Abstract
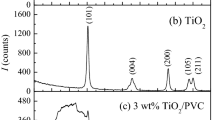
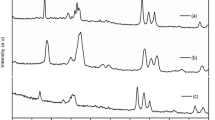
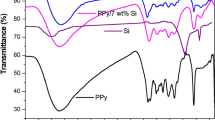
The electrorheological (ER) response of polypyrrole(PPy)-tin oxide nanocomposite ER fluids increased with the increase in the tin oxide/pyrrole weight ratio, particle volume fraction, and electric field strength. The dielectric properties and direct current (dc) conductivity of PPy-tin oxide nanocomposite particles and the dielectric properties of PPy-tin oxide nanocomposite ER fluids agreed with the ER behaviors. The ER behavior of PPy-tin oxide nanocomposite ER fluids was well fitted to τ = 0.0248ϕE 1.5 and showed a transition from that of the polarization model (τ ∼ E 2) to that of the conduction model (τ ∼ E 1.5) depending on the tin oxide/pyrrole weight ratio.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Block, H. and J.P. Kelly, 1988, Electro-rheology, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 21, 1661–1677.
Chae, H.S., W.L. Zhang, S.H. Piao, and H.J. Choi, 2015, Synthesized palygorskite/polyaniline nanocomposite particles by oxidative polymerization and their electrorheology, Appl. Clay Sci. 107, 165–172.
Filisko, F.E. and L.H. Razdilowski, 1990, An intrinsic mechanism for the activity of alumino-silicate based electrorheological materials, J. Rheol. 34, 539–552.
Flitton, R., J. Johal, S. Maeda, and S.P. Armes, 1995, Synthesis of colloidal dispersions of polypyrrole-silica nanocomposites using stringy silica particles, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 173, 135–142.
Gast, A.P. and C.F. Zukoski, 1989, Electroehological fluids as colloidal suspensions, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 30, 153–202.
Kim, M.W., I.J. Moon, H.J. Choi, and Y. Seo, 2016, Facile fabrication of core/shell structured SiO2/polypyrrole nanoparticles with surface modification and their electrorheology, RSC Adv. 6, 56495–56502.
Kim, Y.D. and D.J. Klingenberg, 1996, Two roles of nonionic surfactants on the electrorheological response, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 183, 568–578.
Kim, Y.D. and J.H. Kim, 2008, Synthesis of polypyrrole–polycaprolactone composites by emulsion polymerization and the electrorheological behavior of their suspensions, Colloid Polym. Sci. 286, 631–637.
Klingenberg, D.J., D. Dierking, and C.F. Zukoski, 1991, Stress transfer mechanism in electrorheological suspensions, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 87, 425–430.
Marshall, L., J.W. Goodwin, and C.F. Zukoski, 1989, Effect of electric fields on the rheology of nonaqueous concentrated suspensions, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 85, 2785–2795.
Noh, J., C.-M. Yoon, and J. Jang, 2016, Enhanced electrorheological activity of polyaniline coated mesoporous silica with high aspect ratio, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 470, 237–244.
Parthasarathy, M. and D.J. Klingenberg, 1996, Electrorheology: Mechanisms and models, Mater. Sci. Eng. R17, 57–103.
Shin, K., D. Kim, J.-C. Cho, H.-S. Lim, J.W. Kim, and K-D. Suh, 2012, Monodisperse conducting colloidal dipoles with symmetric dimer structure for enhancing electrorheology properties, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 374, 18–24.
Shulman, Z.P., R.G. Gorodkin, E.V. Korobko, and V.K. Gleb, 1981, The Electrorheological effects and its possible uses, J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 8, 29–41.
Su, S.J. and N. Kuramuto, 2000, Processable polyaniline–titanium dioxide nanocomposites: Effect of titanium dioxide on the conductivity, Synth. Met. 114, 147–153.
Weiss, K.D. and J.D. Carlson, 1993, Material aspects of electrorheological systems, J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 4, 13–34.
Winslow, W.M., 1949, Induced fibration of suspensions, J. Appl. Phys. 20, 1137–1140.
Wu, C.W. and H. Conrad, 1997, Dielectric and conduction effects in ohmic electrorheological fluids, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 30, 2634–2632.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y.D., Yoon, D.J. Electrorheological fluids of polypyrrole-tin oxide nanocomposite particles. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 28, 275–279 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-016-0029-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-016-0029-0