Abstract
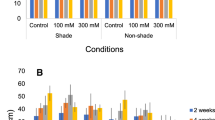
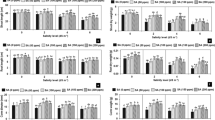
The traditional methods to evaluate salt tolerance of plants use mainly data of growth and crop productivity. In the case of ornamental plants it is also essential to evaluate the effects on the visual quality of the plants, since the beauty in the acquisition of an ornamental plant is not always associated with its size. So, we tested a new method to assess salt tolerance of four ornamental species, comparing with traditional ones. The experimental design was in completely randomized blocks, in a 10 × 4 factorial arrangement, with four replications, ten levels of electrical conductivity of irrigation water—ECw (0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 8.0, 10.0, 12.0 dS m−1) and four ornamental species (Catharanthus roseus, Allamanda cathartica, Ixora coccinea and Duranta erecta). Two salinity tolerance assessment methods, which are based only on quantitative growth data, were evaluated and compared with a new method, named ornamental index (Orn index) that considers growth data and visual analysis. Our results showed that the two traditional assessment methods converge to indicate I. coccinea and D. erecta, respectively, with higher and lower capacity to grow under salt stress. However, these methods present clear differences in the results between quantitative data (biomass production) and qualitative analyses (flower production and overall plant appearance). The new method (Orn index) adequately separated the four ornamental species according to their tolerance to salinity, as follows: I. coccinea (moderately tolerant), C. roseus and D. erecta (moderately sensitive), and A. cathartica (sensitive). Hence, the Orn index, including quantitative and qualitative aspects, should be recommended to evaluate salinity tolerance in ornamental species, especially for garden flowers of commercial interest.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez SM, Sánchez-Blanco J (2015) Comparison of individual and combined effects of salinity and deficit irrigation on physiological, nutritional and ornamental aspects of tolerance in Callistemon laevis plants. J Plant Physiol 185:65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2015.07.009
Ayers RS, Westcot DW (1999) A qualidade da água na agricultura, 2nd edn. UFPB, Campina Grande
Barros HMM, Gheyi HR, Loges V, Santos MS, Soares FAL (2010) Influência da salinidade da água no crescimento de seis genótipos de Helicônias. Rev Bras Hortic Ornam 16:139–145. https://doi.org/10.14295/rbho.v16i2.554
Bernstein L, François LE, Clark RA (1972) Salt tolerance of ornamental shrubs and ground covers. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 97:550–556
Cai X, Niu G, Starman T, Hall C (2014) Response of six garden roses (Rosa × hybrida L.) to salt stress. Sci Hortic 168:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2013.12.032
Cassaniti C, Romano D, Hop MECM, Flowers TJ (2013) Growing floricultural crops with brackish water. Environ Exp Bot 92:65–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.08.006
Dantas JP, Marinho FJL, Ferreira MMM, Amorim MSN, Andrade SIO, Sales AL (2002) Avaliação de genótipos de caupi sob salinidade. Rev Bras Eng Agríc Ambient 6:425–430. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-43662002000300008
Fageria NK (1985) Salt tolerance of rice cultivars. Plant Soil 88:237–243
García-Caparrós P, Llanderal A, Pestana M, Correia PJ, Lao MT (2016) Tolerance mechanisms of three potted ornamental plants grown under moderate salinity. Sci Hortic 201:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2016.01.031
Maas EV, Hoffman GH (1977) Crop salt tolerance—current assessment. J Irrig Drain Div ASCE 103:115–134
Maciel MP, Soares TM, Gheyi HR, Rezende EPL, Oliveira GXS (2012) Produção de girassol ornamental com uso de águas salobras em sistema hidropônico NFT. Rev Bras Eng Agríc Ambient 16:65–172. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-43662012000200006
Miyamoto S, Martinez I, Padilla M, Portillo A, Ornelas D (2004) Landscape plant lists for salt tolerance assessment. USDI, Bureau of Reclamation, Texas Agricultural Experiment Station, El Paso
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092911
Neves ALR, Lacerda CF, Oliveira AC, Sousa CHC, Oliveira FIF, Ribeiro MSS (2018) Respostas quantitativas e qualitativas de Catharanthus roseus à salinidade e biofertilizante. Rev Bras Eng Agríc Ambient 21:22–26. https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-1929/agriambi.v22n1p22-26
Niu G, Rodriguez DS (2006a) Relative salt tolerance of five herbaceous perennials. HortScience 41:1493–1497
Niu G, Rodriguez DS (2006b) Relative salt tolerance of selected herbaceous perennials and groundcovers. Sci Hortic 110:352–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2006.07.020
Niu G, Rodriguez DS, Aguinina L (2007) Growth and landscape performance of ten herbaceous species in response to saline water irrigation. J Environ Hortic 25:204–210
Niu G, Rodriguez DS, Mckenney C (2012) Response of selected wildflower species to saline water irrigation. HortScience 47:1351–1355
Noble CL, Rogers ME (1992) Arguments for the use of physiological criteria for improving the salt tolerance in crops. Plant Soil 146:99–107
Rahnama A, James RA, Poustini K, Munns R (2010) Stomatal conductance as a screen for osmotic stress tolerance in durum wheat growing in saline soil. Funct Plant Biol 37:255–269
Santos Júnior JA, Gheyi HR, Cavalcante AR, Dias NS, Medeiros SS (2016) Produção e pós-colheita de flores de girassóis sob estresse salino em hidroponia de baixo custo. Eng Agríc 36:420–432. https://doi.org/10.1590/1809-4430-Eng.Agric.v36n3p420-432/2016
Silva ARA, Bezerra FML, Lacerda CF, Lima RMM, Araujo MEB, Sousa CHC (2016) Establishment of young dwarf green coconut plants in soil affected by salts and under water deficit. Rev Bras Frutic 38:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1590/0100-29452016206
Soares Filho WS, Gheyi HR, Brito MEB, Nobre RG, Fernandes PD, Miranda RS (2016) Melhoramento genético vegetal e seleção de cultivares tolerantes à salinidade. In: Gheyi HR, Dias NS, Lacerda CF, Gomes Filho E (eds) Manejo da salinidade na agricultura: estudos básicos e aplicados, 2nd edn. Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia em Salinidade, Fortaleza, pp 259–274
Ureña MP, D’árrigo MH, Girón OM (1999) Evaluación sensorial de los alimentos. Universidade Nacional Agrária La Molina, Lima
Wu S, Sun Y, Niu G (2016) Morphological and physiological responses of nine ornamental species to saline water irrigation. HortScience 51:285–290
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the National Institute of Science and Technology in Salinity (INCTSal), National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, E.V., de Lacerda, C.F., Neves, A.L.R. et al. A new method to evaluate salt tolerance of ornamental plants. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 30, 173–180 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40626-018-0112-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40626-018-0112-7