Abstract
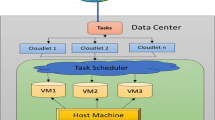
Effective resource distribution to regulate load uniformly in heterogeneous cloud environments is crucial. Resource allotment which is taken after capable task scheduling is a critical worry in cloud environment. The incoming job requests are assigned to resources equally by load balancer in such a way that resources are utilized effectively. Number of cloud clients is very great in number, degree of approaching job requests is uninformed and information is tremendous in cloud application. Resources in cloud environment are constrained. Hence, it is not easy to deploy different applications with unpredictable limits and functionalities in heterogeneous cloud environment. The proposed method has two phases such as allocation of resources and scheduling of tasks. Effective resource allocation is proposed using social group optimization algorithm and scheduling of tasks using shortest-job-first scheduling algorithm for minimizing the makespan time and maximizing throughput. Experimentations are performed for accurate simulations on artificial data for heterogeneous cloud environment. Experimental results are compared with first-in, first-out and genetic algorithm-based shortest-job-first scheduling. Validity of the proposed method noticeably gives improved performance of the system in provisions of makespan time and throughput.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broberg, J.; Venugopal, S.; Buyya, R.: Market-oriented grids and utility computing: the state-of-the-art and future directions. J. Grid Comput. 6(3), 255–276 (2008)
Buyya, R.; Chee, S.Y.; Venugopal, S.; Roberg, J.; Brandic, I.: Cloud computing and emerging IT platforms: vision, hype, and reality for delivering computing as the 5th utility. Future Gener Comput Syst 25(6), 599–616 (2009)
Dahbur, K; Mohammad, B; Tarakji, A.B.: A survey of risks, threats and vulnerabilities in cloud computing. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Intelligent Semantic Web-Services and Applications, p. 12. ACM (2011)
Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.: Testore: exploiting thermal and energy storage to cut the electricity bill for datacenter cooling. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Network and Service Management, pp. 19–27. International Federation for Information Processing (2012)
Mitzenmacher, M.: The power of two choices in randomized load balancing. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 12(10), 1094–1104 (2001)
Pinheiro, E.; Bianchini, R.; Carrera, E.V.; Heath, T.: Load balancing and unbalancing for power and performance in cluster-based systems. In: Workshop on Compilers and Operating Systems for Low Power, vol. 180, pp. 182–195. Barcelona, Spain (2001)
Dean, J.; Ghemawat, S.: Mapreduce: simplified data processing on large clusters. Commun. ACM 51(1), 107–113 (2008)
Hindman, B.; Konwinski, A.; Zaharia, M.; Ghodsi, A.; Joseph, A.D.; Katz, R.H; Shenker, S.; Stoica, I.: Mesos: a platform for fine-grained resource sharing in the data center. In: NSDI, vol. 11, pp. 22–22 (2011)
Satapathy, S.; Naik, A.: Social group optimization (sgo): a new population evolutionary optimization technique. Complex Intell. Syst. 2(3), 173–203 (2016)
Panda, S.K.; Jana, P.K.: A multi-objective task scheduling algorithm for heterogeneous multi-cloud environment. In: 2015 International Conference on Electronic Design Computer Networks & Automated Verification (EDCAV), pp. 82–87. IEEE (2015)
Panda, S.K.; Jana, P.K.: An efficient energy saving task consolidation algorithm for cloud computing systems. In: 2014 International Conference on Parallel Distributed and Grid Computing (PDGC), pp. 262–267. IEEE (2014)
Jena, T.; Mohanty, J.R.; Sahoo, R.: Paradigm shift to green cloud computing. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 77(3), 394–402 (2015)
Jena, T.; Mohanty, J.R.: Disaster recovery services in intercloud using genetic algorithm load balancer. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 6(4), 1 (2016)
Jena, T.; Mohanty, J.R.: Cloud security and jurisdiction: need of the hour. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Frontiers in Intelligent Computing: Theory and Applications, pp. 425–433. Springer (2017)
Katyal, M.; Mishra, A.: A comparative study of load balancing algorithms in cloud computing environment. arXiv preprint arXiv:1403.6918 (2014)
Kumar, V.; Grama, A.Y.; Vempaty, N.R.: Scalable load balancing techniques for parallel computers. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 22(1), 6079 (1994)
Buyya, R.; Ranjan, R.; Calheiros, R.N.: InterCloud: Utility-Oriented Federation of Cloud Computing Environments for Scaling of Application Services, pp. 13–31. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Dasgupta, K.; Mandal, B.; Dutta, P.; Mandal, J.K.; Dam, S.: A genetic algorithm (ga) based load balancing strategy for cloud com-puting. Procedia Technol. 10, 340–347 (2013)
Panda, S.K.; Jana, P.K.: Efficient task scheduling algorithms for het- erogeneous multi-cloud environment. J. Supercomput. 71(4), 1505–1533 (2015)
Wang, T.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Dai, X.: Load balancing task scheduling based on genetic algorithm in cloud computing. In: 2014 IEEE 12th International Conference on Dependable Autonomic and Secure Computing (DASC), pp. 146–152. IEEE (2014)
Chen, S.; Wu, J.; Lu, Z.: A cloud computing resource scheduling policy based on genetic algorithm with multiple fitness. In: 2012 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (CIT), pp. 177–184. IEEE (2012)
Hou, E.S.H.; Ansari, N.; Ren, H.: A genetic algorithm for multiprocessor scheduling. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 5(2), 113–120 (1994)
Randles, M.; Lamb, D.; Taleb-Bendiab, A.: A comparative study into distributed load balancing algorithms for cloud computing. In: 2010 IEEE 24th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops (WAINA), pp. 551–556. IEEE (2010)
Maguluri, S.T.; Srikant, R.; Ying, L.: Stochastic models of load balancing and scheduling in cloud computing clusters. In: INFOCOM, 2012 Proceedings IEEE, pp. 702–710. IEEE (2012)
Li, J.; Qiu, M.; Ming, Z.; Quan, G.; Qin, Xiao; Zonghua, Gu: Online optimization for scheduling preemptable tasks on IaaS cloud systems. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 72(5), 666–677 (2012)
Tejaswi, T.T.; Azharuddin, M.; Jana, P.K.: A ga based approach for task scheduling in multi-cloud environment. CoRR, abs/1511.08707 (2015)
Xiao, Z.; Song, W.; Chen, Q.: Dynamic resource allocation using virtual machines for cloud computing environment. Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 24(6), 1107–1117 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Praveen, S.P., Rao, K.T. & Janakiramaiah, B. Effective Allocation of Resources and Task Scheduling in Cloud Environment using Social Group Optimization. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 4265–4272 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2926-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2926-z