Abstract
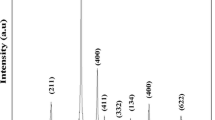
Nano crystalline erbium oxide (Er2O3) was synthesized in the laboratory through sol-gel method. The effect of different annealing temperatures on the crystal structure has been studied using x-ray diffraction (XRD). The comparison of the specific surface area (s); calculated using Brunauer, Emmett & Teller theory and (XRD) results, was made and found in agreement with an approximate error of 7%. The morphology of the samples has been studied using scanning electron microscope (SEM) and particles are found having a spherical morphology. Elemental analysis of the erbium oxide was also carried using energy dispersive spectrum (EDS) of the synthesized samples. Fourier transform infrared spectrum (FTIR) of the prepared samples showed the characteristic peaks for Er2O3. The dielectric properties of Er2O3 were also studied in the wide range of frequency (100 Hz - 5MHz). The activation energy for erbium oxide was found to be between 0.5–0.8 eV in the temperature range of 373 K–573 K. Hall effect measurements were done on the synthesized erbium oxide and it was found that erbium oxide can have useful applications in the Hall effect sensors (HES).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Mohammadi, J. Badraghi, A. B. Moghaddam, Y. Ganjkhanlou, M. Kazemzad, S. Hosseini, and R. Dinarvand, Chem. Eng. Technol. 34, 56 (2011).
W. Cai, T. Gao, H. Hong, and J. Sun, Nanotechnology, Sci. and App. 1, 17 (2008)
Ratyakshi, R. P. Chauhan, Asian J. Chem. 21, 113 (2009)
H. A. I. Y. Tok, L. T. Su, F. Y. C. Boey, and S. H. Ng, J. Electroceramics 17, 75 (2006).
S. Sato, R. Takahashi, M. Kobune, and H. Gotoh, Applied Catalysis A: General 356, 57 (2009).
Y. Zhao, Materials 5, 1413 (2012).
L. Wilkinson, M. Maqbool, and I. Ahmad, BAPS Bulletin of American Physical Society, p. 8, College Park, MD, USA (2010).
M. Fanciulli and G. Scarel, Rare Earth Oxide Thin Films Growth, Characterization, and Applications, p. 331, Springer, Newyork (2007).
Y. Takai, T. Maeda, and T. Tsukatani, Thermal Spray Rare Earth Oxide Particles, Sprayed Components, and Corrosion Resistant Components, http://www. Y. Takai, T. Maeda, T. Tsukatani — US Patent 6,767,636, 2004 - Google Patents (2004).
M. P. A. Neuman, R. Roemero, K. J. McClellen, and J. J. Petrovic, Fabrication and Properties of Erbium Oxide, p. 33, John Wiley and Sons. Inc., Newyork (2008).
L. Xinlian, W. Ping, Q. Hong, C. Sen, and S. Binbin, Thin Solid Films 520, 2316 (2012).
A. Kelly and N. H. Macmillan, Monographs on the Physics and Chemistry of Materials, Strong Solids, p. 180, Clarendon Press, New York, NY (1986).
K. M. Hubbard and B. F. Espinozo, Thin Solid Films 366, 175 (2000).
B. A. Pint, P. F. Tortorelli, A. Jankowskim J. Hayes, T. Muroga, A. Suzuki, O. I. Yeliseyeva, and V. M. Chernov, J. Nucl. Mater. 119, 329 (2004).
A. Sawada, A. Suzuki, H. Maier, F. Koch, T. Terai, and T. Muroga, Fusion Eng. Des. 737, 75 (2005).
F. Koch, R. Brill, H. Maier, D. Levchuk, A. Suzuki, T. Muroga, and H. Bolt, J. Nucl. Mater. 1403, 329 (2004).
D. Levchuk, S. Levchuk, H. Maier, H. Bolt, and A. Suzuki, J. Nucl. Mater. 1033, 367 (2007).
C. Zhao, C. Z. Zhao, M. Werner, S. Taylor, and P. R. Chalker, ISRNNtech 2012, 1 (2012).
C. H. Kao, H. Pan, Y. T. Chiu, J. S. Lu, and T. Chang, Solid State Communications 152, 504 (2012).
A. Bakhsh and A. Maqsood, Electron. Mater. Lett. 8, 605 (2012).
X. Chen, C. Wang, X. R. Hu, K. Stahl, and J. Jiang, Nanotechnology 22, 295708 (2011).
J. Jankowski, S. E. Ahmar, and M. Oszwaldowski, Sensors 11, 876 (2011).
M. Lequitte and D. Autissier, NanoStructured Materials 6, 333 (1955).
W. M. Keely, Anal. Chem. 38, 147 (1996).
X. Dong and G. Hong, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 21, 555 (2005).
E. H. Hall, Am. J. Mathematics 2, 287 (1879).
C. Kittel, Introduction to Solid State Physics, p. 155, John Wiley and Sons Inc., Newyork (1976).
R. Hosseini and A. Kashaninia, World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology 15, 431 (2008).
K. Singh, V. K. Singh, and B. C. Yadav, Int. J. Chem. and Anal. Sci. 2, 136 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azad, F., Maqsood, A. Fabrication, structural characterization, dielectric and electrical parameters of the synthesized nano-crystalline erbium oxide. Electron. Mater. Lett. 10, 557–563 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-013-3195-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-013-3195-y