Abstract
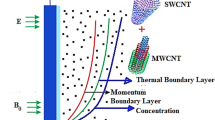
This communication reports on an innovative study of two-dimensional couple stress fluid 3 with effect of viscosity and conductivity. We proposed a new model based on temperature dependent variable thermal conductivity on kinetic theory. Our model assumes that thermal conductivity is a decreasing function of temperature rather than an increasing function. The effect of the three key parameters, viscosity, thermal conductivity and couple stress parameter are analyzed. The coupled non-linear system is further validated numerically using the spectral quasilinearization method. The method is found to be accurate and convergent. Increasing the temperature dependent parameter for viscosity is shown to reduce the heat mass transfer rates at the surface. Increasing thermal conductivity and the couple stress parameter increased the heat mass transfer rates on the boundary surface





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Animasaun, I.: Effects of thermophoresis, variable viscosity and thermal conductivity on free convective heat and mass transfer of non-darcian mhd dissipative casson fluid flow with suction and nth order of chemical reaction. J. Nigerian Math. Soc. 34(1), 11–31 (2015)
Bird, R.B., Stewart, W.E., Lightfoot, E.N.: Transport Phenomena. Wiley, New York (2001)
Bou-Said, B., Boucherit, H., Lahmar, M.: On the influence of particle concentration in a lubricant and its rheological properties on the bearing behavior. Mech. Ind. 13(2), 111–121 (2012)
Bridgman, P.W.: The thermal conductivity of liquids under pressure. Proc. Am. Acad. Arts Sci. 59(7), 141 (1923)
Cengel, Y.A., Cimbala, J.M.: Fluid Mechanics (Mcgraw-Hill Series in Mechanical Engineering). McGraw-Hill Sci. Eng. Math. 9, 198 (2004)
Choudhury, M., Hazarika, G.: The effects of variable viscosity and thermal conductivity on mhd oscillatory free convective flow past a vertical plate in slip flow regime with variable suction and periodic plate temperature. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 6(2), 277–283 (2013)
Choudhury, M., Hazarika, G.C.: The effects of variable viscosity and thermal conductivity on mhd flow due to a point sink. Matematicas EEnsenanza Universitaria 16(2), 183 (2008)
Dhlamini, M., Kameswaran, P.K., Sibanda, P., Motsa, S., Mondal, H.: Activation energy and binary chemical reaction effects in mixed convective nanofluid flow with convective boundary conditions. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 6(2), 149–158 (2019)
Dhlamini, M., Mondal, H., Sibanda, P., Motsa, S.: Spectral quasi-linearization methods for powell-eyring MHD flow over a nonlinear stretching surface. J. Nanofluids 7(5), 917–927 (2018)
Dhlamini, M., Mondal, H., Sibanda, P., Motsa, S.: Activation energy and entropy generation in viscous nanofluid with higher order chemically reacting species. Int. J. Ambient Energy 1–13, 7 (2020)
Dhlamini, M., Mondal, H., Sibanda, P., Motsa, S.: Rotational nanofluids for oxytactic microorganisms with convective boundary conditions using bivariate spectral quasi-linearization method. J. Cent. South Univ. 27(3), 824–841 (2020)
Elbarbary, E.M.E., Elgazery, N.S.: Chebyshev finite difference method for the effects of variable viscosity and variable thermal conductivity on heat transfer from moving surfaces with radiation. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 43(9), 889–899 (2004)
Goqo, S., Oloniiju, S., Mondal, H., Sibanda, P., Motsa, S.: Entropy generation in MHD radiative viscous nanofluid flow over a porous wedge using the bivariate spectral quasi-linearization method. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 12, 774–788 (2018)
Hassanien, I., Essawy, A., Moursy, N.: Variable viscosity and thermal conductivity effects on combined heat and mass transfer in mixed convection over a UHF/UMF wedge in porous media: the entire regime. Appl. Math. Comput. 145(2–3), 667–682 (2003)
Hayat, T., Abbasi, F., Ahmad, B., Alsaedi, A.: Mhd mixed convection peristaltic flow with variable viscosity and thermal conductivity. Sains Malays 43(10), 1583–1590 (2014)
Hayat, T., Imtiaz, M., Alsaedi, A.: Effects of homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in flow of powell-eyring fluid. J. Cent. South Univ. 22(8), 3211–3216 (2015)
Hayat, T., Khan, M.I., Farooq, M., Gull, N., Alsaedi, A.: Unsteady three-dimensional mixed convection flow with variable viscosity and thermal conductivity. J. Mol. Liq. 223, 1297–1310 (2016)
Hayat, T., Waqas, M., Shehzad, S.A., Alsaedi, A.: Mixed convection flow of viscoelastic nanofluid by a cylinder with variable thermal conductivity and heat source/sink. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Heat Fluid Flow 26(1), 214–234 (2016)
Hazarika, G., Jadav, K.: Effects of variable viscosity and thermal conductivity on mhd free convective flow along a vertical porous plate with viscous dissipation. Int. J. Math. Trends Technol. 15(1), 70–85 (2014)
Horibata, S., Yarimitsu, S., Fujie, H.: Influence of synovial fluid pressure increase on the biphasic lubrication property of articular cartilage. Proc. Mech. Eng. Congr. J0260104, 68 (2017)
Kaladhar, K.: Natural convection flow of couple stress fluid in a vertical channel with hall and joule heating effects. Procedia Eng. 127, 1071–1078 (2015)
Kannan, T., Moorthy, M.: Effects of variable viscosity on power-law fluids over a permeable moving surface with slip velocity in the presence of heat generation and suction. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 9(6), 9–22 (2016)
