Abstract
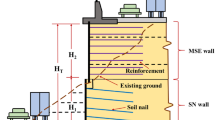
This paper studies the benefit of hybrid systems of earth retaining structures compared to using monotype systems in widening the roadsides to solve traffic congestion problems. Various innovative 2D finite element models including both monotype systems and hybrid systems were used to investigate the behavior of each system separately. The limit equilibrium approach for each system is considered the basic methodology in selecting the parameters used in the finite element analysis. The results are presented in terms of wall deformations, tensile forces in the reinforcements in case of using the soil-nailing wall or the mechanically stabilized earth retaining wall (MSE wall), anchor forces in case of using the anchored sheet pile wall, and the global factor of safety. Through the results of the analysis for each model, a comparison between monotype systems and hybrid systems of earth retaining structures has been done. It has been observed that using the hybrid cantilever/anchored sheet pile wall or using the hybrid MSE/anchored sheet pile wall has a significant effect in reducing the wall deformations and increasing the global factor of safety compared to using the full height monotype systems. In contrast, using the hybrid cantilever/soil-nailing wall or using the hybrid MSE/soil-nailing wall has no effect in reducing the wall deformations or in increasing the global factor of safety compared to using the full height monotype systems.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei Y (2013) Development of equivalent surcharge loads for the design of soil nailed segment of MSE/soil nail hybrid retaining walls based on results from full-scale wall instrumentation and finite element analysis. Doctoral dissertation
Alhabshi A (2006) Finite element design procedures for hybrid MSE/soil-nail retaining wall systems. Texas Tech University, Lubbock
Rabie M (2016) Performance of hybrid MSE/soil nail walls using numerical analysis and limit equilibrium approaches. HBRC J 12:63–70
Brinkgereve RBJ, Vermeer PA (2003) PLAXIS version 8, validation manual. DELFT University of Technology & PLAXIS BV, Delft
Zhu TY (2012) Some useful numbers on the engineering properties of materials (geologic and otherwise). GEOL 615, Department of Geophysics, Stanford University
AASHTO (2007) LRFD bridge design specifications, with 2008 and 2009 Interims, 4th edn, American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials, Washington, DC
Lazarte CA, Elias V, Espinoza RD, Sabatini PJ (2003) Geotechnical engineering circular no. 7: soil nail walls. Federal Highway Administration, Washington, DC
Berg RR, Christopher BR, Samtani NC (2009) Design and construction of mechanically stabilized earth walls and reinforced soil slopes: US Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration, National Highway Institute
Das BM (2015) Principles of foundation engineering. Cengage Learning, Boston
Bilgin Ö, Erten MB (2009) Analysis of anchored sheet pile wall deformations. In: Contemporary topics in ground modification, problem soils, and geo-support (GSP 187), international foundation congress and equipment expo, Florida, pp 137–44
Budek A (2004) Research proposal for TxDOT project no. 0-5205: design procedure for MSE/soil nail hybrid retaining wall systems. Lubbock, Texas Tech University, Dept. of Civil Engineering
Bilgin Ö (2010) Numerical studies of anchored sheet pile wall behavior constructed in cut and fill conditions. Comput Geotech 37:399–407
Babu GS, Singh VP (2009) Simulation of soil nail structures using PLAXIS 2D. Plaxis Bull 25:16–21
Morrison K, Harrison F, Collin J, Dodds A, Arndt B (2006) Shored mechanically stabilized earth (SMSE) wall systems design guidelines. Report no. FHWA-CFL/TD-06-001, FHWA, Lakewood, CO
Kumar N, Dey A (2014) Finite element analysis of flexible anchored sheet pile walls: effect of mode of construction and dewatering. In: Golden jubilee conference of the IGS Bangalore chapter, Geo-Innovations
Brinkgereve RBJ, Vermeer PA (2003) PLAXIS version 8, tutorial manual. DELFT University of Technology & PLAXIS BV, Delft
Petersson M, Pettersson M (2012) In depth study of lateral earth pressure. Chalmers University of Technology, Goteborg
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eldiasty, W.A., Altahrany, A.I. & Elmeligy, M.M. Comparison between monotype and hybrid earth retaining structures. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 4, 30 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-019-0213-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-019-0213-4