Abstract
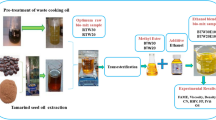
Milk scum is a waste obtained in milk dairies, which can be used as a raw material for producing biodiesel by a transesterification process. In this research study, the biodiesel obtained from milk scum was blended with diesel to make binary blends (B20D80, B60D40 and B100). These binary blends were further blended with ethanol in different percentages to make ternary blends (B20E05D75, B20E10D70, B20E15D65). Physical and chemical properties of binary and ternary blends were investigated and compared. Degradation of physical properties of the prepared biodiesels with respect to time was studied, which is the salient part of the work. Engine performance test was conducted in a single-cylinder diesel engine. Performance of the engine for different blends (both binary and ternary) was recorded and compared. Addition of 5% ethanol showed a decrease in fuel consumption, whereas higher content (15%) of ethanol showed rapid increase in fuel consumption as compared to that of binary blends. Ternary blend containing 5% ethanol showed higher brake thermal efficiency (BTE) compared to D100 (diesel only), while ternary blends containing 10 and 15% ethanol gave lower BTE compared to 5% ethanol and D100. The blend B20E05D75 is considered as better alternative fuel upon comparing mass fuel consumption, air fuel ratio and brake thermal efficiency with all rest of blends tested in this study.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Akhtar, P.K. Tayal, S. Manderna, M.N. Akhtar, Dairy effluent scum: a resourceful material for biogas. Int J Interdiscip Res. 3(1), 2017
P. Sivakumar, K. Anbarasu, S. Renganathan, Bio-diesel production by alkali catalyzed transesterification of dairy waste scum. Fuel 90, 147–151 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2010.08.024
H.V. Srikanth, J. Venkatesh, S. Godiganur, S. Venkateswaran, B. Manne, Bio-based diluents improve cold flow properties of dairy washed milk-scum biodiesel. Renew Energy 111, 168–174 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.03.092
M.E.M. Soudagar et al., The effects of graphene oxide nanoparticle additive stably dispersed in dairy scum oil biodiesel-diesel fuel blend on CI engine: performance, emission and combustion characteristics. Fuel 257, 116015, 1–17 (2019)
M. Nandeesh, C.R. Rajashekar, N.R. Banapurmath, Effect of injection timing on the utilization of B20 blends of dairy scum oil methyl esters (dsome) fulled diesel engine. Eur. J. Sustain Dev. Res. (2019) 3
S.O. Donnell, I. Demshemino, M. Yahaya, L. Okoro, L.Z. Way, A review on the spectroscopic analyses of biodiesel. Eur. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2, 137–146 (2013)
S. Rajesh, B.M. Kulkarni, N.R. Banapurmath, S. Kumarappa, Effect of injection parameters on performance and emission characteristics of a CRDi diesel engine fuelled with acid oil biodiesel–ethanol blended fuels. Biofuels (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/17597269.2016.1271628
A. Sieminski, International energy outlook. Energy Inf. Adm. (2014). http://199.36.140.204/pressroom/presentations/siem
E. Christensen, R.L. McCormick, Long-term storage stability of biodiesel and biodiesel blends. Fuel Process. Technol. 128, 339–348 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.07.045
M.E.M. Soudagar et al., An investigation on the influence of aluminium oxide nano-additive and honge oil methyl ester on engine performance, combustion and emission characteristics. Renew. Energy 146, 2291–2307 (2020)
M.E.M. Soudagar, et al., The effect of nano-additives in diesel-biodiesel fuel blends: a comprehensive review on stability, engine performance and emission characteristics. Energy Convers. Manag 178, 146–177 (2018)
L. Timma, T. Zoss, D. Blumberga, Life after the financial crisis. Energy intensity and energy use decomposition on sectorial level in Latvia. Appl. Energy 162, 1586–1592 (2016)
Mohit Sharma, Rajneesh Kaushal, Performance and emission analysis of a dual fuel variable compression ratio (VCR) CI engine utilizing producer gas derived from walnut shells. Energy 192, 116725 (2020)
M.E.M. Soudagar, et al., Production of honge oil methyl ester (HOME) and its performance test on four stroke single cylinder VCR engine, in AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 2142. no. 1 (AIP Publishing LLC, 2019)
P. Sahoo, L. Das, M. Babu, S. Naik, Biodiesel development from high acid value polanga seed oil and performance evaluation in a CI engine. Fuel 86, 448–454 (2007)
K. Sureshkumar, R. Velraj, R. Ganesan, Performance and exhaust emission characteristics of a CI engine fueled with Pongamia pinnata methyl ester (PPME) and its blends with diesel. Renew. Energy 33, 2294–2302 (2008)
