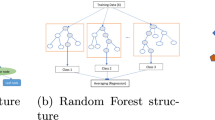
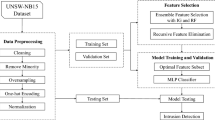
Abstract
Tropospheric ozone (O3), as an air pollutant is increasing at an alarming rate in urban areas. The concentration of ozone is affected by precursor pollutants, such as particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5), carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitric oxide (NO), and meteorological parameters, such as air temperature (AT), relative humidity (RH), global solar radiation (SR), wind direction (WD), and wind speed (WS) of the area. Ozone is a secondary pollutant and strong oxidizing agent injurious to human health. The present study aimed to identify the most crucial factors that influence ozone formation and to develop an ozone prediction model using artificial neural network with optimal inputs. The data obtained from Limbayat, real-time air pollutants monitoring station of Surat city, have been used to evolve the model, followed by feature selection techniques, namely, sensitivity analysis, Boruta algorithm, and recursive feature elimination algorithm (RFE). Finally, 6/14 influencing parameters have been identified using an attribute selection approach. Interestingly, “hour of the day” was found the most prominent and governing parameter among the 14 parameters after applying various feature selection techniques in the experiments. The result showed that the efficiency of the prediction model was 79.4% when six parameters were used in the machine learning algorithms.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Abiodun OI, Jantan A, Omolara AE, Dada KV, Mohamed NA, Arshad H (2018) State-of-the-art in artificial neural network applications: a survey. Heliyon 4:e00938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00938
Arsić M, Mihajlović I, Nikolić D, Živković Ž, Panić M (2020) Prediction of ozone concentration in ambient air using multilinear regression and the artificial neural networks methods. Ozone Sci Eng 42:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919512.2019.1598844
Bachu V, Anuradha J (2019) A review of feature selection and its methods. Cybern Inf Technol 19:3–26. https://doi.org/10.2478/CAIT-2019-0001
Bekesiene S, Meidute-Kavaliauskiene I, Vasiliauskiene V (2021) Accurate prediction of concentration changes in ozone as an air pollutant by multiple linear regression and artificial neural networks. Mathematics 9:1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9040356
Chattopadhyay S, Bandyopadhyay G (2007) Artificial neural network with backpropagation learning to predict mean monthly total ozone in Arosa, Switzerland. Int J Remote Sens 28:4471–4482. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160701250440
Chen RC, Dewi C, Huang SW, Caraka RE (2020) Selecting critical features for data classification based on machine learning methods. J Big Data 7:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-020-00327-4
CPCB (2014) National air quality index report. https://app.cpcbccr.com/ccr_docs/FINAL-REPORT_AQI_.pdf. Accessed date 10 Jun 2021
Degenhardt F, Seifert S, Szymczak S (2019) Evaluation of variable selection methods for random forests and omics data sets. Brief Bioinform 20:492–503. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbx124
Dubey A (2018) Feature Selection Using Random forest. https://towardsdatascience.com/feature-selection-using-random-forest-26d7b747597f. Accessed date 8 June 2021
EduPristine (2018) All about sensitivity analysis. https://www.edupristine.com/blog/all-about-sensitivity-analysis. Accessed date 8 June 2021
Elangasinghe MA, Singhal N, Dirks KN, Salmond JA (2014) Development of an ANN–based air pollution forecasting system with explicit knowledge through sensitivity analysis. Atmos Pollut Res 5:696–708. https://doi.org/10.5094/APR.2014.079
Filali A, Jlassi C, Arous N (2017) Recursive feature elimination with ensemble learning using SOM variants. Int J Comput Intell Appl 16:170004. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1469026817500043
Gunthe S (2006) Study of ozone and its precursors over the Indian tropical Region. Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology
Gupta H, Razavi S (2017) Chapter 20—Challenges and future outlook of sensitivity analysis. Ensitivity analysis in earth observation modelling. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 397–415
Kandya A (2013) Forecasting the tropospheric ozone using artificial neural network modelling approach: a case study of megacity Madras, India. J Civ Environ Eng 01:1–5. https://doi.org/10.4172/2165-784x.s1-006
Kursa MB, Rudnicki WR (2010) Feature selection with the boruta package. J Stat Softw 36:1–13. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v036.i11
Mago VK (2011) Cross-disciplinary applications of artificial intelligence and pattern recognition. IGI Global, Pennsylvania
Nolan SA, Heinzen T (2016) Essentials of statistics for the behavioral sciences. Macmillion, Newyork
Okon AN, Adewole SE, Uguma EM (2020) Artificial neural network model for reservoir petrophysical properties: porosity, permeability and water saturation prediction. Model Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-01012-4
Pisoni E, Albrecht D, Mara TA, Rosati R, Tarantola s, Thunis P, (2018) Application of uncertainty and sensitivity analysis to the air quality SHERPA modelling tool. Atmos Environ 183:84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.04.006
Roche B, Duboz R (2017) Individual-based models for public health. Handb Stat 37:347–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.host.2017.08.008
Shahriar SA, Kayes I, Hasan K, Salam MA, Chowdhury S (2020) Applicability of machine learning in modeling of atmospheric particle pollution in Bangladesh. Air Qual Atmos Health 13:1247–1256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-020-00878-8
Spicer CW, Joseph DW, Ollison WM (2010) A re-examination of ambient air ozone monitor interferences. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 60:1353–1364. https://doi.org/10.3155/1047-3289.60.11.1353
Suruliandi A, Mariammal G, Raja SP (2021) Crop prediction based on soil and environmental characteristics using feature selection techniques. Math Comput Model Dyn Syst 27:117–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/13873954.2021.1882505
Verma N (2018) An investigation of ozone formation through its precursors (CO; NOX; VOC) and Its loss process at a sub-urban site of Agra. Dayalbagh Educational Institute, DayalBagh
Wu T, Zhao Z, Wei H, Peng Y (2020) Research on PM2.5 integrated prediction model based on Lasso-RF-GAM. Commun Comput Inf Sci 1234CCIS:83–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7205-0_8
Zhang JJ, Wei Y, Fang Z (2019) Ozone Pollution : A Major Health Hazard Worldwide. Front Immunol 10:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02518
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Surat Municipal Corporation for providing air quality data for this study.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors were equally involved in analyzing and editing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapadia, D., Jariwala, N. Prediction of tropospheric ozone using artificial neural network (ANN) and feature selection techniques. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 8, 2183–2192 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-021-01220-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-021-01220-6