Abstract
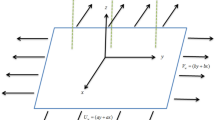
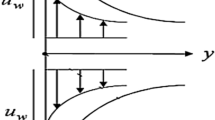
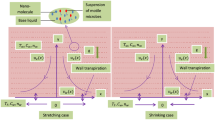
The underlying work includes the time-dependent flow and improved thermal transport for tangent hyperbolic nanofluids across an extending wedge. Self-motile microorganisms are suspended in the fluid to avoid agglomeration of tiny particles. Moreover, magnetic field, heat source, convectively heated boundary, and activation energy are considered. Mathematical formulation based on usual laws of conservation is non dimensionalized with emerging parameters through implementation of similarity transform to yield a corresponding set of ordinary partial differential equations. In the face of convective non linearity, a finite element discretization is harnessed to be coded and run on Matlab platform. The parametric calculation are carried out for faster and slower wedge. The rising strength of wedge angle, unsteadiness, and material law index recede the velocity distribution. The distribution of temperature upgrades directly against growing of Hartman number, thermophoresis, Biot number, material law index, and Brownian motion parameters. The concentration profile of nanoparticles decrease against Lewis number and activation energy, but it rises directly with higher input of activation energy. The computational results obtained through Matlab code blocks are corroborated with the existing literature and found to be a tolerable correlation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, R., Khan, W.A.: Effect of viscous dissipation and internal heat generation/absorption on heat transfer flow over a moving wedge with convective boundary condition. Heat Transf. Asian Res. 42(7), 589–602 (2013)
Akbar, N.S., Nadeem, S., Haq, R.U., Khan, Z.: Numerical solutions of magnetohydrodynamic boundary layer flow of tangent hyperbolic fluid towards a stretching sheet. Indian J. Phys. 87(11), 1121–1124 (2013)
Ali, B., Naqvi, R.A., Nie, Y., Khan, S.A., Sadiq, M.T., Rehman, A.U., Abdal, S.: Variable viscosity effects on unsteady mhd an axisymmetric nanofluid flow over a stretching surface with thermo-diffusion: Fem approach. Symmetry 12(2), 234 (2020)
Ali, B., Nie, Y., Khan, S.A., Sadiq, M.T., Tariq, M.: Finite element simulation of multiple slip effects on mhd unsteady maxwell nanofluid flow over a permeable stretching sheet with radiation and thermo-diffusion in the presence of chemical reaction. Processes 7(9), 628 (2019)
Ali, B., Nie, Y., Hussain, S., Habib, D., Abdal, S.: Insight into the dynamics of fluid conveying tiny particles over a rotating surface subject to cattaneo christov heat transfer, coriolis force, and arrhenius activation energy. Comput. Math. Appl. 93, 130–143 (2021)
Ali, B., Pattnaik, P., Naqvi, R.A., Waqas, H., Hussain, S.: Brownian motion and thermophoresis \(e_ects\) on bioconvection of rotating maxwell nanouid over a riga plate with arrhenius activation energy and cattaneo-christov heat ux theory. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 23, 100863 (2021)
Ali, B., Yu, X., Sadiq, M.T., Rehman, A.U., Ali, L.: A finite element simulation of the active and passive controls of the mhd effect on an axisymmetric nanofluid flow with thermo-diffusion over a radially stretched sheet. Processes 8(2), 207 (2020)
Atif, S., Hussain, S., Sagheer, M.: \(E_ect\) of thermal radiation on mhd micropolar carreau nanouid with viscous dissipation, joule heating, and internal heating.Sci. Iranica 26(6), 3875–3888 (2019)
Ariel, P.: Hiemenz flow in hydromagnetics. Acta Mech. 103(1–4), 31–43 (1994)
Atif, S., Hussain, S., Sagheer, M.: Effect of viscous dissipation and joule heating on mhd radiative tangent hyperbolic nanofluid with convective and slip conditions. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 41(4), 1–17 (2019)
Atif, S., Hussain, S., Sagheer, M.: Heat and mass transfer analysis of time-dependent tangent hyperbolic nanofluid flow past a wedge. Phys. Lett. A 383(11), 1187–1198 (2019)
Atif, S., Hussain, S., Sagheer, M.: Magnetohydrodynamic stratified bioconvective flow of micropolar nanofluid due to gyrotactic microorganisms. AIP Adv. 9(2), 025208 (2019)
