Abstract
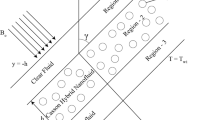
Analysis of thermal and fluid phenomena based on the fluid dynamics theory leads to understanding of fundamental mechanisms in modern technologies. Thermal/fluid transport is critical to many applications, such as photothermal cancer therapy, solar thermal evaporation and polymer composites. The current study focusses to investigate the effect of magnetohydrodynamics, Hall currents and electroosmosis on the propulsion of Sutterby nanofluids in a porous microchannel. The Brownian motion and thermophoresis effects have also been considered. The governing equations for the momentum, temperature and nanoparticle volume fraction have been modified under the suitable non-dimensional quantities. The resulting dimensionless system of equations have been solved using bvp4c package in computational software MATLAB. The pictorial representations have been presented for various flow quantities with respect to sundry fluid parameters. It is noted from the investigation that, there is a decrease in fluid velocity with an increase in Hartmann number, temperature decreases with the increment in radiation parameter and nanoparticle volume fraction reduces with the increment of Prandtl number and thermophoresis parameter. The results obtained for the Sutterby nanofluid propulsion model reveal many engrossing behaviors and has many applications such as disease diagnostics and cancerous tissues destruction, and that provide a further dimension to investigate the nanofluid flow problems with thermophysical properties in two/three dimensions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Das, S.K., Choi, S.U., Yu, W., Pradeep, T.: Nanofluids: Science and Technology. Wiley, New York (2007)
Xuan, Y., Li, Q., Hu, W.: Aggregation structure and thermal conductivity of nanofluids. AIChE J. 49(4), 1038–1043 (2003)
Saidur, R., Leong, K., Mohammed, H.A.: A review on applications and challenges of nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15(3), 1646–1668 (2011)
Akbar, N.S., Nadeem, S.: Nano Sutterby fluid model for the peristaltic flow in small intestines. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 10(10), 2491–2499 (2013)
Akbar, N.S.: Peristaltic flow of a Sutterby nano fluid with double-diffusive natural convection. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 12(8), 1546–1552 (2015)
Hayat, T., Zahir, H., Mustafa, M., Alsaedi, A.: Peristaltic flow of Sutterby fluid in a vertical channel with radiative heat transfer and compliant walls: a numerical study. Results Phys. 6, 805–810 (2016)
Sheikholeslami, M., Ganji, D.D., Javed, M.Y., Ellahi, R.: Effect of thermal radiation on magnetohydrodynamics nanofluid flow and heat transfer by means of two phase model. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 36–43 (2015)
Sheikholeslami, M., Shehzad, S.: Magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid convection in a porous enclosure considering heat flux boundary condition. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 106, 1261–1269 (2017)
Reddy, M.G., Makinde, O.: Magnetohydrodynamic peristaltic transport of Jeffrey nanofluid in an asymmetric channel. J. Mol. Liq. 223, 1242–1248 (2016)
Hayat, T., Muhammad, T., Shehzad, S.A., Alsaedi, A.: On magnetohydrodynamic flow of nanofluid due to a rotating disk with slip effect: a numerical study. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 315, 467–477 (2017)
Pattnaik, P.K., Mishra, S., Bhatti, M.M.: Duan-Rach approach to study Al2O3-Ethylene Glycol C2H6O2 nanofluid flow based upon KKL model. Inventions 5(3), 45 (2020)
Majeed, A., Zeeshan, A., Bhatti, M.M., Ellahi, R.: Heat transfer in magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles suspended in conventional fluids: Refrigerant-134A (C2H2F4), kerosene (C10H22), and water (H2O) under the impact of dipole, Heat Transfer Research, 51(3), 217–232 (2020)
Zhang, L., Bhatti, M.M., Marin, M., Mekheimer, K.S.: Entropy analysis on the blood flow through anisotropically tapered arteries filled with Magnetic Zinc-Oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. Entropy 22(10), 1070 (2020)
Riaz, A., Ellahi, R., Bhatti, M.M., Marin, M.: Study of heat and mass transfer in the Eyring-Powell model of fluid propagating peristaltically through a rectangular compliant channel, Heat Transfer Research, 50(16), 1539–1560 (2019)
Bhatti, M.M., Alamri, S.Z., Ellahi, R., Abdelsalam, S.I.: Intra-uterine particle-fluid motion through a compliant asymmetric tapered channel with heat transfer, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2020) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10233-9
