Abstract
As a painless and minimally invasive method of self-administration, microneedle is very promising to replace subcutaneous injection of insulin for type I diabetes treatment. Since the introduction of microneedles, many scholars have paid attention to and studied this technology, which has made it developed rapidly. However, there is no product on the market or in clinical trials at present. The reason is that there are still many technical problems in microneedle drug delivery system, such as the perfect integration of stable, controllable, fast, long-lasting, safe, and other necessary conditions. Here, we review the achievements that researchers have made that contain one or more of the above factors, and put some ideas to solve the limitations of insulin delivery by microneedles for reference.
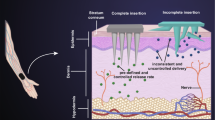
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Tuomi T, Santoro N, Caprio S, Cai M, Weng J, Groop L. The many faces of diabetes: a disease with increasing heterogeneity. Lancet. 2014;383(9922):1084–94.
Ng LC, Gupta M. Transdermal drug delivery systems in diabetes management: a review. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2020;15(1):13–25.
Guo X, Wang W. Challenges and recent advances in the subcutaneous delivery of insulin. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2017;14(6):727–34.
Caucanas M, Heureux F, Muller G, Vanhooteghem O. Atypical hypodermic necrosis secondary to insulin injection: a case report and review of the literature. J Diabetes. 2011;3(1):19–20.
Lee G, Ma Y, Lee Y-H, Jung H. Clinical Evaluation of a Low-pain Long Microneedle for Subcutaneous Insulin Injection. Biochip J. 2018;12(4):309–316.
Lee KJ, Jeong SS, Roh DH, Kim DY, Choi H-K, Lee EH. A practical guide to the development of microneedle systems - In clinical trials or on the market. Int J Pharm. 2020;573.
McAllister DV, Wang PM, Davis SP, Park JH, Canatella PJ, Allen MG, et al. Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecules and nanoparticles: fabrication methods and transport studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100(24):13755–60.
Zhang P, Zhang Y, Liu C-G. Polymeric nanoparticles based on carboxymethyl chitosan in combination with painless microneedle therapy systems for enhancing transdermal insulin delivery. RSC Adv. 2020;10(41):24319–29.
Zhao X, Coulman SA, Hanna SJ, Wong FS, Dayan CM, Birchall JC. Formulation of hydrophobic peptides for skin delivery via coated microneedles. J Control Release. 2017;265:2–13.
Resnik D, Mozek M, Pecar B, Janez A, Urbancic V, Iliescu C, Vrtacnik D. In Vivo Experimental Study of Noninvasive Insulin Microinjection through Hollow Si Microneedle Array. Micromachines. 2018;9(1).
Bolton CJW, Howells O, Blayney GJ, Eng PF, Birchall JC, Gualeni B, Roberts K, Ashraf H, Guy OJ. Hollow silicon microneedle fabrication using advanced plasma etch technologies for applications in transdermal drug delivery. Lab Chip. 2020;20(15):2788–95.
Fonseca DFS, Costa PC, Almeida IF, Dias-Pereira P, Correia-Sa I, Bastos V, et al. Pullulan microneedle patches for the efficient transdermal administration of insulin envisioning diabetes treatment. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;241.
Vora LK, Courtenay AJ, Tekko IA, Larraneta E, Donnelly RF. Pullulan-based dissolving microneedle arrays for enhanced transdermal delivery of small and large biomolecules. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;146:290–8.
Yang S, Wu F, Liu J, Fan G, Welsh W, Zhu H, et al. Phase-transition microneedle patches for efficient and accurate transdermal delivery of insulin. Adv Func Mater. 2015;25(29):4633–41.
Seong K-Y, Seo M-S, Hwang DY, O’Cearbhaill ED, Sreenan S, Karp JM, et al. A self-adherent, bullet-shaped microneedle patch for controlled transdermal delivery of insulin. J Control Release. 2017;265:48–56.
Kirkby M, Hutton ARJ, Donnelly RF. Microneedle mediated transdermal delivery of protein, peptide and antibody based therapeutics: current status and future considerations. Pharm Res. 2020;37(6).
Martanto W, Moore JS, Couse T, Prausnitz MR. Mechanism of fluid infusion during microneedle insertion and retraction. J Control Release. 2006;112(3):357–61.