Awaludin, I., Weidman, P., Ishak, A.: Stability analysis of stagnation-point flow over a stretching/shrinking sheet. AIP Adv. 6(4), 045308 (2016)
Beg, O., Aneja, M., Sharma, S., Kuharat, S., et al.: Computation of electro-conductive gyrotactic bioconvection from a nonlinear inclined stretching sheet under non-uniform magnetic field: simulation of smart bio-nano-polymer coatings for solar energy. Int. J. Modern Phys. B 75, 1–10 (2020)
Buongiorno, J.: Convective transport in nanofluids (2006)
Fatunmbi, E., Adeniyan, A.: Mhd stagnation point-flow of micropolar fluids past a permeable stretching plate in porous media with thermal radiation, chemical reaction and viscous dissipation. J. Adv. Math. Comput. Sci. 1–19 (2018)
Gupta, D., Kumar, L., Beg, O.A., Singh, B.: Finite-element analysis of transient heat and mass transfer in microstructural boundary layer flow from a porous stretching sheet. Comput. Therm. Sci. An Int. J. 6(2), (2014)
Hiemenz, K.: Die grenzschicht an einem in den gleichformigen flussigkeitsstrom eingetauchten geraden kreiszylinder. Dinglers Polytech. J. 326, 321–324 (1911)
Ibrahim, W., Gadisa, G.: Finite element method solution of boundary layer flow of powell-eyring nanofluid over a nonlinear stretching surface. J. Appl. Math. (2019)
Ilias, M.R., Rawi, N.A., Zaki, N.H.M., Shafie, S.: Aligned mhd magnetic nanofluid flow past a static wedge. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 7(3.28), 28–31 (2018)
Ishak, A., Nazar, R., Pop, I.: Falkner-skan equation for flow past a moving wedge with suction or injection. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 25(1–2), 67–83 (2007)
Jyothi, K., Reddy, P.S., Reddy, M.S.: Carreau nanofluid heat and mass transfer flow through wedge with slip conditions and nonlinear thermal radiation. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 41(10), 415 (2019)
Khan, S.A., Nie, Y., Ali, B.: Multiple slip effects on magnetohydrodynamic axisymmetric buoyant nanofluid flow above a stretching sheet with radiation and chemical reaction. Symmetry 11(9), 1171 (2019)
Khan, S.A., Nie, Y., Ali, B.: Multiple slip effects on mhd unsteady viscoelastic nano-fluid flow over a permeable stretching sheet with radiation using the finite element method. SN Appl. Sci. 2(1), 66 (2020)
Khan, S.U., Waqas, H., Bhatti, M., Imran, M.: Bioconvection in the rheology of magnetized couple stress nanofluid featuring activation energy and wu’s slip. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 45(1), 81–95 (2020)
Martínez-Merino, P., Midgley, S., Martín, E.I., Estellé, P., Alcántara, R., Sánchez-Coronilla, A., Grau-Crespo, R., Navas, J.: Novel ws2-based nanofluids for concentrating solar power: performance characterization and molecular-level insights. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. (2020)
Merkin, J.H., Pop, I.: Stagnation point flow past a stretching/shrinking sheet driven by arrhenius kinetics. Appl. Math. Comput. 337, 583–590 (2018)
Mondal, S.K., Pal, D.: Mathematical analysis for brownian motion of nonlinear thermal bioconvective stagnation point flow in a nanofluid using dtm and rkf method. J. Comput. Des. Eng. (2020)
Navarrete, N., Hernández, L., Vela, A., Mondragón, R.: Influence of the production method on the thermophysical properties of high temperature molten salt-based nanofluids. J. Mol. Liq. 302, 112570 (2020)
Pal, D., Mondal, S.K.: Magneto-bioconvection of powell eyring nanofluid over a permeable vertical stretching sheet due to gyrotactic microorganisms in the presence of nonlinear thermal radiation and joule heating. Int. J. Ambient Energy 1–12 (2019)
Platt, J.R.: "bioconvection patterns" in cultures of free-swimming organisms. Science 133(3466), 1766–1767 (1961)
Postelnicu, A., Pop, I.: Falkner-skan boundary layer flow of a power-law fluid past a stretching wedge. Appl. Math. Comput. 217(9), 4359–4368 (2011)
Raju, C., Hoque, M.M., Sivasankar, T.: Radiative flow of casson fluid over a moving wedge filled with gyrotactic microorganisms. Adv. Powder Technol. 28(2), 575–583 (2017)
Reddy, J.N.: Solutions manual for an introduction to the finite element method. McGraw-Hill, New York (1993)
