Abstract
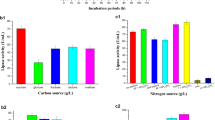
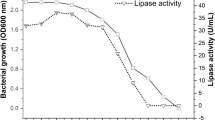
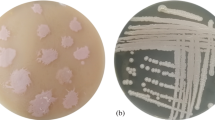
Lipases, particularly microbial lipases, are important industrial biocatalysts. As a result, lipase enzyme screening, synthesis, and purification from microbial strains are constantly evolving to meet the needs of the pharmaceutical and food industries. Thus, the goal of this study was to identify the most potential lipase-producing bacterial strains from Aavin dairy industry effluent contaminated soil. Furthermore, growth parameters, such as pH, temperature, carbon and nitrogen sources, were optimized for lipase enzyme production from selected bacterial strains. According to the findings, 9 strains (V1–V9) of 15 bacterial isolates were found to be lipase producers. However, three strains (V1, V7, and V8) predominated and demonstrated significant lipase-producing activity. These V1, V7, and V8 bacterial strains were identified as Bacillus pumilus V1, Bacillus pumilus V7, and Bacillus subtilis V8 through 16S rRNA sequencing. About 16.6 to 27.8 µg mL−1 of lipase production was recorded under the optimal growth conditions: pH 8, temperature 37 °C, fructose and yeast extract as suitable carbon and nitrogen source. Among these 3 strains B. pumilus V1 showed excellent lipase productivity than others. The molecular weight of this lipase produced by bacteria was determined to be 35 kDa using sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abol-Fotouh D, AlHagar OE, Hassan MA (2021) Optimization, purification, and biochemical characterization of thermoalkaliphilic lipase from a novel Geobacillus stearothermophilus FMR12 for detergent formulations. Int J Biol Macromol 181:125–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.111
Alhamdani MA, Alkabbi HJJ (2016) Isolation and identification of lipase producing bacteria from oil-contaminant soil. J Biol Agric Healthc 6(2):1–7
Aly MM, Tork S, Al-Garni SM et al (2012) Production of lipase from genetically improved Streptomyces exfoliates LP10 isolated from oil-contaminated soil. Afr J Microbiol Res 6(6):1125–1137. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR11.1123
Anusha P, Natarajan D et al (2021) Heavy metal removal competence of individual and bacterial consortium, evolved from metal contaminated soil. Mater Today. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.11.214
Arbeloa FL, Martínez VM, Arbeloa T et al (2007) Photoresponse and anisotropy of rhodamine dye intercalated in ordered clay layered films. J Photochem Photobiol c: Photochemy Rev 8(2):85–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2007.03.003
Balaji L, Jayaraman G (2014) Metal ion activated lipase from halotolerant Bacillus sp. VITL8 displays broader operational range. Int J Biol Macromol 67:380–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.03.050
Bharathi D, Rajalakshmi G (2019) Microbial lipases: An overview of screening, production and purification. Biocatald Agric Biotechnol 22:101368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101368
Chandra P, Enespa Singh R, Arora PK (2020) Microbial lipases and their industrial applications: a comprehensive review. Microb Cell Fact 19(1):169. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01428-8
Ciafardini G, Zullo BA, Iride A (2006) Lipase production by yeasts from extra virgin olive oil. Food Microbiol 23(1):60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2005.01.009
Dikshit PK, Kim BS (2020) Bacterial cellulose production from biodiesel–derived crude glycerol, magnetic functionalization, and its application as carrier for lipase immobilization. Int J Biol Macromol 153:902–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.047
Egbuna C, Awuchi CG, Kushwaha G et al (2021) Bioactive compounds effective against type 2 diabetes mellitus: A Systematic Review”. Cur Topics Med Chem 21:1. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026621666210509161059
Elhussiny NI, Khattab AE-NA, El-Refai HA et al (2020) Biotransesterification capabilities of Mucorales whole-cell lipase isolates and mutants. Biocatald Agric Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101722
Filho DG, Silva AG, Guidini CZ (2019) Lipases: sources, immobilization methods, and industrial applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(18):7399–7423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10027-6
Hassan SWM, Abd El Latif HH, Ali SM (2018) Production of cold-active lipase by free and immobilized marine Bacillus cereus HSS: application in wastewater treatment. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02377/full
Hu J, Cai W, Wang C et al (2018) Purification and characterization of alkaline lipase production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa HFE733 and application for biodegradation in food wastewater treatment. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 32(3):583–590. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2018.1446764
