Abstract
Critical success factors (CSFs) are the enablers to address the successful implementation of sustainable supply chain management (SSCM) practices in organizations. This study identifies and consolidates various relevant factors to develop the SSCM constructs conducive to supply chains in the Indian steel sector. A comprehensive framework of sustainability measurement has been developed through successive stages of data collection, analysis and refinement. Data have been collected from various departments of Tata Steel, SAIL, Essar and Jindal in India. The outcome of this research is a set of reliable, valid and unidimensional first-order measurements that can be subsequently used in conceptualization and measurement of the sustainability of supply chains in steel industry. Using factor analysis, we identify four constructs, namely favourable organizational environment, sustainable procurement initiatives, compliances to sustainability standards and external environmental pressures, which the organizations need to focus on. Additionally, using relative importance index ranking based on the survey data, the top three CSFs are compliance to environmental standards (ISO 14001 certification), safety and health focus (OHSAS 18001 certification) and top leadership commitment and support-all of which are within the organization’s own control. This study contributes to the continuing research of supply chain sustainability and provides supply chain managers with a practical approach for measuring and implementing sustainability practices across the steel supply chains.

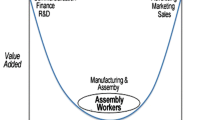
Note: adapted with modification from Mani et al. (2016)

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The advantages of using EFA are: (1) it is not so expensive and simple to run and can be used for a wide variety of situations; (2) it can be used to identify lots of important factor which are not possible through other statistical technique; (3) it is very useful for lots of survey questions; and (4) it is the basis for other instruments (regression analysis with factor scores) and easy to combine with other instruments (confirmatory analysis). However, the use of EFA has some disadvantages: (1) interval scale variables need to be used; (2) it is always difficult to design good set of questionnaires which covers all types of gateway for variation; (3) it is difficult to decide how many factors to be chosen; and (4) sample size should be more than three times than the number of variables.
This validation is as per the recommendation of Field (2009).
See Nunnally (1978).
It stands for Global Reach Initiative.
References
Ahi P, Searcy C (2013) A comparative literature analysis of definitions for green and sustainable supply chain management. J Clean Prod 52:329–341
Akkermans H, van Helden K (2002) Vicious and virtuous cycles in ERP implementation: a case study of interrelations between critical success factors. Eur J Inf Syst 11(1):35–46
Al Zaabi S, Al Dhaheri N, Diabat A (2013) Analysis of interaction between the barriers for the implementation of sustainable supply chain management. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68(1–4):895–905
Alvarez G, Pilbeam C, Wilding R (2010) Nestlé Nespresso AAA sustainable quality program: an investigation into the governance dynamics in a multi-stakeholder supply chain network. Supply Chain Manag Int J 15(2):165–182
Antony J, Leung K, Knowles G, Gosh S (2002) Critical success factors of TQM implementation in Hong Kong industries. Int J Qual Reliab Manag 19(5):551–566
Ashby A, Leat M, Hudson-Smith M (2012) Making connections: a review of supply chain management and sustainability literature. Supply Chain Manag Int J 17(5):497–516
Avittathur B, Jayaram J (2016) Supply chain management in emerging economies. Decision 43(2):117–124
Bai C, Sarkis J (2010) Integrating sustainability into supplier selection with grey system and rough set methodologies. Int J Prod Econ 124(1):252–264
Barclay D, Higgins C, Thompson R (1995) The partial least squares (PLS) approach to causal modeling: personal computer adoption and use as an illustration. Technol Stud 2(2):285–309
Bowen FE, Cousins PD, Lamming RC, Faruk AC (2001) The role of supply management capabilities in green supply. Prod Oper Manag 10:174–189
Brandenburg M, Govindan K, Sarkis J, Seuring S (2014) Quantitative models for sustainable supply chain management: developments and directions. Eur J Oper Res 233(2):299–312