I. Barabas, A. Todoruţ, D. Băldean, Performance and emission characteristics of an CI engine fueled with diesel–biodiesel–bioethanol blends. Fuel 89, 3827–3832 (2010)
H. Aydin, C. Ilkılıc, Effect of ethanol blending with biodiesel on engine performance and exhaust emissions in a CI engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 30, 1199–1204 (2010)
R. Ohlan, Dairy economy of India structural changes in consumption and production. South Asia Res. 36, 241–260 (2016)
N. Ravindranath, C. Lakshmi, R. Manuvie, Biofuel production and implications for land use, food production and environment in India. Energy Policy 39, 5737–5745 (2011)
S. Chopde, S. Chopde, Solar technology: a way to the prosperity of Indian dairy industry. Indian J. Dairy Sci. 69 (2016)
R. Koti, S. Prakash, K. Kiran, An investigation on the performance and emission characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine using safflower oil and milk scum oil as a biodiesel. Int. Ref. J. Eng. Sci. 3, 19–27 (2014)
A. Manjunatha, K. Rajeev, An investigation on the performance and emission characteristics of direct injection diesel engine using milk scum oil as biodiesel. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Technol. 1, 517–525 (2015)
H. Harish, C.R. Shashi Kumar, S.D.G.S.P. Rajanna, Experimental investigation on the performance and emission characteristics of edible and non-edible oil. Int. J. Emerg Technol. Adv. Eng. 4, 648–655 (2014)
S. Sushma, R. Suresh, K.V. Yathish, Production of biodiesel from hybrid oil (dairy waste Scum and Karanja) and characterization and study of its performance on diesel engine. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 3, 686–690 (2014)
K.V. Yatish, H.S. Lalithamba, R. Suresh, S.B. Arun, P.V. Kumar, Optimization of scum oil biodiesel production by using response surface methodology. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 102, 667–672 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.05.026
B. Ranganatha, H. Manjunath. Experimental investigations on four stroke single cylinder diesel engine using mixture of Mahua-milk scum methyl 2, 198–203, (2013)
M.W.G. Qureshi, Z.M. Khan, M. Hussain, F. Ahmed, M. Shoaib, M. Qasim, Experimental evaluation of a diesel engine for combustion, performance and exhaust emissions with fuel blends derived from a mixture of fish waste oil and waste cooking oil biodiesel. Polish J. Environ. Stud. (n.d)
M. Channappagoudra, K. Ramesh, G. Manavendra, Comparative study of standard engine and modified engine with different piston bowl geometries operated with B20 fuel blend. Renew. Energy 133, 216–232 (2019)
A. Afzal, M. Kareemullah, A.R.R.A. Kaladgi, Production of biodiesel from various sources and comparative engine perfor- mance studies by using different biodiesel blends. J. Eng. Res. 6, 1–21 (2018)
S.G. Bojan, S.K. Durairaj, Producing biodiesel from high free fatty acid jatropha curcas oil by a two step method-an indian case study. J. Sustain Energy Environ. 3, 63–66 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.04.015
D.S. Akshatha, G. Manavendra, S. Kumarappa, Performance evaluation of neem biodiesel on Ci engine with. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. 2, 3729–3736 (2013)
R.G. Sinclair, A.F. McKay, R.N. Jones, The infrared absorption spectra of saturated fatty acids and esters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 74, 2570–2575 (1952). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01130a033
R.A. Fattah, N.A. Mostafa, M.S. Mahmoud, W. Abdelmoez, Recovery of oil and free fatty acids from spent bleaching earth using sub-critical water technology supported with kinetic and thermodynamic study. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 5, 261–272 (2014)
O.B. Popovicheva, E.D. Kireeva, S. Steiner, B. Rothen-Rutishauser, N.M. Persiantseva, M.A. Timofeev et al., Microstructure and chemical composition of diesel and biodiesel particle exhaust. Aerosol Air. Qual. Res. 14, 1392–1401 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2013.11.0336
M. Sharma, R. Kaushal, Gasification of walnut shells in an open core downdraft gasifier for the producer gas generation. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Utilization Environ. Eff. 1–12 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1714820
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, H., Kareemullah, M., Ravi, H.C. et al. Combined Effect of Synthesized Waste Milk Scum Oil Methyl Ester and Ethanol Fuel Blend on the Diesel Engine Characteristics. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. C 101, 947–962 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-020-00605-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40032-020-00605-3