Wang PM, Cornwell M, Hill J, Prausnitz MR. Precise microinjection into skin using hollow microneedles. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126(5):1080–7.
Norman JJ, Brown MR, Raviele NA, Prausnitz MR, Felner EI. Faster pharmacokinetics and increased patient acceptance of intradermal insulin delivery using a single hollow microneedle in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2013;14(6):459–65.
Carcamo-Martinez A, Mallon B, Dominguez-Robles J, Vora LK, Kurnia Anjani Q, Donnelly RF. Hollow microneedles: a perspective in biomedical applications. Int J Pharm. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120455,120455-120455.
Wang C, Ye Y, Sun W, Yu J, Wang J, Lawrence DS, et al. Red blood cells for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Adv Mater. 2017;29(18).
Yang R, Wu M, Lin S, Nargund RP, Li X, Kelly T, et al. A glucose-responsive insulin therapy protects animals against hypoglycemia. Jci Insight. 2018;3(1).
Yu J, Zhang Y, Ye Y, DiSanto R, Sun W, Ranson D, et al. Microneedle-array patches loaded with hypoxia-sensitive vesicles provide fast glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(27):8260–5.
Yu J, Qian C, Zhang Y, Cui Z, Zhu Y, Shen Q, et al. Hypoxia and H2O2 dual-sensitive vesicles for enhanced glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Nano Lett. 2017;17(2):733–9.
Xu B, Cao Q, Zhang Y, Yu W, Zhu J, Liu D, et al. Microneedles integrated with ZnO quantum-dot-capped mesoporous bioactive glasses for glucose-mediated insulin delivery. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(7):2473–83.
Yang H, Ma R, Yue J, Li C, Liu Y, An Y, et al. A facile strategy to fabricate glucose-responsive vesicles via a template of thermo-sensitive micelles. Polym Chem. 2015;6(20):3837–46.
Yu J, Wang J, Zhang Y, Chen G, Mao W, Ye Y, et al. Glucose-responsive insulin patch for the regulation of blood glucose in mice and minipigs. Nat Biomed Eng. 2020;4(5):499–506.
Kim SW. Self-regulated glycosylated insulin delivery. J Control Release. 1990;11:193–201.
Tiegs G, Hentschel J, Wendel A. A T cell-dependent experimental liver injury in mice inducible by concanavalin A. J Clin Investig. 1992;90(1):196–203.
Bankar SB, Bule MV, Singhal RS, Ananthanarayan L. Glucose oxidase - an overview. Biotechnol Adv. 2009;27(4):489–501.
Webber MJ, Anderson DG. Smart approaches to glucose-responsive drug delivery. J Drug Target. 2015;23(7–8):651–5.
Kuang DJ. Study on drug delivery of silk fibroin pH sensitive microneedles, Suzhou University. 2019.
Chen W, Tian R, Xu C, Yung BC, Wang G, Liu Y, et al. Microneedle-array patches loaded with dual mineralized protein/peptide particles for type 2 diabetes therapy. Nat Commun. 2017;8.
Chen M, Quan G, Sun Y, Yang D, Pan X, Wu C. Nanoparticles-encapsulated polymeric microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. J Control Release. 2020;325:163–75.
Chen X, Wang L, Yu H, Li C, Feng J, Haq F, et al. Preparation, properties and challenges of the microneedles-based insulin delivery system. J Control Release. 2018;288:173–88.
Chu LY, Choi S-O, Prausnitz MR. Fabrication of dissolving polymer microneedles for controlled drug encapsulation and delivery: bubble and pedestal microneedle designs. J Pharm Sci. 2010;99(10):4228–38.
Sullivan SP, Murthy N, Prausnitz MR. Minimally invasive protein delivery with rapidly dissolving polymer microneedles. Adv Mater. 2008;20(5):933-+.
Zhang Y, Yu J, Kahkoska AR, Wang J, Buse JB, Gu Z. Advances in transdermal insulin delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;139:51–70.
Gupta J, Gill HS, Andrews SN, Prausnitz MR. Kinetics of skin resealing after insertion of microneedles in human subjects. J Control Release. 2011;154(2):148–55.
Hu X, Yu J, Qian C, Lu Y, Kahkoska AR, Xie Z, et al. H2O2-responsive vesicles integrated with transcutaneous patches for glucose-mediated insulin delivery. ACS Nano. 2017;11(1):613–20.
