Abstract
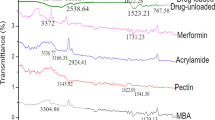
Cellulose acetate phthalate-based pH-responsive hydrogel was synthesized for fabrication of polymeric matrix tablets for gastro-protective delivery of loxoprofen sodium. Cellulose acetate phthalate (CAP) was cross-linked with methacrylic acid (MAA) using free radical polymerization technique. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra confirmed the formation of cross-linked structure of CAP-co-poly(methacrylic acid). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) confirmed the thermal stability of polymeric networks, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectrum (EDS) images unveiled that the prepared formulations were porous in nature and thus the developed formulations had shown better diffusibility. Swelling and in vitro drug release was performed at various pHs and maximum swelling and release was obtained at pH 7.4, while swelling and release rate was very low at pH 1.2 which confirmed the pH-responsive behavior of CAP-co-poly(MAA). CAP-co-poly(MAA) copolymer prevents the release of loxoprofen sodium into the stomach due to reduced swelling at gastric pH while showing significant swelling and drug release in the colon. Cytotoxicity studies revealed higher biocompatibility of fabricated hydrogel. Acute oral toxicity studies were performed for the evaluation and preliminary screening of safety profile of the developed hydrogels. Matrix tablets were evaluated for release behavior at simulated body pH. The investigations performed for analysis of hydrogels and fabricated matrix tablets indicated the controlled drug release and gastro-protective drug delivery of CAP-co-poly(MAA) hydrogels and pH-sensitive matrix tablets for targeted delivery of gastro-sensitive/irritative agents.

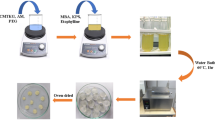
Graphical abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
11 April 2024
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-024-01600-2
References
Vane JR. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nature. 1971;231(25):232–5.
Misaka E, et al. Anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activities of sodium 2-[4-(2-oxocyclopentan-1-ylmethyl) phenyl] propionate dihydrate (CS-600). Pharmacometrics. 1981;21:753–71.
Collier DS, Pain J. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and peptic ulcer perforation. Gut. 1985;26(4):359–63. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.26.4.359.
Kaparissides, C., et al., Advanced drug delivery systems: new developments, new technologies. AzoM com Pvt L Ltd, 2006.
Caló E, Khutoryanskiy VV. Biomedical applications of hydrogels: a review of patents and commercial products. Eur Polym J. 2015;65:252–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.11.024.
Anwar H, Ahmad M, Minhas MU, Rehmani S. Alginate-polyvinyl alcohol based interpenetrating polymer network for prolonged drug therapy, optimization and in-vitro characterization. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;166:183–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.02.080.
Barkat K, et al. Oxaliplatin-loaded crosslinked polymeric network of chondroitin sulfate-co-poly (methacrylic acid) for colorectal cancer: its toxicological evaluation. J Appl Polym Sci.
Saboktakin MR, Tabatabaie R, Maharramov A, Ramazanov MA. Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic chitosan–dextran sulfate hydrogels as nano carriers for colon-specific drug delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 2010;81(2):372–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.02.034.
Mishra V, Jung SH, Park JM, Jeong HM, Lee Hi. Triazole-containing hydrogels for time-dependent sustained drug release. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2014;35(4):442–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.201300585.
Liu T-Y, Lin Y-L. Novel pH-sensitive chitosan-based hydrogel for encapsulating poorly water-soluble drugs. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(4):1423–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2009.10.010.
Yuan Q, Venkatasubramanian R, Hein S, Misra RDK. A stimulus-responsive magnetic nanoparticle drug carrier: magnetite encapsulated by chitosan-grafted-copolymer. Acta Biomater. 2008;4(4):1024–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2008.02.002.
Khalid I, Ahmad M, Usman Minhas M, Barkat K, Sohail M. Cross-linked sodium alginate-g-poly (acrylic acid) structure: a potential hydrogel network for controlled delivery of loxoprofen sodium. Adv Polym Technol. 2016; https://doi.org/10.1002/adv.21747.
