Abstract
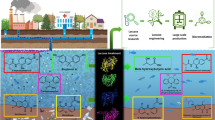
This study reports a potential biotechnical method of 17-β-estradiol removal in aquatic systems. The different bacterial strains isolated from sewage water samples were Bacillus sp., Enterobacter sp. I, Enterobacter sp. II, Klebsiella sp., Aeromonas veronii and Aeromonas punctate. These isolates were characterized on the basis of a single PCR reaction from the 5′ end of the PCR fragment to obtain > 700 bp of high-quality sequence. The adjoining lineages of each organism were obtained by BLAST searches. The identified bacterial species were incubated in a saline media under different concentrations of 17-β-estradiol in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The concentrations of CO2 and 17-β-estradiol were measured by GC and HPLC, respectively. The percentage degradations of 17-β-estradiol in aerobic and anaerobic conditions were 100 and 91.56%, respectively, using Klebsiella and Bacillus species. The developed and reported method is an inexpensive, selective and economic. This method may be used to remove 17-β-estradiol in any water resource.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboul-Enein HY, Ali I (2000) Macrocyclic antibiotics as effective chiral selectors for enantiomeric resolution by liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Chromatographia 52:679–691
Aboul-Enein HY, Ali I (2002) Comparative study of the enantiomeric resolution of chiral antifungal drugs econazole, miconazole and sulconazole by HPLC on various cellulose chiral columns in normal phase mode. J Pharm Biomed Anal 27:441–446
Adeel M, Song X, Wang Y, Francis D, Yang Y (2017) Environmental impact of estrogens on human, animal and plant life: a critical review. Environ Int 99:107–119
Adler P, Steger-Hartmann T, Kalbfus W (2001) Distribution of natural and synthetic estrogenic steroid hormones in water samples from Southern and Middle Germany. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 29:227–241
Afifi R, Elnwishy N, Hannora A, Hedstrom M, Mattiasson B, Omran H, Ali I (2016) SPE and HPLC monitoring of 17-β-estradiol in Egyptian aquatic ecosystems. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 39(8):428–434
Ali I (2010) The quest for active carbon adsorbent substitutes: inexpensive adsorbents for toxic metal ions removal from wastewater. Sep Purf Rev 39:95–171
Ali I, Aboul-Enein HY (2003) Enantioseparation of some clinically used drugs by HPLC using cellulose Tris(3,5-dichlorophenylcarbamate) chiral stationary phase. Biomed Chromatogr 17:113–117
Ali I, Naim L, Ghanem A, Aboul-Enein HY (2006a) Chiral separations of piperidine-2,6-dione analogues on Chiralpak IA and Chiralpak IB columns by using HPLC. Talanta 69:1013–1017
Ali I, Kumerer K, Aboul-Enein HY (2006b) Mechanistic principles in chiral separations using liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Chromatographia 63:295–307
Ali I, Aboul-Enein HY, Gupta VK (2009) Nanochromatography and nanocapillary electrophoresis: pharmaceutical and environmental analyses. Wiley, New York
Ali I, Aboul-Enein HY, Kümmerer K (2011) Analyses of drugs and pharmaceuticals in the environment, In biophysico-chemical processes of anthropogenic organic compounds in environmental systems. In: Xing B, Senesi N, Huang PM (eds) IUPAC sponsored book series. Wiley, New York, pp 439–462
Ali I, Khan TA, Asim M (2012) Removal of arsenate from groundwater by electrocoagulation method. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1668–1676
Ali I, Asim M, Khan TA (2013) Arsenite removal from water by electro-coagulation on zinc–zinc and copper–copper electrodes. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10:377–384
Ali I, Alotham ZA, Alwarthan A, Asim M, Khan TA (2014) Removal of arsenic species from water by batch and column operations on bagasse fly ash. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:3218–3229
Ali I, Alotham ZA, Alwarthan A (2015) Green synthesis of iron nano-impregnated adsorbent for fast removal of fluoride from water. J Mol Liq 211:457–465
Ali I, Alotham ZA, Alwarthan A (2016a) Synthesis of composite iron nano adsorbent and removal of ibuprofen drug residue from water. J Mol Liq 219:858–864