Hunter M, Yuan P, Vavilala D et al (2019) Optimization of protein expression in mammalian cells. Curr Protoc Protein Sci 95(1):e77. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpps.77
Hwang HT, Qi F, Yuan C et al (2014) Lipase-catalyzed process for biodiesel production: protein engineering and lipase production. Biotechnol Bioengi 111(4):639–653. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25162
Ibrahim AM, Hamouda RA, El-Naggar NEA et al (2021) Bioprocess development for enhanced endoglucanase production by newly isolated bacteria, purification, characterization and in-vitro efficacy as anti-biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci Rep 11(1):9754. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-87901-9
Ilesanmi OI, Adekunle AE, Omolaiye JA et al (2020) Isolation, optimization and molecular characterization of lipase producing bacteria from contaminated soil. Sci Afri. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00279
Ji Q, Xiao S, He B et al (2010) Purification and characterization of an organic solvent-tolerant lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa LX1 and its application for biodiesel production. J Mol Catal b: Enzy 66(3):264–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2010.06.001
Kandasamy S, Devarayan K, Bhuvanendran N et al (2021a) Accelerating the production of biooil from hydrothermal liquefaction of microalgae via recycled biochar-supported catalysts. J Environ Chem Engi 9(4):105321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105321
Kandasamy S, He Z, Liu G et al (2021b) Current strategies and prospects in algae for remediation and biofuels: An overview. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102045
Kroll J, Klinter S, Schneider C et al (2010) Plasmid addiction systems: perspectives and applications in biotechnology. Microb Biotechnol 3(6):634–657. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-7915.2010.00170.x
Kumarasamy S, Subramanian V, Ranganathan M et al (2020) Microbial Stereo Inversion of (R) 3 Chloro-1, 2-Propandiol by Wickerhamomyces anomalous MGR6-KY209903. Chem Biointerface Res Appl. https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC105.61576166
Lomthaisong K, Buranarom A, Niamsup H (2012) Investigation of isolated lipase producing bacteria from oil-contaminated soil with proteomic analysis of its proteins responsive to lipase inducer. J Biol Sci 12(3):161–167. https://doi.org/10.3923/jbs.2012.161.167
Magdouli S, Guedri T, Tarek R et al (2017) Valorization of raw glycerol and crustacean waste into value added products by Yarrowia lipolytica. Bioresour Technol 243:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.074
Matias RR, Sepúlveda AMG, Batista BN et al (2021) Degradation of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm using hydrolytic enzymes produced by amazonian endophytic fungi. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 193(7):2145–2161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03542-8
Mehta A, Guleria S, Sharma R et al (2021) The lipases and their applications with emphasis on food industry. In: Ray RC (ed) Microbial Biotechnology in Food and Health. Academic Press
Mohammed HJ (2013) Physicochemical factors affected the partial purified lipase activity of Acinetobacter baumannii local isolates. Iraqi J Pharm Sci. https://doi.org/10.31351/vol22iss1pp82-89
Murthy HN, Lee EJ, Paek KY (2014) Production of secondary metabolites from cell and organ cultures: strategies and approaches for biomass improvement and metabolite accumulation. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 118(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0467-7
Narayanan M, Gokila Devi P, Natarajan D et al (2021a) Green synthesis and characterization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Pouteria campechiana and larvicidal and pupicidal activity on Aedes aegypt. Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111333
Narayanan M, Gopi A, Natarajan D et al (2021b) Hepato and nephroprotective activity of methanol extract of Hygrophila spinosa and its antibacterial potential against multidrug resistant Pandoraea sputorum. Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111594
Narayanan M, Jayashree T, Kandasamy S et al (2021c) Antidermatophytic, antioxidant, and nephroprotectiveactivity of Solanum surattense: an invitro study. Process Biochem 109:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2021.07.008
Narayanan M, Vigneshwari P, Natarajan D et al (2021d) Synthesis and characterization of TiO2 NPs by aqueous leaf extract of Coleus aromaticus and assess their antibacterial, larvicidal, and anticancer potential. Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111335
Nguyen MT, Matsuo M, Niemann S et al (2020) Lipoproteins in gram-positive bacteria: abundance, function, fitness. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.582582/full
Ponniah A, Natarajan D, Chinnathambi A et al (2021) Evaluation of chromium biosorption competence of indigenous Aspergillus tubingensis AF3. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131055
