Z, Mousavi ME, Ehsani M, Javanmard M, Sheehan D (2009) Response surface optimization of an artificial neural network for predicting the size of re-assembled casein micelles. Comput Electron Agr 68:216–221
Madadlou A, Khosrowshahi A, Mosavi ME (2005) Rheology, microstructure and functionality of low-fat Iranian White cheese made whit different concentration of rennet. J Dairy Sci 88:3052–3062
Madadlou A, Khosrowshahi A, Mousavi ME, Emam-Djome Z (2006) Microstructure and rheological properties of Iranian White cheese coagulated at various temperatures. J Dairy Sci 89:2359–2364
Madadlou A, Mousavi ME, Khosrowshahi A, Emam-Djome Z, Zargaran M (2007) Effect of cream homogenization on textural characteristics of low-fat Iranian White cheese. Int Dairy J 17:547–554
Mistry VU (2001) Low fat cheese technology. Int Dairy J 11:413–422
Nunez M, Garcia-Aser C, Rodrigues-Martin A, Medina M, Gaya P (1986) The effect of ripening and cooking temperature on proteolysis and lipolysis in Manchego cheese. Food Chem 21:115–123
Rahimi J, Khosrowshahi A, Madadlou A, Aziznia S (2007) Texture of low-fat Iranian white cheese as influenced by gum tragacanth as a fat replacer. J Dairy Sci 90:4058–4070
Rodriguez J (1998) Recent advances in the development of low-fat cheeses. Trends Food Sci Tech 9:249–254
Romeih EA, Michaelidou A, Biliaderis CG, Zerfiridis GK (2002) Low-fat white-brined cheese made from bovine milk and two commercial fat mimetics: chemical, physical and sensory attributes. Int Dairy J 12:525–540
Rudan MA, Barbano DM, Yun JJ, Kindstedt PS (1999) Effect of fat content reduction on chemical composition, proteolysis, functionality, and yield of Mozzarella. J Dairy Sci 82:661–672
Saha D, Bhattacharya S (2010) Hydrocolloids as thickening and gelling agents in food: a critical review. J Food Sci Tech 47(6):587–597
Sipahioglu O, Alvarez VB, Solano-Lopez C (1999) Structure, physico chemical and sensory properties of Feta cheese made whit tapioca starch and lecithin as fat mimetics. Int Dairy J 9:783–789
Steffe JF (1996) Rheological methods in food process engineering. Freeman Press, East Lansing
Tuinier R, Grotenhuis ET, de Kruif CG (2000) The effect of depolymerised guar gum on the stability of skim milk. Food Hydrocolloid 14:1–7
Volikakis P, Biliaderis CG, Vamvakas C, Zerfiridis GK (2004) Effects of a commercial oat-β-glucan concentration on the chemical, physico-chemical and sensory attributes of a low-fat white-brined cheese product. Food Res Int 37:83–94
Zalazar CA, Zalazar CS, Bernal S, Bertola N, Bevilaequa A, Zaritzky N (2002) Effect of moisture level and fat replacer on physicochemical, rheological and sensory properties of low fat soft cheeses. Int Dairy J 12:45–50
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lashkari, H., Khosrowshahi asl, A., Madadlou, A. et al. Chemical composition and rheology of low-fat Iranian white cheese incorporated with guar gum and gum arabic as fat replacers. J Food Sci Technol 51, 2584–2591 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0768-y
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0768-y