Abstract
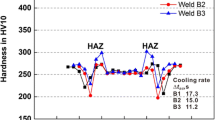
Three high-strength Nb-, Ti- and Ti + V-microalloyed S690QL steels were welded to investigate the formation of softened HAZ and its impact on tensile properties. The welding was performed with three levels of heat input to produce softened zones with different characteristics (softening width, minimum hardness and softening ratio), and then, further tensile tests were done to study their influence on weld performance. The results showed that Ti bearing steel exhibited the lowest resistance to softening with the presence of largest soften width and lowest hardness value, causing final tensile failure occurred at softened HAZ. The metallurgical reason for the lower hardness is the high fraction of coarse ferrite. Nb- and Ti + V-bearing steels suffered moderate softening, due to high hardenability with addition of Mo, Nb and V, but the softening effect did not remarkably influence the tensile properties of these two steels.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raoul J, Günther H-P (2005) Use and application of high-performance steels for steel structures, vol 8. Iabse
Bhadeshia H, Honeycombe R (2011) Steels: microstructure and properties. Butterworth-Heinemann
Zhang L, Kannengiesser T (2014) Austenite grain growth and microstructure control in simulated heat affected zones of microalloyed HSLA steel. Mater Sci Eng A 613:326–335
Bd M (1997) The weldability of modern structural TMCP steels. ISIJ Int 37(6):537–551. doi:10.2355/isijinternational.37.537
Mohandas T, Madhusudan Reddy G, Satish Kumar B (1999) Heat-affected zone softening in high-strength low-alloy steels. J Mater Process Technol 88(1–3):284–294. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(98)00404-X
Shintomi T, Hashimoto Y, Chikushi I, Mochizuki M, Toyoda M (2003) Deformation and ductile crack initiation in weld HAZ softening joints - studies on deformation and strength in welded joints of fine grain steel (report 3). Q J Japan Weld Soc 21(3):411–418. doi:10.2207/qjjws.21.411
Pisarski HG, Dolby RE (2003) The significance of softened HAZs in high strength structural steels. Weld World 47(5–6):32–40. doi:10.1007/bf03266387
Mochizuki M, Shintomi T, Hashimoto Y, Toyoda M (2004) Analytical study on deformation and strength in HAZ-softened welded joints of fine-grained steels. Weld World 48(9–10):2–12. doi:10.1007/bf03263396
Meng W, Li Z, Huang J, Wu Y, Katayama S (2014) Microstructure and softening of laser-welded 960 MPa grade high strength steel joints. J Mater Eng Perform 23(2):538–544. doi:10.1007/s11665-013-0795-5
Kojima T, Hayashi K, Kajita Y (1995) HAZ softening and creep rupture strength of high Cr ferritic steel weldments. ISIJ Int 35(10):1284–1290
Maurer W, Ernst W, Rauch R, Vallant R, Enzinger N (2015) Evaluation of the factors influencing the strength of HSLA steel weld joint with softened HAZ. Weld World 59(6):809–822. doi:10.1007/s40194-015-0262-z
Hochhauser F, Ernst W, Rauch R, Vallant R, Enzinger N (2012) Influence of the soft zone on the strength of welded modern hsla steels. Weld World 56(5–6):77–85. doi:10.1007/bf03321352
Rodrigues DM, Menezes LF, Loureiro A, Fernandes JV (2004) Numerical study of the plastic behaviour in tension of welds in high strength steels. Int J Plast 20(1):1–18. doi:10.1016/S0749-6419(02)00112-2
Ito R, Shiga C, Kawaguchi Y, Nakamura T, Hiraoka K, Hayashi T, Torizuka S (2000) Controlling of the softened region in weld heat affected zone of ultra fine grained steels. ISIJ Int 40:S29–S33
Rahman M, Maurer W, Ernst W, Rauch R, Enzinger N (2014) Calculation of hardness distribution in the HAZ of micro-alloyed steel. Weld World:1–8. doi:10.1007/s40194-014-0156-5
Biro E, McDermid JR, Embury JD, Zhou Y (2010) Softening kinetics in the subcritical heat-affected zone of dual-phase steel welds. Metall Mater Trans A 41A(9):2348–2356. doi:10.1007/s11661-010-0323-2
Farren J, Hunter A, Dupont J, Seidman D, Robino C, Kozeschnik E (2012) Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of fusion welds in an iron-copper-based multicomponent steel. Metall Mater Trans A 43(11):4155–4170. doi:10.1007/s11661-012-1249-7
Zhang L, Pittner A, Michael T, Rhode M, Kannengiesser T (2015) Effect of cooling rate on microstructure and properties of microalloyed HSLA steel weld metals. Sci Technol Weld Join 20(5):371–377. doi:10.1179/1362171815Y.0000000026
Baltazar Hernandez VH, Nayak SS, Zhou Y (2011) Tempering of martensite in dual-phase steels and its effects on softening behavior. Metall Mater Trans A 42(10):3115–3129. doi:10.1007/s11661-011-0739-3
Robertson I (1993) Temper resistance of pressure hull steel microalloyed with niobium, titanium, and vanadium. Mater Sci Technol 9(11):1031–1036
Abson DJ, Pargeter RJ (1986) Factors influencing as-deposited strength, microstructure, and toughness of manual metal arc welds suitable for C-Mn steel fabrications. Int Metals Rev 31(1):141–196. doi:10.1179/imtr.1986.31.1.141
Mohrbacher H (2010) Principal effects of Mo in HSLA steels and cross effects with microalloying elements. Cent Iron Steel Res Inst (CISRI):75–96
Zajac S, Siwecki T, Hutchinson WB, Lagneborg R (1998) Strengthening mechanisms in vanadium microalloyed steels intended for long products. ISIJ Int 38(10):1130–1139
Acknowledgments
The authors thank R. S. Neumann, R. Haecker, D. Schroepfer and T. Michael from Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (Germany) for their kind support. One of the authors (Lei Zhang) also appreciates the funding support from China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended for publication by Commission II - Arc Welding and Filler Metals
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Kannengiesser, T. HAZ softening in Nb-, Ti- and Ti + V-bearing quenched and tempered steel welds. Weld World 60, 177–184 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-016-0299-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-016-0299-7