Abstract
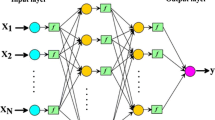
In the recent years, artificial intelligence techniques have been widely developed for modeling hydrologic processes. Determining the best structures of these models such as Wavelet-ANN and Wavelet-ANFIS still remains a difficult task. In fact, there are several factors in the structure of these models that should be optimized. Selecting the best model structure by testing all of the possible combinations of factors is very time consuming and labor intensive. Using the optimization Taguchi method, this study assessed different factors affecting the performance of Wavelet-ANN and Wavelet-ANFIS hybrid models each of which has several levels. A L18 orthogonal array was selected according to the selected factors and levels and experimental tests were performed accordingly. Analysis of the signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio was used to evaluate the models performance. The optimum structures for both models were determined. For Wavelet-ANN, a model having 14 neurons in the hidden layer and trained with 1,000 epochs using Tangent Sigmoid (TanSig) transfer function in both hidden and output layers, and trained with Levenberg–Marquardt (LM) algorithm, whose input data were decomposed using Reverse Bior 1.5 (rbio1.5) wavelet in level 2, is the optimal Wavelet-ANN model. For Wavelet-ANFIS, a model with 700 iterations, using bell-shaped membership function and 5 membership functions, whose input data were decomposed using Daubechies 4 (db4) wavelet in level 2, is the optimal Wavelet-ANFIS model. Confirmation tests were then conducted using the optimum structures. It is also concluded that the best Wavelet-ANFIS model outperforms the best Wavelet-ANN model.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prinos, S.T.; Lietz, A.C.; Irvin, R.B.: Design of a Real-Time Groundwater Level Monitoring Network and Portrayal of Hydrologic Data in Southern Florida. In: USGC Water Resources Investigations Report (2002)
Adamowski, J.; Chan, H.F.: A wavelet neural network conjunction model for groundwater level forecasting. J. Hydrol. 407(1–4), 28–40 (2011)
Kuo Y.-M., Liu C.-W., Lin K.-H.: Evaluation of the ability of an artificial neural network model to assess the variation of groundwater quality in an area of blackfoot disease in Taiwan. Water Res. 38(1), 148–158 (2004)
Aqil M., Kita I., Yano A., Nishiyama S.: Analysis and prediction of flow from local source in a river basin using a Neuro-fuzzy modeling tool. J. Environ. Manag. 85(1), 215–223 (2007)
Nayak, P.C.; Sudheer, K.P.; Rangan, D.M.; Ramasastri, K.S.: A neuro-fuzzy computing technique for modeling hydrological time series. J. Hydrol. 291(1–2), 52–66 (2004)
Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Coulibaly, P.; Tsanis, I.K.: Groundwater level forecasting using artificial neural networks. J. Hydrol. 309(1–4), 229–240 (2005)
Mohammadi, K.: Groundwater table estimation using MODFLOW and artificial neural networks, vol. 68(2). Water Science and Technology Library (2008)
Daubechies, I.: The wavelet transform, time-frequency localization and signal analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 36(5), 961–1005 (1990). doi:10.1109/18.57199
Loboda, N.S.; Glushkov, A.V.; Khokhlov, V.N.; Lovett, L.: Using non-decimated wavelet decomposition to analyse time variations of North Atlantic Oscillation, eddy kinetic energy, and Ukrainian precipitation. J. Hydrol. 322(1–4), 14–24 (2006)
Pasquini, A.I.; Depetris, P.J.: Discharge trends and flow dynamics of South American rivers draining the southern Atlantic seaboard: An overview. J. Hydrol. 333(2–4), 385–399 (2007)
Kisi, Ö.: Stream flow forecasting using neuro-wavelet technique. Hydrol. Process. 22(20), 4142–4152 (2008). doi:10.1002/hyp.7014
Kisi Ö.: Neural networks and wavelet conjunction model for intermittent streamflow forecasting. J. Hydrol. Eng. 14(8), 773–782 (2009)
Nourani V., Alami M.T., Aminfar M.H.: A combined neural-wavelet model for prediction of watershed precipitation, Lighvanchai, Iran. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 16, 1–12 (2009)
Nourani, V.; Kisi, Ö.; Komasi, M.: Two hybrid Artificial Intelligence approaches for modeling rainfall–runoff process. J. Hydrol. 402(1–2), 41–59 (2011)
Vafakhah, M.: Application of artificial neural networks and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system models to short-term streamflow forecasting. Can. J. Civil Eng. 39(4), 402–414 (2012). doi:10.1139/l2012-011
Eslamian, S.S.; Gohari, S.A.; Zareian M.J.; Firoozfar, A.: Estimating Penman–Monteith reference evapotranspiration using artificial neural networks and genetic algorithm: A case study. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 37(4), 935–944 (2012)
Rakhshandehroo, G.A.; Vaghefi, M.; Asadi Aghbolaghi, M.: Forecasting groundwater level in shiraz plain using artificial neural networks. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 37(5), 254–267 (2012)
Taguchi, G.: Introduction to Quality Engineering. McGraw-Hill, New York (1990)
