Abstract
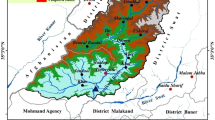
The present study demonstrates the usefulness of remote sensing data for analyzing the flash flood risk in Uhl River watershed situated in the western Lesser Himalayan region. This is one of the most vulnerable flash flood watersheds in Himachal Pradesh which, suffers heavy damages to man-made features almost every year. In this study different morphometric properties that direct the hydrological response and pertinent to flash flood risk of the watershed have been used to prioritize the sub-watersheds using weighted sum analysis (WSA) model. The result indicates that 12.83 and 16.94 percent of the total area come under very high and high flash flood risk respectively. In addition, the Snyder’s synthetic unit hydrograph method was employed to assess the hydrological behavior and prioritization of sub-basins which shows that sub-basins falling under very high and high-risk group have low lag time and high peak discharge per unit of watershed area. This study concludes Watershed 7 and 8 of Uhl River basin in Himachal Pradesh comes under high priority class and is vulnerable to flash floods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Activity Report (2007–2011) Himachal Pradesh State Disaster Management Authority (HP SDMA)
Aher P, Adinarayana J, Gorantiwar S (2014) Quantification of morphometric characterization and prioritization for management planning in semi-arid tropics of India: a remote sensing and GIS approach. J Hydrol 511:850–860
Ahmed MY, Pradhan B, Hassan AH (2011) Flash flood risk estimation along the St. Katherine road, southern Sinai, Egypt using GIS based morphometry and satellite imagery. Environ Earth Sci 62(3):611–623
Angillieri MYE (2008) Morphometric analysis of Colanguil river basin and flash flood hazard, San Juan, Argentina. Environ Geol 55(1):107–111
Arun PS, Jana R, Nathawat MS (2005) A rule based physiographic characterization of a drought prone watershed applying remote sensing and GIS. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 33(2):189
Bajabaa S, Masoud M, Al-Amri N (2014) Flash flood hazard mapping based on quantitative hydrology, geomorphology and GIS techniques (case study of Wadi Al Lith, Saudi Arabia). Arabian J Geosci 7(6):2469–2481
Bloschl G (2008) Interactive comment on “A look at the links between drainage density and flood statistics” by B. Pallard et al. Hydrol. Earth Syst Sci Discuss 5:S2108–S2111
Chandniha SK, Kansal ML (2017) Prioritization of sub-watersheds based on morphometric analysis using geospatial technique in Piperiya watershed, India. Appl Water Sci 7(1):329–338. doi:10.1007/s13201-014-0248-9
Dimri AP, Chevuturi A, Niyogi D, Thayyen RJ, Ray K, Tripathi SN, Pandey AK, Mohanty UC (2017) Cloudbursts in Indian Himalayas: a review. Earth-Science Reviews
District Disaster Management Authority (DDMA) Mandi (2012) The Government of India–UNDP disaster risk reduction (DRR) Programme (2009–12)
Fairfield J, Leymarie P (1991) Drainage networks from grid digital elevation models. Water Resour Res 30(6):1681–1692
Gardener JS (2010) Natural hazards risk in the Kullu district, Himachal Pradesh, India. Geogr Rev 92(2):282–306
Gardiner V, Gregory KJ (1982) Drainage density in rainfall-runoff modelling. In: Singh VP (ed) Rainfall-runoff relationships. Water Resources Publications, Littleton
Ghoneim E, Foody GM (2013) Assessing flash flood hazard in an arid mountainous region. Arab J Geosci 6(4):1191–1202
Greenlee DD (1987) Raster and vector processing for scanned linework. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 53(10):1383–1387
Groundwater information booklet Mandi district, Himachal Pradesh (2013) Central ground water board northern Himalayan region Dharamshala September, 2013
Hewitt K (1982) Natural dams and outburst floods of the Karakoram Himalaya. In: Proceedings of the Exeter symposium IAHS Publ. 138
Hewitt K (1993) Torrential rains in central Karakoram, 9–10 September 1992. Geomorphological impacts and implications for climate change. Mount Res Dev 13(4):371–375
Horton RE (1932) Drainage basin characteristics. Trans Am Geophys Union 13:350–361
Horton RE (1945) Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins: hydro physical approach to quantitative morphology. Geol Soc Am Bull 56:275–370
Jaiswal R et al (2014) Watershed prioritization using Saaty’s AHP based decision support for soil conservation measures. Water Resour Manag 28(2):475–494
Jamwal CS, Wangu AK (2012) Geology and mineral resources of Himachal Pradesh. Misc Publ 30:17
Javed A, Khanday MY, Ahmed R (2009) Prioritization of subwatersheds based on morphometric and land use analysis using remote sensing and GIS techniques. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 37(2):261
Jenson SK, Domingue JO (1988) Extracting topographic structure from digital elevation data for geographic information system analysis. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 54(11):1593–1600
Jonkman SN (2005) Global perspectives on loss of human life caused by floods. Nat Hazards 34(2):151–175
Katiyar R, Gara PK, Jain SK (2006) Watershed prioritization and reservoir sedimentation using remote sensing data. Geocarto Int 21(3):55–60
Kochel RC (1988) Geomorphic impact of large floods: review and new perspectives on magnitude and frequency. In: Baker V, Kochel R, Patton P (eds) Flood geomorphology. Wiley, New York, pp 169–187
Kumar KJA, Walia A (2012) India Disaster Report. National Institute of Disaster Management, IIPA Campus, New Delhi.
