Abstract
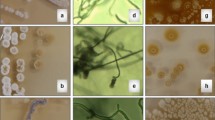
A total of nine isolates of streptomycetes were isolated from scab lesions on potato tubers. Five of nine isolates were pathogenic on potato minitubers. Four of the pathogenic isolates produced thaxtomin A (ThxA) in infected tuber tissues. The lesion surface areas inducing ThxA were highest in treatment of the minitubers with an extract of OMB inoculated with S-66 and S-67, intermediate with that inoculated with S-64 and lowest with S-63. The pathogenic isolates were identified by gray aerial mycelia, melanin pigment productivity, the type of spore chain morphology and carbon utilization asS. scabies strains S-63, S-64 and S-68, andS. acidiscabies strains S-66 and S-67. Strains S-63 and S-64 produced 0.65 and 1.60 mg ThxA per L of OMB, respectively, strains S-66 and S-67 producing similar amounts,viz. 2.36 and 2.10 mg/L, respectively. The optimal temperature for production (by both species) was 28 °C. Production of ThxA byS. scabies strain S-64 andS. acidiscabies strain S-66 was suppressed at least 50-fold at 0.5 and 0.3 % of glucose, respectively. Fructose enhanced the production by both species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams M.J., Lapwood D.H.: Studies on the lenticel development, surface microflora and infection by common scab (Streptomyces scabies) of potato tubers growing in wet and dry soils.Ann. Appl. Biol.90, 335–343 (1978).
Archuleta J., Easton G.D.: The cause of deep-pitted scab of potatoes.Am. Potato J.58, 385–392 (1981).
Babcock M.J., Eckwall E.C., Schottel J.L.: Production and regulation of potato-scab-inducing phytotoxins byStreptomyces scabies.J. Gen. Microbiol.139, 1579–1586 (1993).
Bukhalid R.A., Loria R.: Cloning and expression of a gene fromStreptomyces scabies encoding a putative pathogenicity factor.J. Bacteriol.197, 7776–7783 (1997).
Chadwick D.J., Whelan J. (Eds):Secondary Metabolites: Their Function and Evolution. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester (England) 1992.
Demain A.L.: Carbon source regulation of idiolite biosynthesis in actinomycetes, pp. 121–134 inRegulation of Secondary Metabolism in Actinomycetes (S. Shapiro, Ed.). CRC Press, Boca Raton (Florida) 1989.
Doering-Saad C., Kampfer P., Schalmit M., Kritzman G., Schneider J., Schrempf H., Barash I.: Diversity amongStreptomyces strains causing potato scab.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.58, 3932–3940 (1992).
Dye D.W., Bradbury J.F., Goto M., Hayward A.C., Lelliou R.A., Schroth M.N.: International standards for naming pathovars of phytopathogenic bacteria and a list of pathovar names and pathotype strains.Rev. Plant Pathol.59, 153–168 (1980).
Elesawy A.A., Szabo I.M.: Isolation and characterization ofStreptomyces scabies strains from scab lesions of potato tubers. Designation of the neotype strain ofStreptomyces scabies.Acta Microbiol. (Budapes)26, 311–320 (1979).
Elesawy A.A., Szabo I.M.: A simplified method for isolating and detecting the frequency of occurrence of free livingStreptomyces scabies in infected soils.Acta Phytopathol. (Budapest)16, 67–72 (1981).
Harrison M.D.: Potato russet scab, its cause and factors affecting its development.Am. Potato J.39, 368–387 (1962).
Hobbs G., Frazer C.M., Gardner D.C.J., Fiona-Flett F., Oliver S.G.: Pigmented antibiotic production byStreptomyces cœlicolor A3(2): kinetics and the influence of nutrients.J. Gen. Microbiol.136, 2291–2296 (1990).
Hood D.W., Heidstra R., Swoboda U.K., Hodgson D.A.: Molecular genetic analysis of proline and tryptophan biosynthesis inStreptomyces cœlicolor A3(2): interaction between primary and secondary metabolism.Rev. Genet.115, 5–12 (1992).
Hopwood D.A., Khosla C.: Genes for polyketide secondary metabolic pathways in microorgamisms and plants.Ciba Symp.171, 88–112 (1992).
Keinath A.P., Loria R.: Population dynamics ofStreptomyces scabies and other actinomycetes as related to common scab of potato.Phytopathology79, 681–687 (1989).
King R.R., Lawrence C.H., Clark M.C., Culhoun L.A.: Isolation and characterization of phytotoxins associated withStreptomyces scabies.J. Chem. Soc. (London)13, 849–850 (1989).
