Abstract
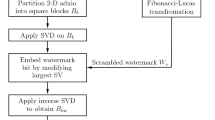
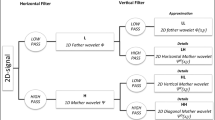
Watermarking has attained wide consideration for copyright security of multimedia information. Audio watermarking scheme using discrete wavelet transform and singular value decomposition (SVD) along with encryption is proposed in this article. Transform domain coefficients undergo SVD and then utilizing Fibonacci numbers encrypted watermark data is inserted into the singular values to ensure achievable acquirement of watermark. Proposed algorithm utilizes chaotic and AES encrypted watermarks for embedding to accelerate the scale of security. High imperceptible attribute, robust nature and high payload are achieved using the proposed strategy. Experimental results show that the audio watermarking scheme is not only inaudible, but also robust against various common signal processing attacks such as noise addition, filtering,equantization, echo, invert and compression.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
No really,rust. http://www.jamendo.com/en/album/7365 (2014). Last Accessed on 13 May 2017
Bhat, V., Sengupta, I., Das, A.: Audio watermarking based on quantization in wavelet domain. In: Sekar, R., Pujari, A.K. (eds.) Information systems security: 4th international conference, ICISS 2008, pp. 235–242. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2008)
Sengupta, I., Das, A., Bhat, K.V.: An audio watermarking scheme using singular value decomposition and dither-modulation quantization. Multimed. Tools Appl. 52(2), 369–389 (2011)
Bhat, K.V., Sengupta, I., Das, A.: A new audio watermarking scheme based on singular value decomposition and quantization. Circ. Syst. Signal Process. 30(5), 915–927 (2011)
Chen, K., Yan, F., Iliyasu, A.M., Zhao, J.: Dual quantum audio watermarking schemes based on quantum discrete cosine transform. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(2), 502–521 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3950-9
Cox, I., Miller, M., Bloom, J., Fridrich, J., Kalker, T.: Digital watermarking and steganography, 2nd edn. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc, Burlington (2008)
Daemen, J., Rijmen, V.: The design of rijndael. Springer, New York (2002)
Dhar, P.K., Shimamura, T.: Blind SVD-based audio watermarking using entropy and log-polar transformation. J. Inf S.ecur. Appl. 20, 74–83 (2015)
El-Bendary, M.A.M., El-Azm, A.E.A., El-Fishawy, N.A., Al-Hosarey, F.S.M., Eltokhy, M.A., El-Samie, F.E.A., Kazemian, H.: JPEG image transmission over mobile network with an efficient channel coding and interleaving. Int. J. Elect. 99(11), 1497–1518 (2012)
Fallahpour, M., Megías, D.: Audio watermarking based on Fibonacci numbers. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 23(8), 1273–1282 (2015)
Fan, M., Wang, H.: Chaos-based discrete fractional sine transform domain audio watermarking scheme. Comput. Elect. Eng. 35(3), 506–516 (2009)
Han, F., Yu, X., Han, S.: Improved baker map for image encryption. In: 1st International Symposium on Systems and Control in Aerospace and Astronautics, pp. 4 pp.–1276 (2006)
Hu, H., Lee, T.: High-performance self-synchronous blind audio watermarking in a unified FFT framework. IEEE Access 7, 19063–19076 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2893646
Hu, H.T., Hsu, L.Y.: Robust, transparent and high-capacity audio watermarking in DCT domain. Signal Process. 109, 226–235 (2015)
Hu, H.T., Hsu, L.Y., Lai, S.Y., Chang, Y.J.: The use of spectral shaping to extend the capacity for DWT-based blind audio watermarking. In: 5th International Conference on IT Convergence and Security (ICITCS), Kuala Lumpur, 2015, pp. 1–5 (2015)
Hu, H.T., Lee, T.T.: Frame-synchronized blind speech watermarking via improved adaptive mean modulation and perceptual-based additive modulation in DWT domain. Digital Signal Process. 87, 75–85 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2019.01.006
Hua, G., Huang, J., Shi, Y.Q., Goh, J., Thing, V.L.: Twenty years of digital audio watermarking—a comprehensive review. Signal Process. 128, 222–242 (2016)
Huang, H.N., Chen, S.T., Lin, M.S., Kung, W.M., Hsu, C.Y.: Optimization-based embedding for wavelet-domain audio watermarking. J. Signal Process. Syst. 80(2), 197–208 (2015)
Johnson, N., Duric, Z., Jajodia, S.: Information hiding: steganography and watermarking-attacks and countermeasures. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Berlin (2001)
Kang, X., Yang, R., Huang, J.: Geometric invariant audio watermarking based on an LCM feature. IEEE Transa. Multimed. 13(2), 181–190 (2011)
Kanhe, A., Gnanasekaran, A.: A blind audio watermarking scheme employing DCT-HT-SD technique. Circ. Syst. Signal Process. 38(8), 3697–3714 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0994-2
