Abstract
Purpose of review
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an autoimmune fibrosing condition which is being increasingly recognized. This condition has been classically managed with glucocorticoids (GC) with variable dosing and frequent relapses. Multiple observational reports studied different GC doses and steroid-sparing agents. Rituximab (RTX) was reported as an effective induction treatment, with less relapses after 1 year of treatment. In the absence of guidelines, an international management consensus was made in 2015.
Recent findings
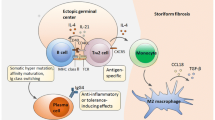
In the last few years, significant advances have been made to clarify IgG4-RD pathophysiology. The new classification criteria will enable investigators to design new clinical trials with more homogeneous populations. Furthermore, B and T lymphocytes have a central role in the inflammatory cascade. More solid evidence has been published supporting treatment with GC, RTX, and some other steroid-sparing agents like mofetil mycophenolate. The combination of GC and immunosuppressants has been pointed by a meta-analysis as the most effective treatment for IgG4-RD, although the number and quality of studies remains limited.
Summary
The use of GC and steroid-sparing agents is effective in IgG4-RD, although the choice between rituximab and other immunosuppressants can be influenced by many factors. Novel agents will be trialed in the following years.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Uchida K, Masamune A, Shimosegawa T, Okazaki K. Prevalence of IgG4-related disease in Japan based on Nationwide survey in 2009. Int J Rheumatol. 2012;2012:1–5.
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:982–4.
Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, Yi EE, Sato Y, Yoshino T, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:1181–92.
Perugino CA, AlSalem SB, Mattoo H, Della-Torre E, Mahajan V, Ganesh G, et al. Identification of galectin-3 as an autoantigen in patients with IgG4-related disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. Elsevier Inc. 2019;143:736–745.e6.
Shiokawa M, Kodama Y, Sekiguchi K, Kuwada T, Tomono T, Kuriyama K, et al. Laminin 511 is a target antigen in autoimmune pancreatitis. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10:1–11.
Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Della-Torre E, Sekigami Y, Carruthers M, Wallace ZS, et al. De novo oligoclonal expansions of circulating plasmablasts in active and relapsing IgG4-related disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol Elsevier Ltd. 2014;134:679–87.
Mattoo H, Stone JH, Pillai S. Clonally expanded cytotoxic CD4 + T cells and the pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. Autoimmunity. 2017;50:19–24.
Della-Torre E, Lanzillotta M, Doglioni C. Immunology of IgG4-related disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015;181:191–206.
Della-Torre E, Rigamonti E, Perugino C, Baghai-Sain S, Sun N, Kaneko N, et al. B lymphocytes directly contribute to tissue fibrosis in patients with IgG4-related disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol: Elsevier Inc.; 2019.
Carruthers MN, Khosroshahi A, Augustin T, Deshpande V, Stone JH. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;74:14–8.
Martínez-Valle F, Fernández-Codina A, Pinal-Fernández I, Orozco-Gálvez O, Vilardell-Tarrés M. IgG4-related disease: evidence from six recent cohorts. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16:168–72.
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22:21–30.
Wallace ZS, Naden RP, Chari S, Choi H, Della-Torre E, Dicaire J-F, et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken, NJ). 2019;0:1–13.
Stone JH, Hoffman GS, Merkel PA, Min Y-I, Uhlfelder ML, Hellmann DB, et al. A disease-specific activity index for Wegener’s granulomatosis: modification of the Birmingham Vasculitis activity score. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:912–20.
Wallace ZS, Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MD, Perugino CA, Choi H, Campochiaro C, et al. An International Multispecialty Validation Study of the IgG4-Related Disease Responder Index. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018;70:1671–8.
Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Carruthers M, Mahajan VS, Della Torre E, Lee H, et al. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:190–5.
Della-Torre E, Bozzalla-Cassione E, Sciorati C, Ruggiero E, Lanzillotta M, Bonfiglio S, et al. A CD8α- Subset of CD4+SLAMF7+ Cytotoxic T Cells Is Expanded in Patients With IgG4-Related Disease and Decreases Following Glucocorticoid Treatment. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken, NJ). 2018;70:1133–43.