Ali I, Alotham ZA, Alwarthan A (2016b) Molecular uptake of congo red dye from water on iron composite nano particles. J Mol Liq 219:171–176
Ali I, Alotham ZA, Alwarthan A (2016c) Green synthesis of functionalized iron nano particles and molecular liquid phase adsorption of ametryn from water. J Mol Liq 211:1168–1174
Ali I, Alotham ZA, Alwarthan A (2016d) Uptake of pantoprazole drug residue from water using novel synthesized composite iron nano adsorbent. J Mol Liq 218:465–472
Ali I, Alotham ZA, Alwarthan A (2016e) Sorption, kinetics and thermodynamics studies of atrazine herbicide removal from water using iron nano-composite material. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10:733–742
Ali I, Alotham ZA, Alwarthan A (2017a) Uptake of propranolol on ionic liquid iron nanocomposite adsorbent: kinetic, thermodynamics and mechanism of adsorption. J Mol Liq 236:205–213
Ali I, Alothman ZA, Alwarthan A (2017b) Supra molecular mechanism of the removal of 17-β-estradiol endocrine disturbing pollutant from water on functionalized iron nano particles. J Mol Liq 441:123–129
Andersen HR, Siegrist H, Halling-Sørensen B, Ternes T (2003) Fate of estrogens in a municipal sewage treatment plant. Environ Sci Technol 37:4021–4026
Andrea W, Josef M, Thomas T (2003) Study on endocrine distupters in drinking water. Final Report ENV.D.1/ETU/2000/0083 Schmallenberg and Wiesbaden, February 26
Ansari FA, Khatoon H (1997) Curing of R plasmids present in gram negative bacteria isolated from poultry in Karachi by ethidium bromide. Pak J Pharm Sci 10:13–16
Burton JL, Wells M (2002) The effect of phytoestrogens on the female genital tract. J Clin Pathol 55:401–407
Caldwell DJ, Mastrocco F, Nowak E, Johnston J, Yekel H, Pfeiffer D, Hoyt M, DuPlessie BM, Anderson PD (2009) An assessment of potential exposure and risk from estrogens in drinking water. Environ Health Perspect 118:338–344
Cook JW, Dodds EC, Hewett CL, Lawson W (1934) The oestrogenic activity of some condensed-ring compounds in relation to their biological activities. Proc R Soc Lond 114:272–286
Fernández L, Louvado A, Esteves VI, Gomes NCM, Almeida A, Cunha  (2017) Biodegradation of 17β-estradiol by bacteria isolated from deep sea sediments in aerobic and anaerobic media. J Hazard Mater 323:359–366
Fujii K, Kikuchi S, Satomi M, Ushio-Sata N, Morita N (2002) Degradation of 17β-estradiol by a gram-negative bacterium isolated from activated sludge in a sewage treatment plant in Tokyo, Japan. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(4):2057–2060
Geize R, Dijkhuizen L (2004) Harnessing the catabolic diversity of rhodococci for environmental and biotechnological applications. Curr Opin Microbiol 7(3):255–261
Hansen PD, Hock HDB, Sherry AMJ, Blaise MMC (1998) A biomarker for endocrine disruptors. Trends Anal Chem 17:448–451
Jahnke GD, Choksi NY, Moore JA, Shelby MD (2003) Thyroid toxicants: assessing reproductive health effects. Environ Health Perspect 112:363–368
Jiang L, Yang J, Chen J (2010) Isolation and characteristics of 17β-estradiol-degrading Bacillus spp. strains from activated sludge. Biodegradation 21(5):729–736
Khanal SK, Xie B, Thompson ML, Sung S, Ong SK, Leeuwent VJ (2007) Fate, transport, and biodegradation of natural estrogens in the environment and engineered systems. Environ Sci Technol 8:6537–6546
Koh YKK, Chiu TY, Boobis A, Cartmell E, Scrimshaw MD, Lester JN (2008) Treatment and removal strategies from wastewater. Environ Technol 29:245–267
Laurenson JP, Bloom RA, Page S, Sadrieh N (2014) Ethinyl estradiol and other human pharmaceutical estrogens in the aquatic environment: a review of recent risk assessment data. AAPS J 16(2):299–310
Le Noir M, Lepeuple AS, Guieysse B, Mattiasson B (2007) Selective removal of 17[beta]-estradiol at trace concentration using a molecularly imprinted polymer. Water Res 41:2825–2831
Lee H, Liu D (2002) Degradation of 17β-estradiol and its metabolites by sewage bacteria. Water Air Soil Pollut 134:353–368
Li S, Liu J, Sun M, Ling W, Zhu X (2017) Isolation, characterization, and degradation performance of the 17β-estradiol-degrading bacterium Novosphingobium sp. E2S. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:115
