Abstract
Background and Objective
When administered for severe infections in intravenous drug users (IDUs) at a daily dose of 6 mg/kg, daptomycin displayed abnormal pharmacokinetic parameters compared with those seen in healthy volunteers; specifically, decreased trough and maximum concentrations (Ctrough; Cmax) and increased clearance (CL). The objective of this study was to evaluate the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of daptomycin administered at a daily dosage of 12 mg/kg for Staphylococcus aureus infective endocarditis (IE) in patients concomitantly treated with methadone, and to compare the results with those published in the literature for healthy controls treated with the same daily dose.
Methods
Antibiotic treatment included daptomycin (12 mg/kg daily) in combination with an antistaphylococcal β-lactam (cefazolin 2 g three times a day). The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of Staphylococcus aureus isolated through blood cultures was used to calculate pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters such as the ratio of the area under the concentration–time curve over 24 h to the MIC (AUC0–24/MIC) and Cmax/MIC.
Results
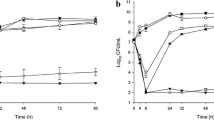
Five IDUs hospitalized for IE were enrolled. The mean measured daptomycin Cmax and Ctrough were 54.1 μg/mL (CV: 0.32) and 8.7 μg/mL (CV: 0.59), respectively; the mean calculated AUC0–24 was 742.7 μg × h/mL (CV: 0.31). The estimated average volume of distribution at the steady state (Vd,ss) and the half-life (t1/2) were 316.5 mL/kg (CV: 0.53) and 14.4 h (CV: 0.30), respectively. The mean daptomycin clearance from plasma normalized for body weight (CLwp) was 17.3 mL/(h × kg) (CV: 0.33). The calculated average Cmax and AUC0–24 (183.7 µg/mL and 1277.4 µg × h/mL, respectively) were lower than and statistically significantly different from (p < 0.001 and p = 0.001, respectively) those expected for healthy volunteers.
Conclusions
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus IE in IDUs on methadone treatment requires the use of high daptomycin daily doses in order to achieve satisfactory pharmacodynamic parameters. Close monitoring of the daptomycin plasma concentration is suggested.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Talha KM, Desimone DC, M Rizwan S, Baddour LM. Pathogen influence on epidemiology, diagnostic evaluation and management of infective endocarditis. Heart. 2020;106):1878–82.
van Hal SJ, Jensen SO, Vaska VL, Espedido BA, Paterson DL, Gosbell IB. Predictors of mortality in Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012;25:362–86.
Akins RL, Rybak MJ. Bactericidal activities of two daptomycin regimens against clinical strains of glycopeptide intermediate-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium, and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model with simulated endocardial vegetations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001;45:454–9.
Habib G, Lancellotti P, Antunes MJ, Bongiorni MG, Casalta JP, Del Zotti F, et al. 2015 ESC guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis. Eur Heart J. 2015;36:3075–128.
Safdar N, Andes D, Craig WA. In vivo pharmacodynamic activity of daptomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:63–8.
Bhavnani SM, Rubino CM, Ambrose PG, Drusano GL. Daptomycin exposure and the probability of elevations in the creatine phosphokinase level: data from a randomized trial of patients with bacteremia and endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50:1568–74.
Rybak MJ, Bailey EM, Lamp KC, Kaatz GW. Pharmacokinetics and bactericidal rates of daptomycin and vancomycin in intravenous drug abusers being treated for gram-positive endocarditis and bacteremia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992;36:1109–14.
Pea F, Crapis M, Cojutti P, Bassetti M. Daptomycin underexposure in a young intravenous drug user who was affected by life-threatening Staphylococcus aureus-complicated skin and soft tissue infection associated with bacteraemia. Infection. 2014;42:207–10.
Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, Davoli M. Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002209.pub2.
Weschules DJ, Bain KT, Richeimer S. Actual and potential drug interactions associated with methadone. Pain Med. 2008;9:315–44.
Gutkowska J, Schiller PW. Renal effects of TAPP, a highly selective mu-opioid agonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1996;119:239–44.