Ross, P.J.: Taguchi techniques for quality engineering, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York (1988)
Chou C.-S., Ho C.-Y., Huang C.-I.: The optimum conditions for comminution of magnetic particles driven by a rotating magnetic field using the Taguchi method. Adv. Powder Technol. 20(1), 55–61 (2009)
Chou, C.-S.; Yang, R.-Y.; Chen, J.-H.; Chou, S.-W.: The optimum conditions for preparing the lead-free piezoelectric ceramic of Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3 using the Taguchi method. Powder Technol. 199(3), 264–271 (2010)
Wang T.-Y., Huang C.-Y.: Improving forecasting performance by employing the Taguchi method. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 176(2), 1052–1065 (2007)
Singaravelu, J.; Jeyakumar, D.; Nageswara Rao, B.: Taguchi’s approach for reliability and safety assessments in the stage separation process of a multistage launch vehicle. Reliab. Eng. Sys. Saf. 94(10), 1526–1541 (2009)
Oztop M.H., Sahin S., Sumnu G.: Optimization of microwave frying of potato slices by using Taguchi technique. J. Food Eng. 79(1), 83–91 (2007)
Al-Darrab I.A., Khan Z.A., Zytoon M.A., Ishrat S.I.: Application of the Taguchi method for optimization of parameters to maximize text message entering performance of mobile phone users. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 26, 469–479 (2009)
Dingal, S.; Pradhan, T.; Sundar, J.; Choudhury, A.; Roy, S.: The application of Taguchi’s method in the experimental investigation of the laser sintering process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 38(9), 904–914 (2008) doi:10.1007/s00170-007-1154-1
Aber, S.; Salari, D.; Parsa, M.R.: Employing the Taguchi method to obtain the optimum conditions of coagulation–flocculation process in tannery wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 162(1), 127–134 (2010)
Zolfaghari, G.; Esmaili-Sari, A.; Anbia, M.; Younesi, H.; Amirmahmoodi, S.; Ghafari-Nazari, A.: Taguchi optimization approach for Pb(II) and Hg(II) removal from aqueous solutions using modified mesoporous carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 192(3), 1046–1055 (2011)
Palanikumar, K.; Prakash, S.; Shanmugam, K.: Evaluation of delamination in drilling GFRP composites. Mater. Manuf. Process. 23(8), 858–864 (2008) doi:10.1080/10426910802385026
Hasçalı k, A.; Çaydaş, U.: Optimization of turning parameters for surface roughness and tool life based on the Taguchi method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 38(9), 896–903 (2008). doi:10.1007/s00170-007-1147-0
Rosa J.L., Robin A., Silva M.B., Baldan C.A., Peres M.P.: Electrodeposition of copper on titanium wires: Taguchi experimental design approach. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209(3), 1181–1188 (2009)
Türkmen, I.; Gül, R.; Çelik, C.: A Taguchi approach for investigation of some physical properties of concrete produced from mineral admixtures. Build. Environ. 43(6), 1127–1137 (2008)
Chang, K.-Y.; Lin, H.-J.; Chen, P.-C.: The optimal performance estimation for an unknown PEMFC based on the Taguchi method and a generic numerical PEMFC model. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 34(4), 1990–1998 (2009)
Zeng, M.; Tang, L.H.; Lin, M.; Wang, Q.W.: Optimization of heat exchangers with vortex-generator fin by Taguchi method. Appl. Thermal Eng. 30(13), 1775–1783 (2010)
Lakshminarayanan A.K., Balasubramanian V.: Process parameters optimization for friction stir welding of RDE-40 aluminum alloy using Taguchi technique. Chin. J. Nonferrous Metals 18, 548–554 (2008)
Yasuri, M.: The study of regional GIS of Mashhad (in Persian). Research plan of Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, p. 159 (2006)
See L., Openshaw S.: Applying soft computing approaches to river level forecasting. Hydrol. Sci. J. 44, 763–777 (1999)
Jang, J.S.R.; Sun, C.T.; Mizutani, E.: Neuro-fuzzy and soft computing: A computational approach to learning and machine intelligence. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ (1997)
Partal, T.: River flow forecasting using different artificial neural network algorithms and wavelet transform. Can. J. Civil Eng. 36(1), 26–38 (2009). doi:10.1139/l08-090
Christopoulou, E.B.; Skodras, A.N.; Georgakilas, A.A.: The “a trous” nvantelet transform versus clasical methods for the improvement of solar images. In: 14th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, 2002. DSP 2002, pp. 885–888 (2002)
Haykin, S.: Neural Networks, A Comprehensive Foundation, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.; (1999)
Madić M.J., Radovanović M.R.: Optimal selection of ANN training and architectural parameters using Taguchi method: A case study. FME Trans. 39(2), 79–86 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moosavi, V., Vafakhah, M., Shirmohammadi, B. et al. Optimization of Wavelet-ANFIS and Wavelet-ANN Hybrid Models by Taguchi Method for Groundwater Level Forecasting. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 1785–1796 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0762-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0762-3