Abstract.
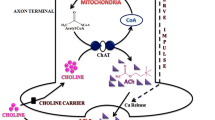
The beta amyloid peptide is the major component of the neuritic plaques, the characteristic lesions in Alzheimer's disease. Mutations in three genes (APP, PS-1, and PS-2) cause familial Alzheimer's disease by alteration of the rate of generation of amyloid peptide or the length of this peptide. However, in the 90% non-familial cases, other factors play a major pathogenetic role. These include the apolipoprotein E genotype, the "plaque-associated" proteins promoting the formation of toxic fibrillar aggregates or the chronic inflammatory responses. The aim of this review is to explain the steps in the complex cascade leading to Alzheimer's disease and, based on this, to report the current efforts to intervene in these different pathophysiological events in order to prevent progression of Alzheimer's disease. Whereas acetylcholine substitution is currently used in clinical practice, future therapeutical strategies to combat Alzheimer's disease may include anti-inflammatory treatments, vaccination against beta amyloid peptide, or treatment with cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fassbender, .K., Masters, .C. & Beyreuther, .K. Alzheimer's disease: molecular concepts and therapeutic targets. Naturwissenschaften 88, 261–267 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001140100237
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001140100237