Brindley C, Oxborrow L (2014) Aligning the sustainable supply chain to green marketing needs: a case study. Ind Mark Manag 43(1):45–55
BS 8903 (2010) Principles and framework for procuring sustainably: guide BSI. British Standard Institute London
Carter CR, Carter JR (1998) Inter-organizational determinants of environmental purchasing: initial evidence from the consumer products industry. Decis Sci 29:28–38
Carter CR, Easton PL (2011) Sustainable supply chain management: evolution and future directions. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 41(1):46–62
Carter CR, Jennings MM (2002) Social responsibility and supply chain relationships. Transp Res E Logist Transp Rev 38(1):37–52
Carter CR, Jennings MM (2004) The role of purchasing in corporate social responsibility: a structural equation analysis. J Bus Logist 25(1):145–186
Carter CR, Rogers DS (2008) A framework of sustainable supply chain management: moving toward new theory. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 38(5):360–387
Carter CR, Kale R, Grimn CM (2000) Environmental purchasing and firm performance: an empirical investigation. Transp Res E 36:219–288
Chan HK, He H, Wang WY (2012) Green marketing and its impact on supply chain management in industrial markets. Ind Mark Manag 41(4):557–562
Čuček L, Klemeš JJ, Kravanja Z (2012) A review of footprint analysis tools for monitoring impacts on sustainability. J Clean Prod 34:9–20
Daniel DR (1961) Management information crisis. Harv Bus Rev 39(5):111–121
Darnall N, Jolley GJ, Handfield R (2008) Environmental management systems and green supply chain management: complements for sustainability? Bus Strateg Environ 17(1):30–45
Delai I, Takahashi S (2013) Corporate sustainability in emerging markets: insights from the practices reported by the Brazilian retailers. J Clean Prod 47(1):211–221
Diabat A, Kannan D, Mathiyazhagan K (2014) Analysis of enablers for implementation of sustainable supply chain management: a textile case. J Clean Prod 83(1):391–403
Dinter B (2013) Success factors for information logistics strategy: an empirical investigation. Decis Support Syst 54(3):1207–1218
Dubey R, Gunasekaran A, Papadopoulos T, Childe SJ (2015a) Green supply chain management enablers: mixed methods research. Sustain Prod Consum 4:72–88
Dubey R, Gunasekaran A, Sushil S, Singh T (2015b) Building theory of sustainable manufacturing using total interpretive structural modelling. Int J SSOL 2(4):231–247
Dubey R, Gunasekaran A, Ali SS (2015c) Exploring the relationship between leadership, operational practices, institutional pressures and environmental performance: a framework for green supply chain. Int J Prod Econ 160(2):120–132
El Khouli RH, Macura KJ, Kamel IR, Jacobs MA, Bluemke DA (2011) 3-T dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of the breast: pharmacokinetic parameters versus conventional kinetic curve analysis. Am J Roentgenol 197(6):1498–1505
Faisal MN (2010) Sustainable supply chains: a study of interaction among the enablers. Bus Process Manag J 16(3):508–529
Falk RF, Miller NB (1992) A primer on soft modeling. The University of Akron Press, Akron
Field A (2009) Discovering statistics using SPSS. Sage, New York
Garg P (2017) Development of sustainability reporting index (SRI) with special reference to companies in India. Decision 44(4):259–273
Gaussin M, Hu G, Abolghasem S, Basu S, Shankar MR, Bidanda B (2013) Assessing the environmental footprint of manufactured products: a survey of current literature. Int J Prod Econ 146(2):515–523
Gold S, Seuring S, Beske P (2010) Sustainable supply chain management and inter-organizational resources: a literature review. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 17(4):230–245
Govindan K, Kaliyan M, Kannan D, Haq AN (2014) Barriers analysis for green supply chain management implementation in Indian industries using analytic hierarchy process. Int J Prod Econ 147(1):555–568
Grimm JH, Hofstetter JS, Sarkis J (2014) Critical factors for sub-supplier management: a sustainable food supply chains perspective. Int J Prod Econ 152:159–173
Hacking T, Guthrie P (2008) A framework for clarifying the meaning of triple bottom-line, integrated, and sustainability assessment. Environ Impact Assess Rev 28(2):73–89
Hair JF (2007) Research methods for business. Wiley, New York
Hair JF, Anderson RE, Tatham RL, Black WC (2010) Multivariate data analysis, 7th edn. Prentice Hall, NJ
Hall J (2001) Environmental supply-chain innovation. Greener Manag Int 9(3):105–119
Handfield RB, Walton SV, Seegers LK, Melnyk SA (1997) ‘Green’ value chain practices in the furniture industry. J Oper Manag 15(4):293–315