Waheed, S., Noreen, S., Hussanan, A.: Study of heat and mass transfer in electroosmotic flow of third order fluid through peristaltic microchannels. Appl. Sci. 9(10), 2164 (2019)
Hui, T.H., Cho, W.C., Fong, H.W., Yu, M., Kwan, K.W., Ngan, K.C., Wong, K.H., Tan, Y., Yao, S., Jiang, H., Gu, Z., Lin, Y.: An electro-osmotic microfluidic system to characterize cancer cell migration under confinement. J. R. Soc. Interface 16(155), 0190062 (2019)
Shih, Y.C., Liao, C.R., Chung, I.C., Chang, Y.S., Chang, P.L.: Simultaneous separation of five major ribonucleic acids by capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence in the presence of electroosmotic flow: Application to the rapid screening of 5S rRNA from ovarian cancer cells. Analytica chimica acta 847, 73–79 (2014)
Nath, B., Raza, A., Sethi, V., Dalal, A., Ghosh, S.S., Biswas, G.: Understanding flow dynamics, viability and metastatic potency of cervical cancer (HeLa) cells through constricted microchannel. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 1–10 (2018)
Ganguly, S., Sarkar, S., Hota, T.K., Mishra, M.: Thermally developing combined electroosmotic and pressure-driven flow of nano fluids in a microchannel under the effect of magnetic field. Chem. Eng. Sci. 126, 10–21 (2015)
Aparajita,A., Satapathy, A.K.: Numerical analysis of heat transfer characteristics of combined electroosmotic and pressure-driven fully developed flow of power law nanofluids in microchannels, Proceedings of the 3rd European Conference on Microfluidics, (2015)
Prakash, J., Ramesh, K., Tripathi, D., Kumar, R.: Numerical simulation of heat transfer in blood flow altered by electroosmosis through tapered micro-vessels. Microvasc. Res. 118, 162–172 (2018)
Tripathi, D., Sharma, A., Beg, O.A.: Electrothermal transport of nano fluids via peristaltic pumping in a finite microchannel: effects of Joule heating and helmholtz- smoluchowski velocity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 111, 138–149 (2017)
Vasu, N., De, S.: Electroosmotic flow of power-law fluids at high zeta potentials. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 368(1–3), 44–52 (2010)
Hatami, M., Ganji, D.: Heat transfer and flow analysis for sa-tio2 non-newtonian nanofluid passing through the porous media between two coaxial cylinders. J. Mol. Liq. 188, 155–161 (2013)
Kameswaran, P., Shaw, S., Sibanda, P., Murthy, P.: Homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in a nanofluid flow due to a porous stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 57(2), 465–472 (2013)
Mahdi, R.A., Mohammed, H., Munisamy, K., Saeid, N.: Review of convection heat transfer and fluid flow in porous media with nanofluid. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 41, 715–734 (2015)
Sheikholeslami, M., Ellahi, R., Ashorynejad, H., Domairry, G., Hayat, T.: Effects of heat transfer in flow of nanofluids over a permeable stretching wall in a porous medium. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 11(2), 486–496 (2014)
Ting, T.W., Hung, Y.M., Guo, N.: Entropy generation of viscous dissipative nanofluid flow in thermal non-equilibrium porous media embedded in microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 81, 862–877 (2015)
Zhang, C., Zheng, L., Zhang, X., Chen, G.: Magnetohydrodynamic flow and radiation heat transfer of nanofluids in porous media with variable surface heat flux and chemical reaction. Appl. Math. Modelling 39(1), 165–181 (2015)
Prakash, J., Ramesh, K., Tripathi, D., Kumar, R.: Numerical simulation of heat transfer in blood flow altered by electroosmosis through tapered micro-vessels. Microvasc. Res. 118, 162–172 (2018)
Lodhi, R.K., Ramesh, K.: Comparative study on electroosmosis modulated flow of MHD viscoelastic fluid in the presence of modified Darcy’s law. Chin. J. Phys. 68, 106–120 (2020)
Hayat, T., Afzal, S., Khan, M.I., Alsaedi, A.: Irreversibility aspects to flow of Sutterby fluid subject to nonlinear heat flux and Joule heating. Appl. Nanosci. 9(5), 1215–1226 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramesh, K., Rawal, M. & Patel, A. Numerical Simulation of Radiative MHD Sutterby Nanofluid Flow Through Porous Medium in the Presence of Hall Currents and Electroosmosis. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 7, 30 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-021-00971-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-021-00971-1