Abstract
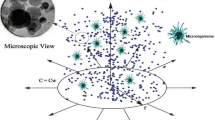
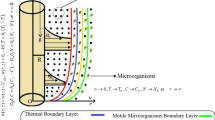
The present exploration examines the Cattaneo–Christov double diffusions theory in magneto-Cross nanomaterial flow conveying gyrotactic microorganisms over an extending horizontal cylinder/plate under the aspects of velocity slippage, and activation energy with chemically reacting features. The phenomena of thermophoresis, Brownian movement, and thermal radiation are also incorporated. Utilization of the adopted similarity transformations makes it convenient to transform our governing nonlinear higher-order coupled PDEs into ODEs which are further solved numerically by adopting well-known MATLAB function bvp4c. The quantitative outcomes of emerging thermo-physical and geometrical parameters on the associated non-dimensional profiles of interest are anatomized via requisite graphs and numerically erected tabular forms. It is detected that fluid velocity components decline due to upgraded magnetic field and velocity slippage parameter. When thermal time relaxation parameter varies from 0.0 to 0.9, Nusselt number augments about \(22.02\%\) for cylindrical surface and about \(23.61\%\) for plate surface. Likewise, with the same variations in thermal time relaxation parameter Sherwood number increases about \(17.32\%\) for cylindrical surface and about \(18.24\%\) for plate surface. Moreover, comparative exploration of the emerging flow features over a flat plate, and cylindrical surface is reported. It is visualized that flat plate offers less temperature than cylindrical surface when flow occurs. The results would offer primary guidance for many industrial, biological, medical and ecological challenges, for instance, bio-fuel, bio-diesel, ethanol, biological tissues, bio-fertilizers, bio-micro-systems, reproduction, infection, and marine life ecosystems, etc.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bird, R.: Useful non-newtonian models. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 8(11), 13–34 (2003)
Khan, M., Manzur, M., Rahman, M.: Boundary layer flow and heat transfer of cross fluid over a stretching sheet, Thermal Sci. 23(9). https://doi.org/10.2298/TSCI160919111K
Cross, M.M.: Rheology of non-Newtonian fluids: a new flow equation for pseudoplastic systems. J. Colloid Sci. 20(5), 417–437 (1965)
Hayat, T., Khan, M.I., Tamoor, M., Waqas, M., Alsaedi, A.: Numerical simulation of heat transfer in MHD stagnation point flow of cross fluid model towards a stretched surface. Results Phys. 7, 1824–1827 (2017)
Khan, W.A., Ali, M., Shahzad, M., Sultan, F., Irfan, M., Asghar, Z.: A note on activation energy and magnetic dipole aspects for cross nanofluid subjected to cylindrical surface. Appl. Nanosci. 10(11), 3235–3244 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01220-0
Naz, R., Noor, M., Hayat, T., Javed, M., Alsaedi, A.: Dynamism of magnetohydrodynamic cross nanofluid with particulars of entropy generation and gyrotactic motile microorganisms. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 110(11), 104431 (2019)
Hina, S., Shafique, A., Mustafa, M.: Numerical simulations of heat transfer around a circular cylinder immersed in a shear-thinning fluid obeying Cross model. Physica A 540(15), 123184 (2020)
Shahzad, M., Ali, M., Sultan, F., Khan, W.A., Hussain, Z.: Computational investigation of magneto-cross fluid flow with multiple slip along wedge and chemically reactive species. Results Phys. 16(1), 102972 (2020)
Kim, S.K.: Forced convection heat transfer for the fullydeveloped laminar flow of the cross fluid between parallel plates. J. Nonnewton. Fluid Mech. 276(1), 104226 (2020)
Hosseinzadeh, K., Roghani, S., Mogharrebi, A.R., Asadi, A., Waqas, M., Ganji, D.D.: Investigation of cross-fluid flow containing motile gyrotactic microorganisms and nanoparticles over a three-dimensional cylinder. Alex. Eng. J. 59(5), 3297–3307 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2020.04.037
Choi, S.U.S.: Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluid with nanoparticales. Develop. Appl. Non-Newtonian Flows 66, 99–105 (1995)
Khan, M.I., Alzahrani, F.: Free convection and radiation effects in nanofluid (silicon dioxide and molybdenum disulfide) with second order velocity slip, entropy generation, Darcy–Forchheimer porous medium. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 46(1), 1362–1369 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.09.240
Khan, M.: Transportation of hybrid nanoparticles in forced convective Darcy-Forchheimer flow by a rotating disk. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 122(3), 105177 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105177
Khan, M., Alzahrani, F.: Nonlinear dissipative slip flow of Jeffrey nanomaterial towards a curved surface with entropy generation and activation energy. Math. Comput. Simul. 185(07), 47–61 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2020.12.004
Nayak, M., Hakeem, A.A., Ganga, B., Khan, M.I., Waqas, M., Makinde, O.: Entropy optimized MHD 3D nanomaterial of non-Newtonian fluid: a combined approach to good absorber of solar energy and intensification of heat transport. Comput. Methods Program. Biomed. 186, 105131 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.105131
