Abstract
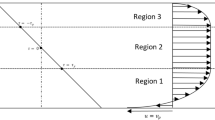
Magneto-Rheological (MR) fluid is a controllable material upon the applied magnetic field, and various MR dampers with different structures are designed to take advantage of this unique property. In the current paper, the squeeze mode MR damper is analyzed. The two-dimensional MR fluid squeeze flow in the damper is simulated using the Navier-Stokes’ equations. The shear stress of MR fluid is characterized by a non-convex constitutive relation, which is capable of capturing the solid-like to liquid-like switching. The two-dimensional velocity field and pressure distribution of MR fluid are obtained, from which the damping force of the MR damper is obtained. The unique hysteresis characteristic of the force versus velocity relation of the MR damper is captured. Further, the dependence on the loading rate and the field strength of the hysteresis characteristic is studied in the current paper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, J. and D.S. Kwon, 2003, Modeling of a magnetorheological actuator including magnetic hysteresis, J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 14, 541–550.
Cha, Y.J., J.Q. Zhang, A.K. Agrawal, B.P. Dong, A. Friedman, S.J. Dyke, and J. Ricles, 2013, Comparative studies of semi-active control strategies for MR dampers: Pure simulation and real-time hybrid tests, J. Struct. Eng. 139, 1237–1248.
Choi, K.M., H.J. Jung, S.W. Cho, and I.W. Lee, 2007, Application of smart passive damping system using MR damper to highway bridge structure, J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 21, 870–874.
Dominguez, A., R. Sedaghati, and I. Stiharu, 2004, Modelling the hysteresis phenomenon of magnetorheological dampers, Smart Mater Struct. 13, 1351–1361.
Felt, D.W., M. Hagenbuchle, J. Liu, and J. Richard, 1996, Rheology of a magnetorheological fluid, J. Intell. Mater Syst. Struct. 7, 589–593.
Gedik, E., H. Kurt, Z. Recebli, and C. Balan, 2012, Two-dimensional CFD simulation of magnetorheological fluid between two fixed parallel plates applied external magnetic field, Comput. Fluids 63, 128–134.
Guo, C.Y., X.L. Gong, S.H. Xuan, Q.F. Yan, and X.H. Ruan, 2013, Squeeze behavior of magnetorheological fluids under constant volume and uniform magnetic field, Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 045020.
Halsey, T.C., J.E. Martin, and D. Adolf, 1992, Rheology of electrorheological fluids, Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 1519–1522.
Hong, S.M., M.Y. Kim, D.J. Min, K.H. Lee, J.H. Shim, D.I. Kim, J.Y. Suh, W.S. Jung, and I.S. Choi, 2014, Unraveling the origin of strain-induced precipitation of M23C6 in the plastically deformed 347 austenite stainless steel, Mater. Charact. 94, 7–13.
Jin, F.Y., 2012, A study on the driving mechanisms of a magnetorheological servo-valve, Master’s thesis, Hangzhou Dianzi University
Jung, I.D., S.H. Kim, S.J. Park, S.J. Kim, T.G. Kang, and J.M. Park, 2014, Rheological modeling of strontium ferrite feedstock for magnetic powder injection molding, Powder Technol. 262, 198–202.
Kim, K.J., C.W. Lee, and J.H. Koo, 2008, Design and modeling of semi-active squeeze film dampers using magneto-rheological fluids, Smart Mater. Struct. 17, 035006.
Kim, S.H., S.J. Kim, S.J. Park, J.H. Mun, T.G. Kang, and J.M. Park, 2012, Rheological behavior of magnetic powder mixtures for magnetic PIM, Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 24, 121–127.
Kim, Y., R. Langari, and S. Hurlebaus, 2009, Semiactive nonlinear control of a building with a magnetorheological damper system, Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 23, 300–315.
Li, W.H., G.Z. Yao, G. Chen, S.H. Yeo, and F.F. Yap, 2000, Testing and steady state modeling of a linear MR damper under sinusoidal loading, Smart Mater. Struct. 9, 95–102.
Nguyen, T.M., C. Ciocanel, and M.H. Elahinia, 2012, A squeezeflow mode magnetorheological mount: Design, modeling, and experimental evaluation, J. Vib. and Acoust. 134, 021013.1–021013.11.
Nilsson, M. and N.G. Ohlson, 2000, An electrorheological fluid in squeeze mode, J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 11, 545–554.
Parlak, Z. and T. Engin, 2012, Time-dependent CFD and quasistatic analysis of magnetorheological fluid dampers with experimental validation, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 64, 22–31.
Prabakar, R.S., C. Sujatha, and S. Narayanan, 2009, Optimal semi-active preview control response of a half car vehicle model with magnetorheological damper, J. of Sound Vibr. 326, 400–420.
Spencer, B.F., S.J. Dyke, M.K. Sain, and J.D. Carlson, 1997, Phenomenological model for magnetorheological dampers, J. Eng. Mech. 123, 230–238.
de Vicente, J., D.J. Klingenberg, and R. Hidalgo-Alvarez, 2011, Magnetorheological fluids: A review, Soft Matter 7, 3701–3710.
Wang, L.X. and H. Kamath, 2006, Modelling hysteretic behaviour in magnetorheological fluids and dampers using phase-transition theory, Smart Mater. Struct. 15, 1725–1733.
Wang, X.J. and F. Gordaninejad, 2007, Flow analysis and modeling of field-controllable, electro- and magneto-rheological fluid dampers, J. Appl. Mech. 74, 13.
Zhang, C., Z.W. Chen, and L.X. Wang, 2015, An investigation on the field strength and loading rate dependences of the hysteretic dynamics of magnetorheological dampers, Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 19, 61–74.
Zhu, X.C., X.J. Jing, and L. Cheng, 2012, Magnetorheological fluid dampers: A review on structure design and analysis, J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 23, 839–873.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Ying, ZX. & Wang, LX. Simulation on hysteresis characteristic of squeeze mode magneto-rheological damper based on non-convex constitutive relation. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 33, 261–271 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-021-0020-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-021-0020-2