Abstract
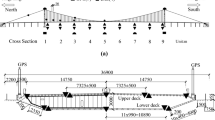
This paper addresses the temperature-induced variations of measured modal frequencies of steel box girder for a suspension bridge using long-tem monitoring data. The output-only modal frequency identification of the bridge is effectively carried out using the Iterative Windowed Curve-fitting Method (IWCM) in the frequency-domain. The daily and seasonal correlations of frequency-temperature are investigated in detail and the analysis results reveal that: (i) the identified modal frequencies using IWCM provide an effective indication for changes of the bridge due to the ambient temperature variations; (ii) temperature is the critical source causing modal variability, and there is an overall decrease in modal frequency with temperature for all the identified modes; (iii) the random variations in measured modal frequencies mainly arise from the identification algorithm due to the nonstationary loadings, which can be effectively eliminated using multi-sample averaging technique; (iv) the daily averaged modal frequencies of vibration modes have remarkable seasonal correlations with the daily averaged temperature and the seasonal correlation models of frequency-temperature are suitable for structural damage warning if future seasonal correlation models deviate from these normal models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel Wahab, M. and De Roeck, G. (1997). “Effect of temperature on dynamic system parameters of a highway bridge.” Structural Engineering International, 7(4), pp. 266–270.
Cornwell, P., Farrar, C. R., Doebling, S. W., and Shoh, H. (1999). “Environmental variability of modal properties.” Experimental Techniques, 23(6), pp. 45–48.
Ding, Y. L., Li, A. Q., and Liu, T. (2008a). “Environmental variability study on the measured responses of Runyang Cable-stayed Bridge using wavelet packet analysis.” Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 51(5), pp. 517–528.
Ding, Y. L., Li, A. Q., Sun, J., and Deng, Y. (2008b). “Experimental and analytical studies on static and dynamic characteristics of steel box girder for Runyang Cable-stayed Bridge.” Advances in Structural Engineering, 11(4), pp. 425–438.
Doebling, S. W., Farrar, C. R., and Prim, M. B. (1998). “A summary review of vibration-based damage identification methods.” Shock and Vibration Digest, 30(2), pp. 91–105.
Han, S. H., Cho, H. N., Cho, T. J., Shin, S. W., and Kim, T. S. (2010). “Risk assessments of long-span bridges considering life-cycle cost concept and near-fault ground motion effect.” International Journal of Steel Structures, 10(1), pp. 51–63.
Hsieh, K. H., Halling, M. W., and Barr, P. J. (2006). “Overview of vibrational structural health monitoring with representative case studies.” Journal of Bridge Engineering, 11(6), pp. 707–715.
Hua, X. G., Ni, Y. Q., Ko, J. M., and Wong, K. Y. (2007). “Modeling of temperature-frequency correlation using combined principal component analysis and support vector regression technique.” Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 21(2), pp. 122–135.
Ko, J. M. and Ni, Y. Q. (2005). “Technology developments in structural health monitoring of large-scale bridges.” Engineering Structures, 27(12), pp. 1715–1725.
Lee, J. W., Choi, K. H., and Huh, Y. C. (2010). “Damage detection method for large structures using static and dynamic strain data from distributed fiber optic sensor.” International Journal of Steel Structures, 10(1), pp. 91–97.
Macdonald, J. H. G. (2000). Identification of the dynamic behaviour of a cable-stayed bridge from full-scale testing during and after construction. Ph. D. thesis, University of Bristol, UK.
Ni, Y. Q., Hua, X. G., Fan, K. Q., and Ko, J. M. (2005). “Correlating modal properties with temperature using long-term monitoring data and support vector machine technique.” Engineering Structures, 27(12), pp. 1762–1773.
Ni, Y. Q., Ko, J. M., Hua, X. G., and Zhou, H. F. (2007). “Variability of measured modal frequencies of a cable-stayed bridge under different wind conditions.” Smart Structures and Systems, 3(3), pp. 341–356.
Ni, Y. Q., Zhou, H. F., and Ko, J. M. (2009). “Generalization capability of neural network models for temperature-frequency correlation using monitoring data.” Journal of Structural Engineering, ASCE, 135(10) pp. 1290–1300.
Peeters, B. and De Roeck, G. (2001). “One-year monitoring of the Z24-Bridge: environmental effects versus damage events.” Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 30(2), pp. 149–171.
Ren, W. X. and Peng, X. L. (2005). “Baseline finite element modeling of a large span cable-stayed bridge through field ambient vibration tests.” Computers and Structures, 83(8–9), pp. 536–550.
Ren, W. X., Lin, Y. Q., and Peng, X. L. (2007). “Field load tests and numerical analysis on Qingzhou Cable-stayed Bridge.” Journal of Bridge Engineering, ASCE, 12(2), pp. 261–270.
Sohn, H., Dzwonczyk, M., Straser, E. G., Kiremidjian, A. S., Law, K. H., and Meng, T. (1999). “An experimental study of temperature effect on modal parameters of the Alamos Canyon Bridge.” Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 28(8), pp. 879–897.
Zhang, Q. W., Fan, L. C., and Yuan, W. C. (2002). “Traffic-induced variability in dynamic properties of cable-stayed bridge.” Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 31(11), pp. 2015–2021.
Zhou, H. F., Ni, Y. Q., and Ko, J. M. (2010). “Constructing input to neural networks for modeling temperature-caused modal variability: Mean temperatures, effective temperatures, and principal components of temperatures.” Engineering Structures, 32(6), pp. 1747–1759.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Note.-Discussion open until November 1, 2011. This manuscript for this paper was submitted for review and possible publication on January 20, 2010; approved on May 9, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Li, A. Temperature-induced variations of measured modal frequencies of steel box girder for a long-span suspension bridge. Int J Steel Struct 11, 145–155 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-011-2004-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-011-2004-4