Khan, W., Yousafzai, F.: On the exact solutions of couple stress fluids. Adv. Trends Math. 1, 27–32 (2014)
Khan, Y., Wu, Q., Faraz, N., Yildirim, A.: The effects of variable viscosity and thermal conductivity on a thin film flow over a shrinking/stretching sheet. Comput. Math. Appl. 61(11), 3391–3399 (2011)
Khound, P., Hazaika, G.: The effect of variable viscosity and thermal conductivity on liquid film on an unsteady stretching surface. Proc. 46th Ann. Tech. Session Ass. Sc. Soc. 22, 47–56 (2000)
Lai, F., Kulacki, F.: The effect of variable viscosity on convective heat transfer along a vertical surface in a saturated porous medium. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 33(5), 1028–1031 (1990)
Lai, W.M., Kuei, S.C., Mow, V.C.: Rheological equations for synovial fluids. J. Biomech. Eng. 100(4), 169 (1978)
Lin, J.-R.: Linear stability analysis of rotor-bearing system: couple stress fluid model. Comput. Struct. 79(8), 801–809 (2001)
Lin, J.-R., Lu, Y.-M.: Steady-state performance of wide parabolic-shaped slider bearings with a couple stress fluid. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 12(4), 239–246 (2004)
Manjunatha, S., Gireesha, B.: Effects of variable viscosity and thermal conductivity on MHD flow and heat transfer of a dusty fluid. Ain Shams Eng. J. 7(1), 505–515 (2016)
Misra, J.C., Adhikay, S.D., Mallick, B., Sinha, A.: Mathematical modeling of blood flow in arteries subject to vibrating environment. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 18(01), 1850001 (2018)
Monica, M., Vittal, C., Reddy, M.C.K.: Stagnation point flow of a mhd powell-eyring fluid over a nonlinearly stretching sheet in the presence of heat source/sink. J. Progress. Res. Math. 8(2), 1290–1300 (2016)
Motsa, S.S., Magagula, V.M., Sibanda, P.: A bivariate chebyshev spectral collocation quasilinearization method for nonlinear evolution parabolic equations. Sci. World J. 2014, 1–13 (2014)
Motsa, S.S., Mutua, S.F., Stanford, S.: Solving nonlinear parabolic partial differential equations using multidomain bivariate spectral collocation method. Nonlinear Syst. Des. Anal. Estim. Control 2, 174 (2016). https://doi.org/10.5772/64600
Pal, D., Mondal, H.: Effects of temperature-dependent viscosity and variable thermal conductivity on MHD non-darcy mixed convective diffusion of species over a stretching sheet. J. Egypt. Math. Soc. 22(1), 123–133 (2014)
Panigrahi, S., Reza, M., Mishra, A.K.: Mixed convective flow of a powell-eyring fluid over a non-linear stretching surface with thermal diffusion and diffusion thermo. Procedia Eng. 127, 645–651 (2015)
Patil, P.M.: Effects of surface mass transfer on steady mixed convection flow from vertical stretching sheet with variable wall temperature and concentration. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Heat Fluid Flow 22(3), 287–305 (2012)
Polezhaev, Y.V., Frolov, G.A.: Influence of thermal conductivity of a material on an unsteady heat removal parameter. J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys. 62, 391–396 (1992)
Ram, N.: Influence of couple stress lubricants on hole-entry hybrid journal bearings. J. Tribol. 14, 32–49 (2017)
Rao, T.V.V.L.N., Sufian, S., Mohamed, N.M.: Analysis of nanoparticle additive couple stress fluids in three-layered journal bearing. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 431, 012023 (2013)
Sahu, M., Sharma, S., Agrawal, A.: Study of arterial blood flow in stenosed vessel using non-newtonian couple stress fluid model. Int. J. Dyn. Fluids 6(2), 248–257 (2000)
Samyuktha, N., Ravindran, R.: Thermal radiation effect on mixed convection flow over a vertical stretching sheet embedded in a porous medium with suction (injection). Procedia Eng. 127, 767–774 (2015)
Singh, C.: Lubrication theory for couple stress fluids and its application to short bearings. Wear 80(3), 281–290 (1982)
Sinha, P., Singh, C., Prasad, K.: Couple stresses in journal bearing lubricants and the effect of cavitation. Wear 67(1), 15–24 (1981)
Sithole, H., Mondal, H., Goqo, S., Sibanda, P., Motsa, S.: Numerical simulation of couple stress nanofluid flow in magnetoporous medium with thermal radiation and a chemical reaction. Appl. Math. Comput. 339, 820–836 (2018)
Srinivasacharya, D., Kaladhar, K.: Mixed convection flow of couple stress fluid in a non-darcy porous medium with soret and dufour effects. Journal of Porous Media 15(4), 415–422 (2012)
Srinivasacharya, D., Rao, G.M.: Mathematical model for blood flow through a bifurcated artery using couple stress fluid. Math. Biosci. 278, 37–47 (2016)
Stokes, V.K.: Couple stresses in fluids. Phys. Fluids 9(9), 1709–1715 (1966)
Wang, X., Zhu, K., Gui, C.: A study of a journal bearing lubricated by couple stress fluids considering thermal and cavitation effects. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 216(5), 293–305 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mlamuli Dhlamini, Hiranmoy Mondal, prepared original drafts of the research article and also write the methodology. Using the software validate our results. Prof. Sibanda and Prof. Motsa edited and review of our article
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhlamini, M., Mondal, H., Sibanda, P. et al. Numerical Analysis of Couple Stress Nanofluid in Temperature Dependent Viscosity and Thermal Conductivity. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 7, 48 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-021-00983-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-021-00983-x