Hasan M (2013) Sustainable supply chain management practices and operational performance. Am J Ind Bus Manag 3(1):42
Hassini E, Surti C, Searcy C (2012) A literature review and a case study of sustainable supply chains with a focus on metrics. Int J Prod Econ 140(1):69–82
Heese HS, Cattani K, Ferrer G, Gilland W, Roth AV (2005) Competitive advantage through take-back of used products. Eur J Oper Res 164(1):143–157
Herva M, Roca E (2013) Review of combined approaches and multi-criteria analysis for corporate environmental evaluation. J Clean Prod 39:355–371
Hooley GJ, Saunders JA (1993) Competitive positioning: the key to marketing strategy. Prentice Hall, NJ
Hulland J (1999) Use of partial least squares (PLS) in strategic management research: a review of four recent studies. Strateg Manag J 20(2):195–204
Huo B, Ye Y, Zhao X, Shou Y (2016) The impact of human capital on supply chain integration and competitive performance. Int J Prod Econ 178:132–143
Hussain M, Khan M, Al-Aomar R (2016) A framework for supply chain sustainability in service industry with confirmatory factor analysis. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 55:1301–1312
Iyer KC, Jha KN (2005) Factors affecting cost performance: evidence from Indian construction projects. Int J Proj Manag 23:283–295
Jawahir IS, Rouch KE, Dillon OW, Holloway L, Hall A (2007) Design for sustainability (DFS): new challenges in developing and implementing a curriculum for next generation design and manufacturing engineers. Int J Eng Educ 23(6):1053–1064
Johnson G, Scholes K, Whittington R (2008) Exploring corporate strategy: text & cases. Pearson Education, London
Kim J, Rhee J (2012) An empirical study on the impact of critical success factors on the balanced scorecard performance in Korean green supply chain management enterprises. Int J Prod Res 50(9):2465–2483
Kline RB (2010) Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. Guilford Press, New York
Koh SCL, Gunasekaran A, Tseng CS (2012) Cross-tier ripple and indirect effects of directives WEEE and RoHS on greening a supply chain. Int J Prod Econ 140(1):305–317
Krause DR, Vachon S, Klassen RD (2009) Special topic forum on sustainable supply chain management: introduction and reflections on the role of purchasing management. J Supply Chain Manag 45(4):18–25
Kuei CH, Madu CN, Chow WS, Chen Y (2015) Determinants and associated performance improvement of green supply chain management in China. J Clean Prod 95:163–173
Larson AL (2000) Sustainable innovation through an entrepreneurship lens. Bus Strategy Environ 9(5):304–317
Leidecker JK, Bruno AV (1984) Identifying and using critical success factors. Long Range Plan 17(1):23–32
Li S, Ragu-Nathan B, Ragu-Nathan TS, Rao SS (2006) The impact of supply chain management practices on competitive advantage and organizational performance. Omega 34(2):107–124
Linton JD, Klassen R, Jayaraman V (2007) Sustainable supply chains: an introduction. J Oper Manag 25:1075–1082
Lowes B, Pass CL, Sanderson S (1994) Companies and markets: understanding business strategy and the market environment. Blackwell, Oxford
Luthra S, Kumar V, Kumar S, Haleem A (2011) Barriers to implement green supply chain management in automobile industry using interpretive structural modeling technique: an Indian perspective. J Ind Eng Manag 4(2):231–257
Luthra S, Qadri MA, Garg D, Haleem A (2014) Identification of critical success factors to achieve high green supply chain management performances in indian automobile industry. Int J Logist Syst Manag 1 18(2):170–199
Luthra S, Garg D, Haleem A (2015a) An analysis of interactions among critical success factors to implement green supply chain management towards sustainability: an Indian perspective. Resour Policy 46(1):37–50
Luthra S, Garg D, Haleem A (2015b) Critical success factors of green supply chain management for achieving sustainability in Indian automobile industry. Prod Plan Control 26:339–362
Luthra S, Mangla SK, Kumar S, Garg D, Haleem A (2017) Identify and prioritise the critical factors in implementing the reverse logistics practices: a case of Indian auto component manufacturer. Int J Bus Syst Res 11(1–2):42–61
Mangla S, Madaan J, Sarma PRS, Gupta MP (2014) Multi-objective decision modelling using interpretive structural modelling for green supply chains. Int J Logist Syst Manag 17(2):125–142
Mani V, Agarwal R, Gunasekaran A, Papadopoulos T, Dubey R, Childe SJ (2016) Social sustainability in the supply chain: construct development and measurement validation. Ecol Ind 71:270–279