Li J, Mooney DJ. Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat Rev Mater. 2016;1(12):16071. https://doi.org/10.1038/natrevmats.2016.71.
Fu C, et al. Injectable micellar supramolecular hydrogel for delivery of hydrophobic anticancer drugs. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27(4):1–7.
Williams RO III, Liu J. Influence of processing and curing conditions on beads coated with an aqueous dispersion of cellulose acetate phthalate. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2000;49(3):243–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0939-6411(00)00065-5.
Hua D, Liu Z, Wang F, Gao B, Chen F, Zhang Q, et al. pH responsive polyurethane (core) and cellulose acetate phthalate (shell) electrospun fibers for intravaginal drug delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;151:1240–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.06.066.
Minhas MU, et al. Synthesis of chemically cross-linked polyvinyl alcohol-co-poly (methacrylic acid) hydrogels by copolymerization; a potential graft-polymeric carrier for oral delivery of 5-fluorouracil. Daru. 2013;21(1):44. https://doi.org/10.1186/2008-2231-21-44.
Vermuë M, Sikkema J, Verheul A, Bakker R, Tramper J. Toxicity of homologous series of organic solvents for the gram-positive bacteria Arthrobacter and Nocardia Sp. and the gram-negative bacteria Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas Sp. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1993;42(6):747–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260420610.
Stacey N, Winder C. Toxicity of organic solvents. Occupational toxicology. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2004. p. 364–89.
Sohail M, Ahmad M, Minhas MU, Ali L, Khalid I, Rashid H. Controlled delivery of valsartan by cross-linked polymeric matrices: synthesis, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm. 2015;487(1):110–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.04.013.
Jalil A, Khan S, Naeem F, Haider MS, Sarwar S, Riaz A, et al. The structural, morphological and thermal properties of grafted pH-sensitive interpenetrating highly porous polymeric composites of sodium alginate/acrylic acid copolymers for controlled delivery of diclofenac potassium. Des Monomers Polym. 2017;20(1):308–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/15685551.2016.1259834.
Akhtar MF, Ranjha NM, Hanif M. Effect of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate on swelling and on metformin hydrochloride release behavior of chemically crosslinked pH–sensitive acrylic acid–polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel. DARU J Pharm Sci. 2015;23(1):1.
Minhas MU, et al. Synthesis of chemically cross-linked polyvinyl alcohol-co-poly (methacrylic acid) hydrogels by copolymerization; a potential graft-polymeric carrier for oral delivery of 5-fluorouracil. DARU J Pharm Sci. 2013;21(1):44. https://doi.org/10.1186/2008-2231-21-44.
Piburn, G. and A. Barron, An introduction to energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Physical methods in chemistry and nano science. Connexions/Rice University, Houston, 2013: p. 90–98.
Jaiswal M, Koul V. Assessment of multicomponent hydrogel scaffolds of poly (acrylic acid-2-hydroxy ethyl methacrylate)/gelatin for tissue engineering applications. J Biomater Appl. 2011:0885328211428524.
Wang K, Xu X, Wang YJ, Yan X, Guo G, Huang MJ, et al. Synthesis and characterization of poly (methoxyl ethylene glycol-caprolactone-co-methacrylic acid-co-poly (ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate) pH-sensitive hydrogel for delivery of dexamethasone. Int J Pharm. 2010;389(1):130–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.01.026.
Chaturvedi K, Kulkarni AR, Aminabhavi TM. Blend microspheres of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) and cellulose acetate phthalate for colon delivery of 5-fluorouracil. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2011;50(18):10414–23. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie2011005.
Huang S, Wang J, Shang Q. Development and evaluation of a novel polymeric hydrogel of sucrose acrylate-co-polymethylacrylic acid for oral curcumin delivery. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2017;28(2):194–206. https://doi.org/10.1080/09205063.2016.1262162.
Choi S-H, Kim SY, Ryoo JJ, Lee KP. Complexation of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug loxoprofen with modified and unmodified β-cyclodextrins. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 2001;40(1):139–46. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011175206514.
