Abstract
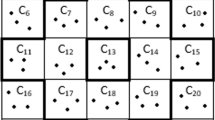
Security of wireless sensor networks is a major issue to protect sensor nodes from the attacker. Key management or key pre-distribution (KPS) is the preliminary step in the security of a sensor network, where secret keys are loaded into the sensor node’s memory before placement of the node in target positions. Various schemes for KPS have been proposed for location dependent as well as location independent wireless sensor networks. Costas arrays are \(n \times n\) matrices grid represented where dots are placed for the l’s and leave blanks for the 0’s of the matrix for a positive integer n with the property that the vectors connecting two dots of the grid are all distinct as vectors. Costas arrays have a wide range of application including the construction of sonar signal pattern, cryptography, etc. Due to the Costas arrays property of uniqueness among their elements, it can be used in key pre-distribution of wireless sensor networks, especially in a location-dependent grid-based network. In this paper, we have proposed a Costas array based key pre-distribution scheme. Simulations are done on different network scenarios and the results were analyzed. Comparative performance analysis of the scheme is shown for different grid sized network considering various order of Costas array.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Du W, Deng J, Han YS, Varshney PK, Katz J, Khalili A (2005) A pairwise key predistribution scheme for wireless sensor networks. ACM Trans Inf Syst Secur 8(2):228–58
Bokareva T, Hu W, Kanhere S, Ristic B, Gordon N, Bessell T, Rutten M, Jha S (2006) Wireless sensor networks for battlefield surveillance. In: Proceedings of the land warfare conference, October 24, pp 1–8
Barnes EM, Sudduth KA, Hummel JW, Lesch SM, Corwin DL, Yang C, Daughtry CS, Bausch WC (2003) Remote-and ground-based sensor techniques to map soil properties. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 69(6):619–30
Colhoun J (1973) Effects of environmental factors on plant disease. Annu Rev Phytopathol 11(1):343–64
Billings WD (1952) The environmental complex in relation to plant growth and distribution. Q Rev Biol 27(3):251–65
Hodge VJ, O’Keefe S, Weeks M, Moulds A (2014) Wireless sensor networks for condition monitoring in the railway industry: a survey. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 16(3):1088–106
Drakakis K (2006) A review of Costas arrays. J Appl Math 2006:26385
Golomb SW, Taylor H (1984) Constructions and properties of Costas arrays. Proc IEEE 72(9):1143–1163
Costas JP (1965) Medium constraints on sonar design and performance. Technical Report Class 1 Rep. R65EMH33, GE Co.
Barker L, Drakakis K, Rickard S (2009) On the complexity of the verification of the Costas property. Proc IEEE 97(3):586–593. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2008.2011947
Golomb S (1984) Algebraic constructions for Costas arrays. J Comb Theory Ser A 37(1):13–21
Taylor K, Rickard S, Drakakis K (2010) Costas arrays: survey, standardization and MATLAB toolbox. ACM Trans Math Softw 37(4):1–31
Blackburn SR, Etzion T, Martin KM, Paterson MB (2010) Two-dimensional patterns with distinct differences constructions, bounds, and maximal anticodes. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 56(3):3961–3972
Blackburn SR, Etzion T, Martin KM, Paterson MB (2010) Distinct difference configurations: multihop paths and key predistribution in sensor networks. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 56(8):1216–1229
Rickard S (2006) Open problems in Costas arrays. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics in Signal, Cirencester, UK
Saikia M, Acharjamayum I, Hussain MA (2015) A review on desirable measures for good key pre-distribution scheme in wireless sensor network. In: Green computing and internet of things (ICGCIoT). IEEE, pp 129–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saikia, M., Hussain, A. Costas array based key pre-distribution scheme (CAKPS) for WSN and its performance analysis. CSIT 8, 347–354 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-020-00300-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-020-00300-9