Zhang Y, Wang J, Yu J, Wen D, Kahkoska AR, Lu Y, et al. Bioresponsive microneedles with a sheath structure for H2O2 and pH cascade-triggered insulin delivery. Small. 2018;14(14).
Aronoff S, Chen TC, Cheveldayoff M. Complexation of D-glucose with borate. Carbohydr Res. 1975;40:299–309.
Sauerborn M, Brinks V, Jiskoot W, Schellekens H. Immunological mechanism underlying the immune response to recombinant human protein therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2010;31(2):53–9.
Patel S, Jani P, Manseta P. Pharmaceutical approaches related to systemic delivery of protein and peptide drugs: an overview. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2012;12(1).
Zhu DD, Zhang XP, Shen CB, Cui Y, Guo XD. The maximum possible amount of drug in rapidly separating microneedles. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019;9(6):1133–42.
Kim S, Yang H, Eum J, Ma Y, Lahiji SF, Jung H. Implantable powder-carrying microneedles for transdermal delivery of high-dose insulin with enhanced activity. Biomaterials. 2020;232.
Zhu M, Liu Y, Jiang F, Cao J, Kundu SC, Lu S. Combined silk fibroin microneedles for insulin delivery. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(6):3422–9.
Chen S, Matsumoto H, Moro-oka Y, Tanaka M, Miyahara Y, Suganami T, et al. Microneedle-array patch fabricated with enzyme-free polymeric components capable of on-demand insulin delivery. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(7).
Prausnitz MR, Mikszta JA, Cormier M, Andrianov AK. Microneedle-based vaccines. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009;333:369–93.
Wang QL, Ren JW, Chen BZ, Jin X, Zhang CY, Guo XD. Effect of humidity on mechanical properties of dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. J Ind Eng Chem. 2018;59:251–8.
Serrano-Castaneda P, Juan Escobar-Chavez J, Marlen Rodriguez-Cruz I, Maria Melgoza-Contreras L, Martinez-Hernandez J. Microneedles as enhancer of drug absorption through the skin and applications in medicine and cosmetology. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2018;21:73–93.
Vicente-Perez EM, Larraneta E, McCrudden MTC, Kissenpfennig A, Hegarty S, McCarthy HO, et al. Repeat application of microneedles does not alter skin appearance or barrier function and causes no measurable disturbance of serum biomarkers of infection, inflammation or immunity in mice in vivo. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017;117:400–7.
Huang Q, Wang L, Yu H, Ur-Rahman K. Advances in phenylboronic acid-based closed-loop smart drug delivery system for diabetic therapy. J Control Release. 2019;305:50–64.
Ma R, Shi L. Phenylboronic acid-based glucose-responsive polymeric nanoparticles: synthesis and applications in drug delivery. Polym Chem. 2014;5(5):1503–18.
Huang C-M. Topical vaccination: the skin as a unique portal to adaptive immune responses. Semin Immunol. 2007;29(1):71–80.
Quinn HL, Bonham L, Hughes CM, Donnelly RF. Design of a dissolving microneedle platform for transdermal delivery of a fixed-dose combination of cardiovascular drugs. J Pharm Sci. 2015;104(10):3490–500.
McCrudden MTC, Alkilani AZ, McCrudden CM, McAlister E, McCarthy HO, Woolfson AD, et al. Design and physicochemical characterisation of novel dissolving polymeric microneedle arrays for transdermal delivery of high dose, low molecular weight drugs. J Control Release. 2014;180:71–80.
Wu W, Zhou S. Responsive materials for self-regulated insulin delivery. Macromol Biosci. 2013;13(11):1464–77.
Yu J, Zhang Y, Bomba H, Gu Z. Stimuli-responsive delivery of therapeutics for diabetes treatment. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine. 2016;1(3):323–37.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the support of Wuya College of Innovation of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qida Zong: collected important background information and drafted the manuscript. Ranran Guo and Naijun Dong: proofread and revised the contents of the manuscript. Guixia Ling and Peng Zhang: contributed to the conception of this study; helped with constructive discussions and performed manuscript review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
Shenyang Pharmaceutical University agrees to the submission of this paper to the journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zong, Q., Guo, R., Dong, N. et al. Design and development of insulin microneedles for diabetes treatment. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. 12, 973–980 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-021-00981-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-021-00981-y