Lastra J, Fernandez E, Diez-Herrero A, Marquinez J (2008) Flood hazard delineation combining geomorphological and hydrological methods: an example in the Northern Iberian Peninsula. Nat Hazards 45(2):277–293
Magesh NS, Jitheshlal KV, Chandrasekar N, Jini KV (2013) Geographical information system based morphometric analysis of Bharathapuzha river basin, Kerala, India. Appl Water Sci 3(2):467–477
Maidment DR (2002) ArcHydro GIS for water resources. Esri Press, California
Martin D, Saha SK (2007) Integrated approach of using remote sensing and GIS to study watershed prioritization and productivity. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 35(1):21–30
Merz R, Bloschl G (2008) Flood frequency hydrology: 1. Temporal, spatial, and causal expansion of information, Water Resource Research
Moussa R (2003) On morphometric properties of basins, scale effects and hydrological response. Hydrol Process 17(1):33–58
Miller VC (1953) A quantitative geomorphologic study of drainage basin characteristics in the Clinch Mountain area, Virginia and Tennessee, Project NR 389042, Tech Report 3. Columbia University Department of Geology, ONR Geography Branch, New York
Nag SK, Chakraborty S (2003) Influence of rock types and structures in the development of drainage network in the hard rock area. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 31(1):25–35
Nookaratanam K, Srivastava YK, Venkateshwara RV, Amminedu E, Murthy KSR (2005) Check dam positioning by prioritization of micro-watersheds using SYI model and morphometric analysis—remote sensing and GIS perspective. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 33(1):25
Patton PC (1988) Flood geomorphology. Wiley, New York
Patton PC, Baker VR (1976) Morphometry and floods in small drainage basins subject to diverse hydrogeomorphic controls. Water Resour Res 12(5):941–952
Pradhan B (2010) Flood susceptible mapping and risk area estimation using logistic regression, GIS and remote sensing. J Spat Hydrol 9(2):2–12
Pradhan B, Shafie M (2009) Flood hazard assessment for cloud prone rainy areas in a typical tropical environment. Disaster Adv 2(2):7–15
Reddy OGP, Maji AK, Gajbhiye SK (2004) Drainage morphometry and its influence on landform characteristics in a basaltic terrain, Central India—a remote sensing and GIS approach. Int J Appl Earth Observation Geoinf 6(1):1–16
Romshoo S, Bhat S, Rashid I (2012) Geoinformatics for assessing the morphometric control on hydrological response at watershed scale in the upper Indus basin. J Earth Syst Sci 121(3):659–686
Sah MP, Mazari RK (1998) Anthropogenically accelerated mass movement in the Kullu valley, Himachal Pradesh, India. Geomorphology 26(1):123–138
Schumm SA (1956) Evolution of drainage systems and slopes in Badlands at Perth Amboy, New Jersey. Geol Soc Am Bull 67:597–646
Snyder FF (1938) Synthetic unit graphs. Trans Am Geophys Union 19:447–454
Sreedevi PD, Owais S, Khan HH, Ahmed S (2009) Morphometric analysis of a watershed of south India using SRTM data and GIS.J Geol Soc India 73(4):543–552
State of Environment Report on Himachal Pradesh. Department of Environment, Science and Technology, Government of Himachal Pradesh. Naryan Villa, Shimla (Himachal Pradesh)
Strahler AN (1964) Handbook of applied hydrology. McGraw Hill Book Company, New York
Sujatha ER, Selvakumar R, Rajasimman UAB (2014) Watershed prioritization of Palar sub-watershed based on the morphometric and land use analysis. J Mt Sci. doi:10.1007/s11629-012-2628-7
Tarboton DG, Bras RL, Rodriguez I (1991) On the extraction of channel networks from digital elevation data. Hydrol Process 5(1):81–100
Thomas J, Joseph S, Thrivikramji KP, Abe G, Kannan N (2012) Morphometrical analysis of two tropical mountain river basins of contrasting environmental settings in the southernWestern Ghats, India. Environ Earth Sci 66:8
US Army Corps of Engineers (1959) Engineering construction flood control. Engg School, Fort Belvoir
Youssef AM, Hegab MA (2005) Using geographic information systems and statistics for developing a database management system of the flood hazard for Ras Gharib area, Eastern Desert, Egypt. In: The fourth international conference on the geology of Africa, vol 2
Youssef A, Pradhan B, Hassan A (2011) Flash flood risk estimation along the St. Katherine Road, Southern Sinai, Egypt using GIS based morphometry and satellite imagery. Environ Earth Sci 62:611–623. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0551-1
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India for providing fund and supporting this work. We are thankful to Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) for providing Cartosat-1 Digital Elevation Model (CartoDEM) data. We also extend our thanks to Forest survey of India for providing forest cover map of the study area.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, R.N., Pani, P. Geo-hydrological analysis and sub watershed prioritization for flash flood risk using weighted sum model and Snyder’s synthetic unit hydrograph. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 3, 1491–1502 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0354-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0354-4