Abstract
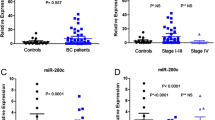
MiRNA-21 is recognized as the main active candidate and high expression in many solid tumors consequential cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and closely related to metastasis of disease. The study aimed to evaluate the serum miRNA-21 expression and therapy outcome in breast cancer patients and cell lines. Seventy-five histopathologically confirmed newly diagnosed breast cancer patients were included in the study; before and after therapy, patient’s blood sample were collected and analyzed for serum microRNA-21 expression by quantitative real-time PCR. In patients, 8.9 mean fold increased microRNA-21 expression was observed compared to controls. Increased expression was found to be associated with advanced stage (11.72-fold), lymph node involvement (11.12-fold), and distant metastases (20.17-fold). After treatment significant decrease in miRNA-21 expression was observed and found to be significant (p < 0.0001). Patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy had significant impact on miRNA-21 suppression and found to be significantly associated with different clinicopathological features of patients. Increased miRNA-21 expression was also found to be significantly associated with poor survival of breast cancer patients (p = 0.002). MicroRNA-21 expression could be used as promising predictive indicators for breast cancer prognosis. MicroRNA-21 over-expression was associated with response to neoadjuvant therapy and may perhaps be considered as primary treatment choice.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flynt AS, Lai EC. Biological principles of microRNA-mediated regulation: shared themes amid diversity. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:831–42.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:10513–8.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T. MicroRNA- 21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:647–58.
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, et al. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:2128–36.
Papagiannakopoulos T, Shapiro A, Kosik KS. MicroRNA-21 targets a network of key tumor-suppressive pathways in glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68:8164–72.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7065–70.
Luo X, Burwinkel B, Tao S, Brenner H. MicroRNA signatures: novel biomarker for colorectal cancer? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011;20(7):1272–86.
Skrzypski M, Dziadziuszko R, Jassem J. MicroRNA in lung cancer diagnostics and treatment. Mutat Res. 2011;717(1–2):25–31.
Zhao L, Chen X, Cao Y. New role of microRNA: carcinogenesis and clinical application in cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin Shanghai. 2011;43(11):831–9.
Moore LM, Zhang W. Targeting miR-21 in glioma: a small RNA with big potential. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010;14(11):1247–57.
Selcuklu SD, Donoghue MT, Spillane C. miR-21 as a key regulator of oncogenic processes. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009;37(Pt 4):918–25.
Krichevsky AM, Gabriely G. miR-21: a small multi-faceted RNA. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(1):39–53.
Rossi S, Shimizu M, Barbarotto E, Nicoloso MS, Dimitri F, Sampath D, et al. microRNA fingerprinting of CLL patients with chromosome 17p deletion identify a miR-21 score that stratifies early survival. Blood. 2010;116(6):945–52.
Tang J, Ahmad A, Sarkar FH. The role of microRNAs in breast cancer migration, invasion and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:13414–37.
Corcoran C, Friel AM, Duffy MJ, Crown J, O’Driscoll L. Intracellular and extracellular microRNAs in breast cancer. Clin Chem. 2011;57:18–32.
Mei M, Ren Y, Zhou X, Yuan XB, Han L, Wang GX, et al. Downregulation of miR-21 enhances chemotherapeutic effect of taxol in breast carcinoma cells. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2010;9:77–86.
Chen L, Bourguignon LY. Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction promotes c-Jun signaling and miRNA21 expression leading to Bcl-2 expression and chemoresistance in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:52.
Dong J, Zhao YP, Zhou L, Zhang TP, Chen G. Bcl-2 upregulation induced by miR-21 via a direct interaction is associated with apoptosis and chemoresistance in MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells. Arch Med Res. 2011;42:8–14.
Fu X, Han Y, Wu Y, Zhu X, Lu X, Mao F, et al. Prognostic role of microRNA-21 in various carcinomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J ClinInvest. 2011;41(11):1245–53. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2011.02535.x7.
Kumarswamy R, Volkmann I, Thum T. Regulation and function of miRNA-21 in health and disease. RNA Biol. 2011;8(5):706–13. doi:10.4161/rna.8.5.16154.
Mishra PJ, Merlino G. MicroRNA reexpression as differentiation therapy in cancer. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:2119–23.
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008;18:997–1006.
Asaga S, Kuo C, Nguyen T, Terpenning M, Giuliano AE, Hoon DS. Direct serum assay for microRNA-21 concentrations in early and advanced breast cancer. Clin Chem. 2011;57:84–91.
Wang ZX, Bian HB, Wang JR, Cheng ZX, Wang KM, De W. Prognostic significance of serum miRNA-21 expression in human non-small cell lung cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2011;104:847–51.
Si H, Sun X, Chen Y, Cao Y, Chen S, Wang H, et al. Circulating microRNA-92a and microRNA-21 as novel minimally invasive biomarkers for primary breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013;139(2):223–9.
Ng EK, Li R, Shin VY, Jin HC, Leung CP, Ma ES, et al. Circulating microRNAs as specific biomarkers for breast cancer detection. PLoS One. 2013;8(1), e53141.
Sempere LF, Kauppinen S. In: Bradshaw RA, Dennis EA, editors. Translational implications of microRNAs in clinical diagnostics and therapeutics: handbook of cell signaling. Oxford: Academic; 2009. p. 2965–e2981.
Schwartz GF, Hortobagyi GN, Masood S, Palazzo J, Holland R, Page D. Proceedings of the consensus conference on neoadjuvant chemotherapy in carcinoma of the breast, April 26–28, 2003, Philadelphia, PA. Hum Pathol. 2004;35:781–4.
Kaufmann M, von Minckwitz G, Bear HD, Buzdar A, McGale P, Bonnefoi H, et al. Recommendations from an international expert panel on the use of neoadjuvant (primary) systemic treatment of operable breast cancer: new perspectives 2006. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:1927–34.
Chia S, Swain SM, Byrd DR, Mankoff DA. Locally advanced and inflammatory breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:786–90.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all the study subjects who were part of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by Institutional Ethics Committee, Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Prasant Yadav, Alpana Saxena and Masroor Mirza contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, P., Mirza, M., Nandi, K. et al. Serum microRNA-21 expression as a prognostic and therapeutic biomarker for breast cancer patients. Tumor Biol. 37, 15275–15282 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5361-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5361-y