Zhang J, Chen H, Ma Y, Xiao Y, Niu N, Lin W, et al. Characterizing IgG4-related disease with 18F-FDG PET/CT: a prospective cohort study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:1624–34.
van der Heijde D, Aletaha D, Carmona L, Edwards CJ, Kvien TK, Kouloumas M, et al. 2014 update of the EULAR standardised operating procedures for EULAR-endorsed recommendations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:8–13.
Kamisawa T, Okazaki K, Kawa S, Ito T, Inui K, Irie H, et al. Amendment of the Japanese consensus guidelines for autoimmune pancreatitis, 2013 III. Treatment and prognosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2014;49:961–70.
Masaki Y, Matsui S, Saeki T, Tsuboi H, Hirata S, Izumi Y, et al. A multicenter phase II prospective clinical trial of glucocorticoid for patients with untreated IgG4-related disease. Mod Rheumatol Taylor & Francis. 2017;27:849–54.
Wu Q, Chang J, Chen H, Chen Y, Yang H, Fei Y, et al. Efficacy between high and medium doses of glucocorticoid therapy in remission induction of IgG4-related diseases: a preliminary randomized controlled trial. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017;20:639–46.
Kamisawa T, Shimosegawa T, Okazaki K, Nishino T, Watanabe H, Kanno A, et al. Standard steroid treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2009;58:1504–7.
de Pretis N, Amodio A, Bernardoni L, Campagnola P, Capuano F, Chari ST, et al. Azathioprine maintenance therapy to prevent relapses in autoimmune pancreatitis. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2017;8:e90.
Yunyun F, Yu C, Panpan Z, Hua C, Di W, Lidan Z, et al. Efficacy of cyclophosphamide treatment for immunoglobulin G4-related disease with addition of glucocorticoids. Sci Rep. 2017;7:6195.
Zhang P, Gong Y, Liu Z, Liu Y, Lin W, Li J, et al. Efficacy and safety of iguratimod plus corticosteroid as bridge therapy in treating mild IgG4-related diseases: a prospective clinical trial. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019;22:1479–88.
Wang Y, Li K, Gao D, Luo G, Zhao Y, Wang X, et al. Combination therapy of leflunomide and glucocorticoids for the maintenance of remission in patients with IgG4-related disease: a retrospective study and literature review. Intern Med J. 2017;47:680–9.
Della-torre E, Campochiaro C, Bozzolo EP, Dagna L, Scotti R, Nicoletti R, et al. Methotrexate for maintenance of remission in igg4-related disease. Rheumatol (United Kingdom). 2015;54:1934–6.
Yunyun F, Yu P, Panpan Z, Xia Z, Linyi P, Jiaxin Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of low dose Mycophenolate mofetil treatment for immunoglobulin G4-related disease: a randomized clinical trial. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019;58:52–60.
Wang L, Zhang P, Wang M, Feng R, Lai Y, Peng L, et al. Failure of remission induction by glucocorticoids alone or in combination with immunosuppressive agents in IgG4-related disease: A prospective study of 215 patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20:1–12.
Takanashi S, Kaneko Y, Takeuchi T. Effectiveness of tacrolimus on IgG4-related disease. Mod Rheumatol. 2019;29:892–4.
Huggett MT, Culver EL, Kumar M, Hurst JM, Rodriguez-Justo M, Chapman MH, et al. Type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis is associated with extrapancreatic organ failure, malignancy, and mortality in a prospective UK cohort. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:1675–83.
Carruthers MN, Topazian MD, Khosroshahi A, Witzig TE, Wallace ZS, Hart PA, et al. Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: a prospective, open-label trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:1171–7.
Campochiaro C, Della-Torre E, Lanzillotta M, Bozzolo E, Baldissera E, Milani R, et al. Long-term efficacy of maintenance therapy with rituximab for IgG4-related disease. Eur J Intern Med. 2019.
Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Takano K, Shimizu Y, Sakurai N, Suzuki C, et al. Efficacy of abatacept for IgG4-related disease over 8 months. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75:1576–8.
Simpson RS, Lau SKC, Lee JK. Dupilumab as a novel steroid-sparing treatment for IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;0:2–3.
Pasquali T, Schoenfield L, Spalding SJ, Singh AD. Orbital inflammation in IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Orbit. 2011;30:258–60.
Khan ML, Colby TV, Viggiano RW, Fonseca R. Treatment with bortezomib of a patient having hyper IgG4 disease. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. Elsevier company. 2010;10:217–9.
Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Stone JH, Shinagare S, Sainani N, Hasserjian RP, et al. Rethinking Ormond’s disease: “idiopathic” retroperitoneal fibrosis in the era of IgG4-related disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 2013;92:82–91.
Fernández-Codina A, Martínez-Valle F, Castro-Marrero J, Detorres I, Vilardell-Tarrés M, Ordi-Ros J. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: a clinicopathological study in 24 Spanish cases. Clin Rheumatol. 2013;32:889–93.
Kuraishi Y, Muraki T, Ashihara N, Ozawa M, Nakamura A, Watanabe T, et al. Validity and safety of endoscopic biliary stenting for biliary stricture associated with IgG4-related pancreatobiliary disease during steroid therapy. Endosc Int Open. 2019;07:E1410–8.
Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, Akamizu T, Azumi A, Carruthers MN, et al. International Consensus Guidance Statement on the Management and Treatment of IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken, NJ). 2015;67:1688–99.
Hellmich B, Agueda A, Monti S, Buttgereit F, de Boysson H, Brouwer E, et al. 2018 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of large vessel vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79:19–30.
Ebbo M, Grados A, Samson M, Groh M, Loundou A, Rigolet A, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of rituximab in IgG4-related disease: data from a French nationwide study of thirty-three patients. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0183844.
Charles P, Terrier B, Perrodeau É, Cohen P, Faguer S, Huart A, et al. Comparison of individually tailored versus fixed-schedule rituximab regimen to maintain ANCA-associated vasculitis remission: results of a multicentre, randomised controlled, phase III trial (MAINRITSAN2). Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:1143–9.
Fernández-Codina A, Pinilla B, Pinal-Fernández I, López C, Fraile-Rodríguez G, Fonseca-Aizpuru E, et al. Treatment and outcomes in patients with IgG4-related disease using the IgG4 responder index. Jt Bone Spine. 2018;85:721–6.
Omar D, Chen Y, Cong Y, Dong L. Glucocorticoids and steroid sparing medications monotherapies or in combination for IgG4-RD: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019.
Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Kulikova M, Lu L, Deshpande V, et al. Predictors of disease relapse in IgG4-related disease following rituximab. Rheumatology. 2016;55:1000–8.
Berti A, Della-Torre E, Gallivanone F, Canevari C, Milani R, Lanzillotta M, et al. Quantitative measurement of 18F-FDG PET/CT uptake reflects the expansion of circulating plasmablasts in IgG4-related disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017;56:2084–92.
Martínez-Valle F, Orozco-Gálvez O, Fernández-Codina A. Update in ethiopathogeny, diagnosis and treatment of the IgG4 related disease. Med Clin (Barc). Elsevier España, S.L.U. 2018;151:18–25.
Lin W, Zhang P, Chen H, Chen Y, Yang H, Zheng W, et al. Circulating plasmablasts/plasma cells: a potential biomarker for IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Res Ther. Arthritis Research & Therapy. 2017;19:25.
Carruthers MN, Stone JH, Deshpande V, Khosroshahi A. Development of an IgG4-RD responder index. Int J Rheumatol. 2012;2012:1–7.
Perugino CA, Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Maehara T, Wallace ZS, Pillai S, et al. Emerging Treatment Models in Rheumatology: IgG4-Related Disease: Insights Into Human Immunology and Targeted Therapies. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken, NJ). 2017;69:1722–32.
Viela Bio Reports Third Quarter 2019 Financial Results and Business Highlights [Internet]. [cited 2020 Apr 8]. Available from: https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1734517/000156459019043518/ck0001734517-ex991_6.htm.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Dr. Fernandez Codina reports grants from Scleroderma Society of Ontario, grants from Saint Joseph’s Health Care London Foundation, personal fees from Actelion, grants from Medicina, other from Catalan-Balearic Society of Internal Medicine, outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest relevant to this manuscript.
Human and Animal Rights
All reported studies/experiments with human or animal subjects performed by the authors have been previously published and compiled with all applicable ethical standards (including the Helsinki declaration and its amendments, institutional/national research committee standards, and international/national/institutional guidelines).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Vasculitis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández-Codina, A., Orozco-Gálvez, O. & Martínez-Valle, F. Therapeutic Options in IgG4-Related Disease. Curr Treat Options in Rheum 6, 191–204 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40674-020-00147-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40674-020-00147-w