Li JS, Sexton DJ, Mick N, Nettles R, Fowler VG, Ryan T, et al. Proposed modifications to the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;30:633–8.
Mariani B, Corbella M, Seminari E, Sacco L, Cambieri P, Capra Marzani F, et al. Evaluation of a model to improve collection of blood cultures in patients with sepsis in the emergency room. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018;37:241–6.
Dvorchik B, Arbeit RD, Chung J, Liu S, Knebel W, Kastrissios H. Population pharmacokinetics of daptomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:2799–807.
European Medicines Agency. Guideline on bioanalytical method validation. Avaialble from https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-bioanalytical-method-validation_en.pdf. Accessed 28 May 2021
Benvenuto M, Benziger DP, Yankelev S, Vigliani G. Pharmacokinetics and tolerability of daptomycin at doses up to 12 milligrams per kilogram of body weight once daily in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:3245–9.
Mellors JW, Horwitz RJ, Coleman DF. Multicenter collaborative evaluation of a standardized serum bactericidal test as a prognostic indicator in infective endocarditis. Am J Med. 1985;79:A49.
Bellomo R, McEvoy S, Kai Lo S, Myburgh J, Neal B, Norton R, et al. Effect of baseline serum albumin concentration on outcome of resuscitation with albumin or saline in patients in intensive care units: analysis of data from the Saline versus Albumin Fluid Evaluation (SAFE) study. Br Med J. 2006;333:1044–6.
Soraluce A, Asín-Prieto E, Rodríguez-Gascón A, Barrasa H, Maynar J, Carcelero E, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of daptomycin in critically ill patients. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018;52:158–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.03.008.
Di Paolo A, Tascini C, Polillo M, Gemignani G, Nielsen EI, Bocci G, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of daptomycin in patients affected by severe Gram-positive infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013;42:250–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2013.06.006.
Falcone M, Russo A, Cassetta MI, Lappa A, Tritapepe L, D’Ettorre G, et al. Variability of pharmacokinetic parameters in patients receiving different dosages of daptomycin: Is therapeutic drug monitoring necessary? J Infect Chemother. 2013;19:732–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-013-0559-z.
Rybak MJ, Lerner SA, Levine DP, Albrecht LM, McNeil PL, Thompson GA, et al. Teicoplanin pharmacokinetics in intravenous drug abusers being treated for bacterial endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991;35:696–700.
King CH, Creger RJ, Ellner JJ. Pharmacokinetics of tobramycin and gentamicin in abusers of intravenous drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985;27:285–90.
Tsukada H, Tsuji Y, Yamashina T, Tsuruta M, Hiraki Y, Tsuruyama M, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of daptomycin in a clinical setting. J Infect Chemother. 2020;26:230–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiac.2019.08.017.
Miller CR, Dey S, Smolenski PD, Kulkarni PS, Monk JM, Szubin R, et al. Distinct subpopulations of intravalvular methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with variable susceptibility to daptomycin in tricuspid valve endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64:1–7.
Rudasill SE, Sanaiha Y, Mardock AL, Khoury H, Xing H, Antonios JW, et al. Clinical outcomes of infective endocarditis in injection drug users. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73:559–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.10.082.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by a BlueSky research grant (n. 08072320).
Conflicts of interest
All authors: none to declare.
Ethics approval
All procedures in this study were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration (and its amendments). The study was approved by the local ethics committee (protocol number 20200006979).
Consent to participate
A written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Avaliability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
Conceptualization: ES, SDG ADS. Methodology: MDM. Validation: SDG, VM. Formal analysis: ADS. Investigation: AB, IG, MC, SB. Writing—original draft preparation: ES, SDG, RB. Writing—review and editing: RB. Supervision: ES.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Gregori, S., De Silvestri, A., Molinaro, M.D. et al. Daptomycin Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics in Patients on Methadone Substitution Therapy. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 46, 547–554 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-021-00690-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-021-00690-4