Martin BA (2005) Creating value with proactive environmental strategies. Environ Qual Manag 15(2):21–25
Mayyas A, Qattawi A, Omar M, Shan D (2012) Design for sustainability in automotive industry: a comprehensive review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16(4):1845–1862
Miao Z, Cai S, Xu D (2012) Exploring the antecedents of logistics social responsibility: a focus on Chinese firms. Int J Prod Econ 140(1):18–27
Mohanty RP, Deshmukh SG (1997) Strategic adoption of a flexible manufacturing system: case study of an Indian electronics enterprise. Prod Plan Control 8(8):797–805
Mollenkopf D, Stolze H, Tate WL, Ueltschy M (2010) Green, lean, and global supply chains. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 40(1/2):14–41
Morali O, Searcy C (2013) A review of sustainable supply chain management practices in Canada. J Bus Ethics 117(3):635–658
Mori K, Christodoulou A (2012) Review of sustainability indices and indicators: towards a new City Sustainability Index (CSI). Environ Impact Assess Rev 32(1):94–106
Mudgal RK, Shankar R, Talib P, Raj T (2009) Greening the supply chain practices: an Indian perspective of enablers’ relationships. Int J Adv Oper Manag 1(2–3):151–176
Muduli K, Barve A (2011) Role of green issues of mining supply chain on sustainable development. Int J Innov Manag Technol 2(6):484–489
Muduli K, Barve A (2013) Sustainable development practices in mining sector: a GSCM approach. Int J Environ Sustain Dev 12(3):222–243
Munro MC, Wheeler BR (1980) Planning, critical success factors, and management’s information requirements. MIS Q 4(4):27–38
Nah FF, Lee-Shang Lau J, Kuang J (2001) Critical factors for successful implementation of enterprise systems. Bus Process Manag J 7(3):285–296
Neves AR, Leal V (2010) Energy sustainability indicators for local energy planning: review of current practices and derivation of a new framework. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 14(9):2723–2735
Nunnally JC (1978) Psychometric theory, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, Hillsdale
Oloruntoba A (2001) Research manager’s post training job performance in Nigerian Agricultural Research Institutes. J Adv Stud Educ Manag 1(1–2):239–244
Pagell M, Wu Z (2009) Building a more complete theory of sustainable supply chain management using case studies of 10 exemplars. J Supply Chain Manag 45(2):37–56
Peppard J, Ward J (2003) Strategic planning for information systems. Wiley, New York
Porter ME, Van der Linde C (1995a) Green and competitive: ending the stalemate. Harv Bus Rev 73(5):120–134
Porter ME, Van der Linde C (1995b) Toward a new conception of the environment–competitiveness relationship. J Econ Perspect 9(4):97–118
Pradhan RP, Verma A, Bele SK, Gaurav K (2016) Critical success factors in Indian scenario for PPP projects in infrastructure development: the Indian scenario. Indian J Reg Sci 48(2):12–27
Prasad DS (2017) Critical success factors for sustainable supply chain management in Indian steel sector. PHD thesis, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, India
Qi Y, Huo B, Wang Z, Yeung HYJ (2017) The impact of operations and supply chain strategies on integration and performance. Int J Prod Econ 185:162–174
Quesada H, Gazo R (2007) Methodology for determining key internal business processes based on critical success factors: a case study in furniture industry. Bus Process Manag J 13(1):5–20
Rao P (2002) Greening the supply chain: a new initiative in South East Asia. Int J Oper Prod Manag 22(6):632–655
Rao P, Holt D (2005) Do green supply chains lead to competitiveness and economic performance? Int J Oper Prod Manag 25(9):898–916
Raut RD, Narkhede B, Gardas BB (2017) To identify the critical success factors of sustainable supply chain management practices in the context of oil and gas industries: ISM approach. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 68:33–47
Roca LC, Searcy C (2012) An analysis of indicators disclosed in corporate sustainability reports. J Clean Prod 20(1):103–118
Rockart JF (1979) Chief executives define their own data needs. Harv Bus Rev 57(2):81–93
Sarkis J (2003) A strategic decision framework for green supply chain management. J Clean Prod 11:397–409
Sarkis J (2012) A boundaries and flows perspective of green supply chain management. Supply Chain Manag Int J 17(2):202–216
Sarkis J, Zhu Q, Lai KH (2011) An organizational theoretic review of green supply chain management literature. Int J Prod Econ 130(1):1–15