Ibrahim, M., Khan, M.I.: Mathematical modeling and analysis of SWCNT-water and MWCNT-water flow over a stretchable sheet. Comput. Methods Program. Biomed. 187, 105222 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.105222
Khan, M.I., Alzahrani, F.: Entropy optimized magnetohydrodynamics Darcy-Forchheimer second order velocity slip flow of nanomaterials between two stretchable disks. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 234(21), 4190–4199 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406220920317
Kuznetsov, A., Avramenko, A.: Effect of small particles on the stability of bioconvection in a suspension of gyrotactic microorganisms in a layer of finite depth. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 31(01), 1–10 (2004)
Sokolov, A., Goldstein, R., Feldchtein, F., Igor, S.: Enhanced mixing and spatial instability in concentrated bacterial suspensions. Phys. Rev. E 80(9), 031903 (2009)
Siddiqa, S., Sulaiman, M., Hossain, M.A., Islam, S., Gorla, R.S.: Gyrotactic bioconvection flow of a nanofluid past a vertical wavy surface. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 108(5), 244–250 (2016)
Sk, M., Das, K., Kundu, P.: Multiple slip effects on bioconvection of nanofluid flow containing gyrotactic microorganisms and nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 220(8), 518–526 (2016)
De, P.: Impact of dual solutions on nanofluid containing motile gyrotactic micro-organisms with thermal radiation, BioNanoScience 9(12). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-018-0584-6
Ferdows, M., Reddy, M.G., Sun, S., Alzahrani, F.: Two-dimensional gyrotactic microorganisms flow of hydromagnetic power law nanofluid past an elongated sheet. Adv. Mech. Eng. 11(11), 1–17 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814019881252
Khan, W., Rashad, A., Abdou, M.M.M., Tlili, I.: Natural bioconvection flow of a nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms about a truncated cone. Eur. J. Mech.-B/Fluids 75, 133–142 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechflu.2019.01.002
Khan, M., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A.: Heat transport and nonlinear mixed convective nanomaterial slip flow of Walter-B fluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms. Alex. Eng. J. 59(3), 1761–1769 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2020.04.042
Cattaneo, C.: Sulla conduzione del calore. Atti Sem. Mat. Fis. Univ. Modena 3(01), 83–101 (1948)
Christov, C.: On frame indifferent formulation of the Maxwell–Cattaneo model of finite-speed heat conduction. Mech. Res. Commun. 36(06), 481–486 (2009)
Straughan, B.: Thermal convection with the Cattaneo–Christov model. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 53(01), 95–98 (2010)
Tibullo, V., Zampoli, V.: A uniqueness result for the Cattaneo–Christov heat conduction model applied to incompressible fluids. Mech. Res. Commun. 38, 77–79 (2011)
Han, S., Zheng, L., Li, C., Zhang, X.: Coupled flow and heat transfer in viscoelastic fluid with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model. Appl. Math. Lett. 38(12), 87–93 (2014)
Hayat, T., Khan, M., Farooq, M., Waqas, M., Alsaedi, A., Yasmeen, T.: Impact of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model in flow of variable thermal conductivity fluid over a variable thicked surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 99(4), 702–710 (2016)
Sohail, M., Naz, R.: Modified heat and mass transmission models in the magnetohydrodynamic flow of sutterby nanofluid in stretching cylinder. Physica A 549, 124088 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2019.124088
Khan, M.I., Alzahrani, F., Hobiny, A., Ali, Z.: Modeling of Cattaneo–Christov double diffusions (CCDD) in Williamson nanomaterial slip flow subject to porous medium. J. Market. Res. 9(3), 6172–6177 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.04.019
Khan, M., Alzahrani, F.: Cattaneo–Christov double diffusion (CCDD) and magnetized stagnation point flow of non-Newtonian fluid with internal resistance of particles. Phys. Scr. 95(11), 125002 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/abc0c2
Mehmood, Y., Sagheer, M., Hussain, S., Bilal, M.: MHD stagnation point flow and heat transfer in viscoelastic fluid with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model. Neural Comput. Appl. 30, 2979–2986 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-2902-2
Hayat, T., Khan, S., Khan, M., Momani, S., Alsaedi, A.: Cattane–Christov (cc) heat flux model for nanomaterial stagnation point flow of Oldroyd-b fluid. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 187(12), 105247 (2019)
Ahmad, I., Aziz, S., Khan, S., Ali, N.: Periodically moving surface in an Oldroyd-B fluid with variable thermal conductivity and Cattaneo–Christov heat flux features. Heat Transf.-Asian Res. 49(6), 3246–3266 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/htj.21772
Ahmad, S., Nadeem, P.D.S., Muhammad, N., Khan, M.: Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model for stagnation point flow of micropolar nanofluid toward a nonlinear stretching surface with slip effects. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 143(3), 1187–1199 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09504-2