Karajeh, H., Khatib, T., Rajab, L., Maqableh, M.: A robust digital audio watermarking scheme based on DWT and Schur decomposition. Multimed. Tools Appl. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7214-3
Katzenbeisser, S., Petitcolas, F.A. (eds.): Information hiding techniques for steganography and digital watermarking, 1st edn. Artech House, Inc, Norwood (2000)
Kaur, A., Dutta, M.K., Soni, K., Taneja, N.: Localized and self adaptive audio watermarking algorithm in the wavelet domain. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 33, 1–15 (2017)
Lei, B., Soon, I.Y.: Perception-based audio watermarking scheme in the compressed bitstream. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 69(1), 188–197 (2015)
Lei, B., Soon, I.Y., Zhou, F., Li, Z., Lei, H.: A robust audio watermarking scheme based on lifting wavelet transform and singular value decomposition. Signal Process. 92(9), 1985–2001 (2012)
Lin, Y.Q., Abdulla, W.H.: Audio watermarking for copyrights protection. Tech. rep., University of Auckland, Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering (2006)
Nair, U., Birajdar, G.: A secure audio watermarking employing AES technique. Int. Conf. Inven. Comput. Technol. (ICICT) 3, 1–5 (2016)
Natgunanathan, I., Xiang, Y.: A novel pseudonoise sequence for time-spread echo based audio watermarking. In: GLOBECOM 2009–2009 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, Honolulu, HI, pp. 1–6 (2009)
Nickel, J.: Mathematics: Is God Silent? Ross House Books (2001)
Özer, H., Sankur, B., Memon, N.: An SVD-based audio watermarking technique. In: Proceedings of the 7th Workshop on Multimedia and Security, pp. 51–56. ACM (2005)
Rezaei, A., Khalili, M.: A robust blind audio watermarking scheme based on DCT-DWT-SVD. In: Montaser Kouhsari, S. (ed.) Fundamental research in electrical engineering, pp. 101–113. Springer, Singapore (2019)
Saadi, S., Merrad, A., Benziane, A.: Novel secured scheme for blind audio/speech norm-space watermarking by Arnold algorithm. Signal Process. 154, 74–86 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.08.011
Sekhar, A.C., Suneetha, C., NagaLakshmi, G., RaviKumar, B.V.: Fast Fourier transforms and quadratic forms for digital audio watermarking. In: 2009 International Conference on Advances in Recent Technologies in Communication and Computing, pp. 449–452 (2009)
Sharma, B., Dave, M.: Robust hybrid image and audio watermarking using cyclic codes and Arnold transform. In: 2019 International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), pp. 309–315 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCES45898.2019.9002117
Srivastava, S., Chandra, M., Sahoo, G.: Robust voiceprint based audio watermarking using wavelet transform. In: Nath, V., Mandal, J.K. (eds.) Nanoelectronics, circuits and communication systems, pp. 457–467. Springer, Singapore (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-0776-8-42
Standards, N. I. & Technology.: Advanced Encryption Standard. NIST FIPS PUB 197 (2001)
Wang, X., Qi, W., Niu, P.: A new adaptive digital audio watermarking based on support vector regression. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 15(8), 2270–2277 (2007)
Wang, X.Y., Ma, T.X., Niu, P.P.: A pseudo-Zernike moment based audio watermarking scheme robust against desynchronization attacks. Comput. Elect. Eng. 37(4), 425–443 (2011)
Wen, X., Ding, X., Li, J., Gao, L., Sun, H.: An audio watermarking algorithm based on fast Fourier transform. In: 2009 International Conference on Information Management, Innovation Management and Industrial Engineering, vol. 1, pp. 363–366 (2009)
Widmer, G., Rocchesso, D., Välimäki, V., Erkut, C., Gouyon, F., Pressnitzer, D., Penttinen, H., Polotti, P., Volpe, G.: Sound and music computing: research trends and some key issues. J. N. Music Res. 36, 169–184 (2007)
Xiang, S.: Audio watermarking robust against D/A and A/D conversions. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2011(1), 3 (2011)
Yan, Y., Rong, H., Mintao, X.: A novel audio watermarking algorithm for copyright protection based on DCT domain. In: 2009 Second International Symposium on Electronic Commerce and Security, vol. 1, pp. 184–188 (2009)
Zhang, J., Peng, X., Zhang, S.: Robust audio watermarking algorithm based on moving average and DCT. In: Sun, X., Pan, Z., Bertino, E. (eds.) Artificial intelligence and security, pp. 419–429. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24271-8-38
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Editors and anonymous reviewers for their valuable remarks and comments which significantly contributed to the quality of a paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, U., Birajdar, G.K. Compressed domain secure, robust and high-capacity audio watermarking. Iran J Comput Sci 3, 217–232 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42044-020-00059-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42044-020-00059-x