Zaman M, et al. Formulation and in-vitro evaluation of sustained release matrix tablets of cellulose based hydrophilic and hydrophobic polymers loaded with loxoprofen sodium Indo American. J Pharma Res. 2013;3:7389–98.
Wang W, Wang A. Synthesis and swelling properties of pH-sensitive semi-IPN superabsorbent hydrogels based on sodium alginate-g-poly (sodium acrylate) and polyvinylpyrrolidone. Carbohydr Polym. 2010;80(4):1028–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.01.020.
Yang C, Liu HZ, Fu ZX, Lu WD. Oxaliplatin long-circulating liposomes improved therapeutic index of colorectal carcinoma. BMC Biotechnol. 2011;11(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-11-21.
Samanta HS, Ray SK. Synthesis, characterization, swelling and drug release behavior of semi-interpenetrating network hydrogels of sodium alginate and polyacrylamide. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;99:666–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.09.004.
Hua S, Wang A. Synthesis, characterization and swelling behaviors of sodium alginate-g-poly (acrylic acid)/sodium humate superabsorbent. Carbohydr Polym. 2009;75(1):79–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.06.013.
Roxin P, Karlsson A, Singh SK. Characterization of cellulose acetate phthalate (CAP). Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1998;24(11):1025–41. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639049809089946.
Shi Y, Liu Z, Yang Y, Xu X, Li Y, Li T. Design of poly (mPEGMA-co-MAA) hydrogel-based mPEG-b-PCL nanoparticles for oral meloxicam delivery. Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;76:975–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.163.
DiNunzio JC, Miller DA, Yang W, McGinity JW, Williams RO. Amorphous compositions using concentration enhancing polymers for improved bioavailability of itraconazole. Mol Pharm. 2008;5(6):968–80. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp800042d.
Miller DA, DiNunzio JC, Yang W, McGinity JW, Williams RO III. Targeted intestinal delivery of supersaturated itraconazole for improved oral absorption. Pharm Res. 2008;25(6):1450–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-008-9543-1.
Rashid H, et al. Synthesis and characterization of poly (hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) cross linked polymeric network for the delivery of analgesic agent. J Chem Soc Pak. 2015;37(5)
Hashem M, Sharaf S, Abd el-Hady MM, Hebeish A. Synthesis and characterization of novel carboxymethylcellulose hydrogels and carboxymethylcellulolse-hydrogel-ZnO-nanocomposites. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;95(1):421–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.03.013.
Yadav DK, Patki PE. Effect of acetyl esterification on physicochemical properties of chick pea (Cicer arietinum L.) starch. J Food Sci Technol. 2015;52(7):4176–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1388-5.
Chang C, Duan B, Zhang L. Fabrication and characterization of novel macroporous cellulose–alginate hydrogels. Polymer. 2009;50(23):5467–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2009.06.001.
Zhang R, Tang M, Bowyer A, Eisenthal R, Hubble J. A novel pH-and ionic-strength-sensitive carboxy methyl dextran hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2005;26(22):4677–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.11.048.
Liu J, Lin S, Li L, Liu E. Release of theophylline from polymer blend hydrogels. Int J Pharm. 2005;298(1):117–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.04.006.
Higuchi T. Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J Pharm Sci. 1963;52(12):1145–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600521210.
Dash S, Murthy PN, Nath L, Chowdhury P. Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Pol Pharm. 2010;67(3):217–23.
Korsmeyer RW, Gurny R, Doelker E, Buri P, Peppas NA. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int J Pharm. 1983;15(1):25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5173(83)90064-9.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Higher Education Commission of Pakistan for the financial support through Project No. 21-487/SRGP/R&D/HEC/2015. This study became possible due to support of Higher Education Commission of Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail:https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-024-01600-2
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, S.A., Sohail, M., Minhas, M.U. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: pH-responsive CAP-co-poly(methacrylic acid)-based hydrogel as an efficient platform for controlled gastrointestinal delivery: fabrication, characterization, in vitro and in vivo toxicity evaluation. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. 9, 555–577 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-018-0486-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-018-0486-8