King R.R., Lawrence C.H., Clark M.C.: Correlation of phytotoxin production with pathogenicity ofStreptomyces scabies isolates from scab intected potato tubers.Am. Potato J.68, 675–680 (1991).
King R.R., Lawrence C.H., Calhoun L.A.: Chemistry of phytotoxins associated withStreptomyces scabies, the causal organism of potato common scab.J. Agric. Food Chem.40, 834–837 (1992).
King R.R., Lawrence C.H., Calhoun L.A., Ristaino J.B.: Isolation and characterization of thaxtomin-type phytotoxins associated withStreptomyces ipomœae.J. Agric. Food. Chem.42, 1791–1794 (1994).
Lambert D.H., Loria R.:Streptomyces scabies sp.nov., nom.rev.Internat. J. Syst. Bacteriol.39, 387–392 (1989).
Lambert D.H., Loria R.:Streptomyces acidiscabies sp.nov.Internat. J. Syst. Bacteriol.39, 393–396 (1989).
Lawrence C.H., Clarli M.C., King R.R.: Induction of common scab symptoms in aseptically cultured potato tubers by the vivotoxin, thaxtomin.Phytopathology80, 606–608 (1990).
Leiner R.H., Fry B.A., Carling D.E., Loria R.: Probably involvement of thaxtomin A in pathogenicity ofStreptomyces scabies on seedlings.Phytopathology86, 709–713 (1996).
Loria R., Kempter B.A.: Relative resistance of potato tubers produced from stem cuttings and seed-pieces propagated plants toStreptomyces scabies.Plant Dis.70, 1146–1148 (1986).
Loria R., Wilde J.R., Slack S.A.: Etiology of potato scab in Wisconsin.Phytopathology78, 1509 (1988).
Loria R., Bukhalid R.A., Creath R.A., Leiner R.H., Olivier M., Steffens J.C.: Differential production of thaxtomins by pathogenicStreptomyces speciesin vitro.Phytopathology85, 537–541 (1995).
Natsume M., Yamada A., Tashiro N., Abe H.: Differential production of the phytotoxins thaxtomin A and concanamycins A and B by potato common scab causingStreptomyces spp.Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Japan64, 202–204 (1998).
Person L.H., Martin W.J.: Soil rot of sweet potatoes in Louisiana.Phytopathology30, 913–926 (1940).
Quigley N.B., Gross D.C.: Syringomycin production among strains ofPseudomonas syringae pv.syringae: conservation of thesyrB andsyrD genes and activation of phytotoxin production by plant signal molecules.Mol. Plant Microbe Interact.7, 78–90 (1994).
Shirling E.B., Gottlieb D.: Methods for characterization ofStreptomyces species.Internat. J. Syst. Bacteriol.16, 313–340 (1966).
Shirling E.B., Gottlieb D.: Retrospective evaluation ofInternational Streptomyces Project taxonomic criteria, pp. 9–41 inActinomycetes: The Boundary Microorganisms (T. Arai, Ed.). Toppen Co. Ltd., Tokyo 1976.
Slabbert R., de Klerk A., Pretorius E.: Isolation of the phytotoxin thaxtomin A associated withStreptomyces scabies (common scab) in potatoes.J. South. Afr. Soc. Hort. Sci.4, 33–34 (1994).
Tanaka F.: Pathogens of scab disease of potato in Hokkaido, and its cultural control. (In Japan)Soil Microorg.38, 33–39 (1996).
Tashiro N., Miyashita K., Suzuki T.: Taxonomic studies on theStreptomyces species, isolated as causal organisms of potato common scab.Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Japan56, 73–82 (1990).
Vilches C., Mendez C., Hardisson C., Salas J.A.: Biosynthesis of oleandomycin byStreptomyces antibioticus, influence of nutritional conditions and development of resistance.J. Gen. Microbiol.136, 1447–1454 (1990).
Wasserman H.H., Shaw C.K., Sykes R.J., Cushley R.J.: The biosynthesis of metacycloprodigiosin and undecyloprodigiosin.Tetrahedron Lett.33, 2787–2790 (1974).
Williams S.T., Davies F.L., Hall D.M.: A practical approach to the taxonomy of actinomycetes isolated from soil, pp. 107–117 inThe Soil Ecosystem (J.D. Sheals, Ed.). Systematics Association Publication no. 8, London 1969.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Sayed, ES.A. Production of thaxtomin a by two species ofStreptomyces causing potato scab. Folia Microbiol 45, 415–422 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02817614
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02817614