Li M, Zhao X, Zhang X, Wu D, Leng S (2018) Biodegradation of 17β-estradiol by bacterial co-culture isolated from manure. Sci Rep 8(1):3787
Liu D, Strachan WM, Thomson K, Kwasniewska K (1981) Determination of the biodegradability of organic compounds. Environ Sci Technol 15(7):788–793
Ng KP, Datuin JP, Bern HA (2001) Effects of estrogens in vitro and in vivo on cartilage growth in the Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Gen Comparat Endocrinol 121:295–304
Parawira W, Read JS, Mattiasson B, Björnsson L (2008) Energy production from agricultural residues: high methane yields in pilot-scale two-stage anaerobic digestion. Biomass Bioenergy 32:44–50
Pauwels B, Wille K, Noppe H, De Brabander H, Van de Wiele T, Verstraete W, Boon N (2008) 17α-Ethinylestradiol cometabolism by bacteria degrading estrone, 17β-estradiol and estriol. Biodegradation 19(5):683–693
Ra JS, Lee SH, Lee J, Kim HY, Lim BJ, Kim SH, Kim SD (2011) Occurrence of estrogenic chemicals in South Korean surface waters and municipal wastewaters. J Environ Monit 13:101–109
Ryan KJ (1982) Biochemistry of aromatase: significance to female reproductive physiology. Cancer Res 42:3342–3344
Sambrook J, Fritschi EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Shi J, Fujisawa S, Nakai S, Hosomi M (2004) Biodegradation of natural and synthetic estrogens by nitrifying activated sludge and ammonia-oxidizing bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea. Water Res 38(9):2323–2330
Singer RS, Cooke CL, Maddox CW, Isaacson RE, Wallace RL (2006) Use of pooled samples for the detection of salmonella in feces by polymerase chain reaction. J Veter Diag Invest 18:319–325
Straus D, Ausubel FM (1990) Genomic subtraction for cloning DNA corresponding to deletion mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci 87:1889–1893
Tawfic M (2006) Persistent organic pollutants in Egyrpt: an overview. In: Twardowska I, Allen HE, Häggblom MM, Stefaniak S (eds) Soil and water pollution monitoring, protection and remediation. Springer, Berlin, pp 25–38
Tikko A, Tripathi AK, Verma SC, Agrawal N, Nath G (2001) Application of PCR fingerprinting techniques for identification and discrimination of salmonella isolates. Cur Sci 80:1049–1052
Weber S, Leuschner P, Kämpfer P, Dott W, Hollender J (2005) Degradation of estradiol and ethinyl estradiol by activated sludge and by a defined mixed culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67(1):106–112
WHO (2009) Department of reproductive health and research, World health organization, CH-1211 Geneva, Switzerland. Commentary/Contraception 80:325–326
Woźniak B, Kłopot A, Matraszek-Żuchowska I, Sielska K, Żmudzki J (2014) Determination of natural and synthetic oestrogens in surface water using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 58(4):603–611
Xu P, Zhaaou X, Xu D, Xiang Y, Ling W, Chen M (2018) Contamination and risk assessment of estrogens in livestock manure: a case study in Jiangsu Province, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(1):125
Yaghjyan L, Colditz GA (2011) Estrogens in the breast tissue: a systematic review. Can Causes Control 22:529–540
Yoshimoto T, Nagai F, Fujimoto J, Watanabe K, Mizukoshi H, Makino T, Kimura K, Saino H, Sawada H, Omura H (2004) Degradation of estrogens by Rhodococcus zopfii and Rhodococcus equi isolates from activated sludge in wastewater treatment plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(9):5283–5289
Yu CP, Roh H, Chu KH (2007) 17β-Estradiol-degrading bacteria isolated from activated sludge. Environ Sci Technol 41(2):486–492
Yu CP, Deeb AA, Chu KH (2013a) Microbial degradation of steroidal estrogens. Chemosphere 91:1225–1235
Yu CP, Deeb RA, Chu KH (2013b) Microbial degradation of steroidal estrogens. Chemosphere 91(9):1225–1235
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibilty: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khattab, R.A., Elnwishy, N., Hannora, A. et al. Biodegradation of 17-β-estradiol in water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 4935–4944 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1929-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1929-y