Scott WR (2008) Approaching adulthood: the maturing of institutional theory. Theory Soc 37(5):427–442
Seuring S (2013) A review of modeling approaches for sustainable supply chain management. Decis Support Syst 54:1513–1520
Seuring S, Muller M (2008) From a literature review to a conceptual framework for sustainable supply chain management. J Clean Prod 16(15):1699–1710
Srivastava SK (2007) Green supply chain management: a state-of the-art literature review. Int J Manag Rev 9:53–80
Sundarakani B, de Souza R, Goh M, Van Over D, Manikandan S, Koh SL (2010a) A sustainable green supply chain for globally integrated network. Enterprise networks and logistics for agile manufacturing. Springer, London, pp 191–206
Sundarakani B, De Souza R, Goh M, Wagner SM, Manikandan S (2010b) Modeling carbon footprints across the supply chain. Int J Prod Econ 128(1):43–50
Trkman P (2010) The critical success factors of business process management. Int J Inf Manag 30(2):125–134
Turcu C (2013) Re-thinking sustainability indicators: local perspectives of urban sustainability. J Environ Plan Manag 56(5):695–719
Vachon S, Klassen RD (2006) Extending green practices across the supply chain: the impact of upstream and downstream integration. Int J Oper Prod Manag 26(7):795–821
Vachon S, Klassen RD (2008) Environmental management and manufacturing performance: the role of collaboration in the supply chain. Int J Prod Econ 111:299–315
van Hock R, Erasmus I (2000) From reversed logistics to green supply chain. Logist Solut 2:28–33
Walker H, Jones N (2012) Sustainable supply chain management across the UK private sector. Supply Chain Manag Int J 17(1):15–28
Walker H, Sisto LD, McBain D (2008) Drivers and barriers to environmental supply chain management practices: lessons from the public and private sectors. J Purch Supply Manag 14:69–85
Walley N, Whitehead B (1994) It’s not easy being green. Harv Bus Rev 72(3):46–51
Walton SV, Handfield RB, Melnyk SA (1998) The green supply chain: integrating suppliers into environmental management processes. J Supply Chain Manag 34(1):2–11
Watson GH (1993) How process benchmarking supports corporate strategy. Plan Rev 21(1):12–15
WEO (2016) World Energy Outlook (WEO), International Energy Agency (IEA), Paris
World Commission on Environment and Development (1987) Our common future. Oxford University Press, Oxford
WSD (2016) World Steel Dynamics (WSD) Inc., Englewood Cliffs
Yadav DK, Barve A (2015) Analysis of critical success factors of humanitarian supply chain: an application of interpretive structural modeling. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 12(1):213–225
Yusof SRM, Aspinwall E (1999) Critical success factors for total quality management implementation in small and medium enterprises. Total Qual Manag 10(4–5):803–809
Zailani SHM, Eltayeb TK, Hsu CC, Choon Tan K (2012a) The impact of external institutional drivers and internal strategy on environmental performance. Int J Oper Prod Manag 32(6):721–745
Zailani S, Jeyaraman K, Vengadasan G, Premkumar R (2012b) Sustainable supply chain management (SSCM) in Malaysia: a survey. Int J Prod Econ 140(1):330–340
Zhou Q, Huang W, Zhang Y (2011) Identifying critical success factors in emergency management using a fuzzy DEMATEL method. Saf Sci 49(2):243–252
Zhu Q, Sarkis J, Geng Y (2005) Green supply chain management in china: pressures, practices and performance. Int J Oper Prod Manag 25(5):449–468
Zhu Q, Sarkis J, Lai KH (2008) Confirmation of a measurement model for green supply chain management practices implementation. Int J Prod Econ 111(2):261–273
Zhu Q, Geng Y, Lai KH (2010) Circular economy practices among Chinese manufacturers varying in environmental-oriented supply chain cooperation and the performance implications. J Environ Manag 91(6):1324–1331
Zhu Q, Sarkis J, Lai KH (2012) Examining the effects of green supply chain management practices and their mediations on performance improvements. Int J Prod Res 50(5):1377–1394
Zsidisin GA, Hendrick TE (1998) Purchasing’s involvement in environmental issues: a multi-country perspective. Ind Manag Data Syst 7(1):313–320
Zsidisin GA, Siferd SP (2001) Environmental purchasing: a framework for theory development. Eur J Purch Supply Manag 7(1):61–73
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, D.S., Pradhan, R.P., Gaurav, K. et al. Analysing the critical success factors for implementation of sustainable supply chain management: an Indian case study. Decision 45, 3–25 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40622-017-0171-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40622-017-0171-7