S. Choi: Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticle, in: Development and Applications of Non-Newtonian Flow. ASME Fluids Eng. Division vol. 231/, pp. 99–105 (1995). https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/196525/
Shah, Z., Kumam, P., Deebani, W.: Radiative mhd casson nanofluid flow with activation energy and chemical reaction over past nonlinearly stretching surface through entropy generation. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–14 (2020)
Shahzad, A., Ali, R., Hussain, M., Kamran, M.: Unsteady axisymmetric flow and heat transfer over time-dependent radially stretching sheet. Alexandria Eng. J. 56(1), 35–41 (2017)
Swapna, G., Kumar, L., Rana, P., Singh, B.: Finite element modeling of a double-diffusive mixed convection flow of a chemically-reacting magneto-micropolar fluid with convective boundary condition. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 47, 18–27 (2015)
Turkyilmazoglu, M.: Single phase nanofluids in fluid mechanics and their hydrodynamic linear stability analysis. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 187, 105171 (2020)
Ullah, I., \(Sha_e\), S., Makinde, O.D., Khan, I.: Unsteady mhd falkner-skan ow of casson nanouid with generative/destructive chemical reaction. Chem. Eng. Sci. 172, 694–706 (2017)
Uddin, M., Rana, P., Bég, O.A., Ismail, A.M.: Finite element simulation of magnetohydrodynamic convective nanofluid slip flow in porous media with nonlinear radiation. Alexandria Eng. J. 55(2), 1305–1319 (2016)
Ullah, I., Shafie, S., Khan, I.: Mhd heat transfer flow of casson fluid past a stretching wedge subject to suction and injection. Malaysian J. Fund. Appl. Sci. 13(4), 637–641 (2017)
Ullah, I., Shafie, S., Khan, I.: Heat generation and absorption in mhd flow of casson fluid past a stretching wedge with viscous dissipation and newtonian heating. Jurnal Teknologi 80(3),(2018)
Waqas, H., Khan, S.U., Bhatti, M., Imran, M.: Significance of bioconvection in chemical reactive flow of magnetized carreau–yasuda nanofluid with thermal radiation and second-order slip. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 1–14 (2020)
Waqas, H., Khan, S.U., Shehzad, S., Imran, M., Tlili, I.: Activation energy and bioconvection aspects in generalized second-grade nanofluid over a riga plate: a theoretical model. Appl. Nanosci. 1–14 (2020)
White, F.M.: Viscous fluid flow, magraw-hillMagraw-hill Inc, New York (1991)
Yih, K.: Mhd forced convection flow adjacent to a non-isothermal wedge. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 26(6), 819–827 (1999)
Zadeh, S.M.H., Mehryan, S., Sheremet, M.A., Izadi, M., Ghodrat, M.: Numerical study of mixed bio-convection associated with a micropolar fluid. Thermal Sci. Eng. Progress 100539 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to convey their sincere thanks to all the esteemed reviewers for their comments and suggestions based upon which the present version of the manuscript has been revised. One of the authors (B. Ali) is thankful to the Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xian, China, for providing sufficient research facility to carried out this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bagh Ali: Modeled the problem, methodology, Matlab software, and writing the original draft. Sajjad Hussain: Contributed to the results and discussions, supervision, and project administration. Syed Irfan Raza Naqvi: Thoroughly checked the mathematical modeling and English corrections. Danial Habib: Writing-review, Editing, and visualization. Sohaib Abdal: Writing review and editing. All authors finalized the manuscript after its internal evaluation. Declaration
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, B., Hussain, S., Naqvi, S.I.R. et al. Aligned Magnetic and Bioconvection Effects on Tangent Hyperbolic Nanofluid Flow Across Faster/Slower Stretching Wedge with Activation Energy: Finite Element Simulation. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 7, 149 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-021-01097-0
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-021-01097-0