Rajendran A, Palanisamy A, Thangavelu V (2008) Evaluation of medium components by Plackett-Burman statistical design for lipase production by Candida rugosa and kinetic modeling. Chin J Biotechnol 24(3):436–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1872-2075(08)60024-2
Rasmey AHM, Aboseidah AA, Gaber S (2017) Characterization and optimization of lipase activity produced by Pseudomonas monteilli 2403-KY120354 isolated from ground beef. Afr J Biotechnol 16(2):96–105
Rodrigues RC, Volpato G, Wada K et al (2008) Enzymatic synthesis of biodiesel from transesterification reactions of vegetable oils and short chain alcohols. J Am Oil Chem Soc 85(10):925–930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-008-1284-0
Sahoo RK, Das A, Gaur M et al (2020) Parameter optimization for thermostable lipase production and performance evaluation as prospective detergent additive. Prepar Biochem Biotechnol 50(6):578–584. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2020.1719513
Saranyadevi S, Suresh K, Muthusamy R et al (2021) Silver nanoparticles synthesized using asafoetida resin, characterization of their broad spectrum and larvicidal activity. Ann Romanian Soc Cell Biol 25(4):15035–15049
Sarmah N, Revathi D, Sheelu G et al (2018) Recent advances on sources and industrial applications of lipases. Biotechnol Prog 34(1):5–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.2581
Sharma D, Kumbhar BK, Verma AK et al (2014) Optimization of critical growth parameters for enhancing extracellular lipase production by alkalophilic Bacillus sp. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 3(4):205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2014.04.004
Sharma P, Sharma N, Pathania S et al (2017) Purification and characterization of lipase by Bacillus methylotrophicus PS3 under submerged fermentation and its application in detergent industry. J Gene Engin Biotechnol 15(2):369–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2017.06.007
Sirisha E, Rajaseka N, Narasu ML (2010) Isolation and optimization of lipase producing bacteria from oil contaminated soils. Adv Biol Res 4(5):249–252
Sivaramakrishnan R, Incharoensakdi A (2016) Purification and characterization of solvent tolerant lipase from Bacillus sp for methyl ester production from algal oil. J Biosci Bioengin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2015.09.005
Soman S, Kumarasamy S, Narayanan M (2020) Biocatalyst: Phytase production in solid state fermentation by OVAT strategy. Chem Biointerface Res Appl. https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC105.61196127
Soman S, Suresh K, Muthusamy R et al (2020) Chemically defined medium for the production of phytase by Hanseniaspora guilliermondii S1, Pichia fermentans S2 and its secondary structure prediction of 16S rRNA. Biointerface Res Appl Chem. https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC105.62626272
Uchida Y, Mogi H, Hamamoto T et al (2018) Changes in denitrification potentials and riverbank soil bacterial structures along Shibetsu River. Japan Appl EnvironSoil Sci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2530946
Vijayan S, Umadevi G, Mariappan R et al (2020) High luminescence efficiency of Copper doped Zinc Sulfide (Cu: ZnS) nanoparticles towards LED applications. Procee Mater Today. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.11.214
Whangchai K, Hung T, Al-Rashed S et al (2021) Biodegradation competence of Streptomyces toxytricini D2 isolated from leaves surface of the hybrid cotton crop against β cypermethrin. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130152
Willerding AL, Oliveira LAD, Moreira FW et al (2011) Lipase activity among bacteria isolated from amazonian soils. Enz Res. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/720194
Yadav AN, Kour D, Kaur T et al (2021) Biodiversity, and biotechnological contribution of beneficial soil microbiomes for nutrient cycling, plant growth improvement and nutrient uptake. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 33:102009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102009
Yele VU, Desai K (2015) A new thermostable and organic solvent-tolerant lipase from Staphylococcus warneri; optimization of media and production conditions using statistical methods. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175(2):855–869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1331-2
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the DST-FIST (SR/FIST/LSI-673/2016) for strengthening the instrumentation facility of the Biotechnology Department of Periyar University, Salem, Tamil Nadu. This project was supported by Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP-2021/385) King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kandasamy, S., Vijayalakshmi, V.S., Salmen, S.H. et al. Screening, characterization, and optimization of lipase enzyme producing bacteria isolated from dairy effluents contaminated muddy soil. Appl Nanosci 13, 1443–1451 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-02062-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-02062-5