Khan, M., Alzahrani, F.: Transportation of heat through Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model in non-Newtonian fluid subject to internal resistance of particles. Appl. Math. Mech. 41, 1157–1166 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-020-2641-9
Bestman, A.: Natural convection boundary layer with suction and mass transfer in a porous medium. Int. J. Energy Res. 14(05), 389–396 (1990)
Makinde, O.D., Olanrewaju, P.O., Charles, W.M.: Unsteady convection with chemical reaction and radiative heat transfer past a flat porous plate moving through a binary mixture. Afr. Mat. 22(04), 65–78 (2011)
Kumar, R.V.M.S.S.K., Kumar, G.V., Raju, C.S.K., Shehzad, S.A., Varma, S.V.K.: Analysis of Arrhenius activation energy in magnetohydrodynamic Carreau fluid flow through improved theory of heat diffusion and binary chemical reaction. J. Phys. Commun. 2(3), 035004 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2399-6528/aaafff
Khan, M., Qayyum, S., Kadry, S., Khan, W., Abbas, S.: Irreversibility analysis and heat transport in squeezing nanoliquid flow of non-Newtonian (second-grade) fluid between infinite plates with activation energy. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 45, 4939–4947 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04442-5
Ijaz Khan, M., Haq, F., Khan, S.A., Hayat, T., Imran Khan, M.: Development of thixotropic nanomaterial in fluid flow with gyrotactic microorganisms, activation energy, mixed convection. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 187, 105186 (2020)
Irfan, M., Khan, W., Khan, M., Waqas, M.: Evaluation of Arrhenius activation energy and new mass flux condition in Carreau nanofluid: dual solutions. Appl. Nanosci. 10(06), 5279–5289 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01449-0
Azam, M., Xu, T., Shakoor, A., Khan, M.: Effects of Arrhenius activation energy in development of covalent bonding in axisymmetric flow of radiative-cross nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 113(04), 104547 (2020)
Khan, M., Alzahrani, F.: Entropy-optimized dissipative flow of Carreau–Yasuda fluid with radiative heat flux and chemical reaction. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 516 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00532-3
Khan, M., Alzahrani, F.: Activation energy and binary chemical reaction effect in nonlinear thermal radiative stagnation point flow of Walter-B nanofluid: Numerical computations. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 34(5), 2050132 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217979220501325
Khan, M.I., Alzahrani, F.: Dynamics of activation energy and nonlinear mixed convection in Darcy–Forchheimer radiated flow of Carreau nanofluid near stagnation point region. J. Thermal Sci. Eng. Appl. 13(5), 051009 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4049434
Khan, M.I., Alzahrani, F.: Binary chemical reaction with activation energy in dissipative flow of non-Newtonian nanomaterial. J. Theor. Comput. Chem. 19(3), 2040006 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219633620400064
Khan, M.I., Alzahrani, F.: Numerical simulation for the mixed convective flow of non-Newtonian fluid with activation energy and entropy generation. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 44(9), 7766–7777 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.6919
Khan, M.I., Waqas, M., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A.: A comparative study of Casson fluid with homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 498, 85–90 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.03.024
Sarkar, S., Jana, R., Das, S.: Activation energy impact on radiated magneto-Sisko nanofluid flow over a stretching and slipping cylinder: entropy analysis. Multidiscip. Model. Mater. Struct. 16(5), 1085–1115 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1108/MMMS-09-2019-0165
Naz, R., Noor, M., Shah, Z., Sohail, M., Kumam, P., Thounthong, P.: Entropy generation optimization in MHD Pseudoplastic fluid comprising motile microorganisms with stratification effect. Alex. Eng. J. 59(1), 485–496 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2020.01.018
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to anonymous reviewers for their fruitful comments and constructive suggestions to improve our manuscript.
Funding
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. Ali: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Investigation, Writing–original draft, review & editing. S. Sarkar: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing–original draft. S. Das: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing–review & editing, Supervision. R.N. Jana: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing–review & editing, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, A., Sarkar, S., Das, S. et al. Investigation of Cattaneo–Christov Double Diffusions Theory in Bioconvective Slip Flow of Radiated Magneto-Cross-Nanomaterial Over Stretching Cylinder/Plate with Activation Energy. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 7, 208 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-021-01144-w
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-021-01144-w